Soil as a Resource
... the nutrients over time – In areas where climates are monsoonal, soil may form ‘brick’ hard surfaces – Lateritic soils are difficult to farm or work for people to grow food with ...
... the nutrients over time – In areas where climates are monsoonal, soil may form ‘brick’ hard surfaces – Lateritic soils are difficult to farm or work for people to grow food with ...
soil as a resource
... Pedocals are alkaline soils that develop in drier climates and retain soluble compounds such as calcium carbonate. ...
... Pedocals are alkaline soils that develop in drier climates and retain soluble compounds such as calcium carbonate. ...
CSS 200 notes wk1
... Examples: FLOODPLAINS – like Nile river DELTAS – river deposits when reach ocean, very fertile GRAVITY – hilly, mountainous areas where deposits move downhill by gravity are called COLLUVIUM Example: TALUS – deposits of rock and soil at the bottom of hill, often seen hiking VOLCANIC SOILS – ash ...
... Examples: FLOODPLAINS – like Nile river DELTAS – river deposits when reach ocean, very fertile GRAVITY – hilly, mountainous areas where deposits move downhill by gravity are called COLLUVIUM Example: TALUS – deposits of rock and soil at the bottom of hill, often seen hiking VOLCANIC SOILS – ash ...
METAMORPHIC ROCKS, PART 3 CONTACT/REGIONAL AND
... generally have sutured (interlocking) contacts. Kyanite is an example of neomineraliztion, or the growth of new minerals by metamorphism. Kyanite grows only in carbonate free rocks. Although elongated it may not exactly parallel the foliation. Kyanite is a metamorphic mineral formed during the regio ...
... generally have sutured (interlocking) contacts. Kyanite is an example of neomineraliztion, or the growth of new minerals by metamorphism. Kyanite grows only in carbonate free rocks. Although elongated it may not exactly parallel the foliation. Kyanite is a metamorphic mineral formed during the regio ...
Permeability Tests Constant Head vs. Falling
... both for coarse-grained soils as well as fine-grained soils ...
... both for coarse-grained soils as well as fine-grained soils ...
Con/regional and Metasomatic Rocks
... and generally have sutured (interlocking) contacts. Kyanite is an example of neomineraliztion, or the growth of new minerals by metamorphism. Kyanite grows only in carbonate free rocks. Although elongated it may not exactly parallel the foliation. Kyanite is a metamorphic mineral formed during the r ...
... and generally have sutured (interlocking) contacts. Kyanite is an example of neomineraliztion, or the growth of new minerals by metamorphism. Kyanite grows only in carbonate free rocks. Although elongated it may not exactly parallel the foliation. Kyanite is a metamorphic mineral formed during the r ...
Weathering, soil formation and initial ecosystem evolution on a
... 1996). White and Brantley (2003) further suggested that extrinsic controls, like climate, have an additional influence on the dissolution rate observed in the field compared to rates derived in the laboratory. One major problem for a better understanding of weathering processes is the upscaling from l ...
... 1996). White and Brantley (2003) further suggested that extrinsic controls, like climate, have an additional influence on the dissolution rate observed in the field compared to rates derived in the laboratory. One major problem for a better understanding of weathering processes is the upscaling from l ...
Major Concepts Terms and Phrases Introductory Assignments Main
... The atomic structure of an element determines how it can bond with other elements to form compounds. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid element or compound with a definite composition, and most importantly, an orderly arrangement of atoms. The composition and structure of minerals m ...
... The atomic structure of an element determines how it can bond with other elements to form compounds. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid element or compound with a definite composition, and most importantly, an orderly arrangement of atoms. The composition and structure of minerals m ...
a geological fieldwork report on the geology of
... This geological report describes an area that is around Matuu town towards the North of Ikaatini and from Katulani towards Mavoloni to the west located in the North of Machakos County in Kenya. It is bounded by Northings 98 72 and 9884 and Easting 3208 and 3469. It lies on the east Africa Mozambique ...
... This geological report describes an area that is around Matuu town towards the North of Ikaatini and from Katulani towards Mavoloni to the west located in the North of Machakos County in Kenya. It is bounded by Northings 98 72 and 9884 and Easting 3208 and 3469. It lies on the east Africa Mozambique ...
QUS 112 Intro Engineering Geology - Unesco
... and gas giants. The "planetesimals" would slowly collide with each other and become more massive. 10. Eventually, after ten to a hundred million years, you end up with ten or so planets, in stable orbits, and that's a solar system. These planets and their surfaces may be heavily modified by the last ...
... and gas giants. The "planetesimals" would slowly collide with each other and become more massive. 10. Eventually, after ten to a hundred million years, you end up with ten or so planets, in stable orbits, and that's a solar system. These planets and their surfaces may be heavily modified by the last ...
Weathering and Soii
... This increases surface area of rocks and allows them to be exposed more to chemical agents. ...
... This increases surface area of rocks and allows them to be exposed more to chemical agents. ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Look at each picture and decide if it is an example or chemical weathering or mechanical weathering ...
... Look at each picture and decide if it is an example or chemical weathering or mechanical weathering ...
Chapter 2 Minerals and Rocks Lecture Notes Earth Science
... are sand particles, followed by silt particles. Clay particles are the smallest. Texture is important for plant growth. Plants can "drown" for lack of air in clay soil, and they may die from lack of water in sandy soil. The best soil for growing most plants is loam, which is soil that is made up of ...
... are sand particles, followed by silt particles. Clay particles are the smallest. Texture is important for plant growth. Plants can "drown" for lack of air in clay soil, and they may die from lack of water in sandy soil. The best soil for growing most plants is loam, which is soil that is made up of ...
IP004 - Institute of Safety Management
... The “Transported soil” (gravels, sand, silts & clays) are soils that have been transported by water on the basis that as the flowing water velocity slows the heavies particles that it carries are deposited first with the silts then clays being the last particles to be deposited, The upper section of ...
... The “Transported soil” (gravels, sand, silts & clays) are soils that have been transported by water on the basis that as the flowing water velocity slows the heavies particles that it carries are deposited first with the silts then clays being the last particles to be deposited, The upper section of ...
lab 2: silicate minerals
... from NaAlSi3O8 (albite) to CaAl2Si2O8 (anorthite). Na-rich plagioclase tends to white in hands sample, whereas Ca-rich plagioclase tends to be dark grey. Twinning is the intergrowth of two or more crystals in a symmetrical fashion by the sharing of lattice points in adjacent crystals. In plagioclase ...
... from NaAlSi3O8 (albite) to CaAl2Si2O8 (anorthite). Na-rich plagioclase tends to white in hands sample, whereas Ca-rich plagioclase tends to be dark grey. Twinning is the intergrowth of two or more crystals in a symmetrical fashion by the sharing of lattice points in adjacent crystals. In plagioclase ...
WEATHERING Over millions of years, weathering has changed
... thick, but in other places it is only a few centimeters thick. Five factors— climate, slope of the land, types of rock, types of plants, and the amount of time that rock has been weathering—affect soil formation. For example, different types of soil develop in tropical areas than in polar regions. S ...
... thick, but in other places it is only a few centimeters thick. Five factors— climate, slope of the land, types of rock, types of plants, and the amount of time that rock has been weathering—affect soil formation. For example, different types of soil develop in tropical areas than in polar regions. S ...
Sedimentary rock
... sometimes within a few hours or days. However, large lava flows may take years to cool and harden completely. ...
... sometimes within a few hours or days. However, large lava flows may take years to cool and harden completely. ...
Weathering, Erosion, and Mass
... weathered material by water, wind, ice, or gravity. Mass wasting is the transfer or movement of rock or soil down slope primarily by gravity. Deposition is the process by which weathered and eroded materials are laid down or placed in a location that is different from their source. ...
... weathered material by water, wind, ice, or gravity. Mass wasting is the transfer or movement of rock or soil down slope primarily by gravity. Deposition is the process by which weathered and eroded materials are laid down or placed in a location that is different from their source. ...
CHAPTER 11CSOIL AS A RESOURCE
... Pedocals are alkaline soils that develop in drier climates and retain soluble compounds such as calcium carbonate. Laterites are severely leached, nutrient-poor soils that develop in tropical climates. The classification scheme used by soil scientists is much more elaborate. 7. The United States is ...
... Pedocals are alkaline soils that develop in drier climates and retain soluble compounds such as calcium carbonate. Laterites are severely leached, nutrient-poor soils that develop in tropical climates. The classification scheme used by soil scientists is much more elaborate. 7. The United States is ...
Studying Rocks and Soil
... Topsoil is the first layer. It has rock pieces mixed with decayed parts of plant and animal remains. The decayed remains are called humus. Humus has a lot of what plants need to grow. Subsoil is the soil under topsoil. It is lighter in color. It has less humus. It has pieces of broken rocks. The roo ...
... Topsoil is the first layer. It has rock pieces mixed with decayed parts of plant and animal remains. The decayed remains are called humus. Humus has a lot of what plants need to grow. Subsoil is the soil under topsoil. It is lighter in color. It has less humus. It has pieces of broken rocks. The roo ...
Midterm 1 Key - Florida Atlantic University
... True-False - Print the letter T or F in the blank to indicate if each of the following statements is true or false. Illegible answers are wrong. (1 point each) ...
... True-False - Print the letter T or F in the blank to indicate if each of the following statements is true or false. Illegible answers are wrong. (1 point each) ...
Save 0 - Science Lec | Home
... •Source of ores of many metals such as: iron, manganese, lead ores, and others.… • Raw materials for the ceramic and Portland cement industries industries. • Some of them are used as fertilizers such as phosphates, some nitrates. • Some of them used as raw materials for building as sand and gravel. ...
... •Source of ores of many metals such as: iron, manganese, lead ores, and others.… • Raw materials for the ceramic and Portland cement industries industries. • Some of them are used as fertilizers such as phosphates, some nitrates. • Some of them used as raw materials for building as sand and gravel. ...
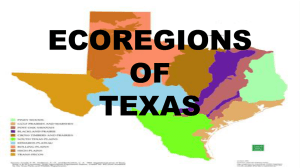
Texas eco regions 2016
... • The area is know as “brush Country” due to the shorter trees and many shrubs. • Over grazing of the lands has allowed nutrient rich top soil to erode away by wind and water erosion. • Rocky, dry soil can not support grasses, trees can survive because of their deeper root system. • The Rio Grande i ...
... • The area is know as “brush Country” due to the shorter trees and many shrubs. • Over grazing of the lands has allowed nutrient rich top soil to erode away by wind and water erosion. • Rocky, dry soil can not support grasses, trees can survive because of their deeper root system. • The Rio Grande i ...
Weathering 2015
... down by water. Weak acids in water dissolve the minerals bonds that hold rock together. Acid Precipitation The high level of acidity in acid precipitation can cause very rapid weathering of rock. Acids in Groundwater When acidic groundwater comes into contact with limestone underground, the limeston ...
... down by water. Weak acids in water dissolve the minerals bonds that hold rock together. Acid Precipitation The high level of acidity in acid precipitation can cause very rapid weathering of rock. Acids in Groundwater When acidic groundwater comes into contact with limestone underground, the limeston ...
Laterite

Laterite is a soil and rock type rich in iron and aluminium, and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and long-lasting weathering of the underlying parent rock. Tropical weathering (laterization) is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned altogether. At least a few researchers specializing in regolith development have considered that hopeless confusion has evolved around the name. There is no likelihood, however, that the name will ever be abandoned; for material that looks highly similar to the Indian laterite occurs abundantly worldwide, and it is reasonable to call such material laterite.Historically, laterite was cut into brick-like shapes and used in monument-building. After 1000 CE, construction at Angkor Wat and other southeast Asian sites changed to rectangular temple enclosures made of laterite, brick and stone. Since the mid-1970s, some trial sections of bituminous-surfaced, low-volume roads have used laterite in place of stone as a base course. Thick laterite layers are porous and slightly permeable, so the layers can function as aquifers in rural areas. Locally available laterites have been used in an acid solution, followed by precipitation to remove phosphorus and heavy metals at sewage-treatment facilities.Laterites are a source of aluminium ore; the ore exists largely in clay minerals and the hydroxides, gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore, which resembles the composition of bauxite. In Northern Ireland they once provided a major source of iron and aluminium ores. Laterite ores also were the early major source of nickel.