Rocks and Minerals
... The Rock Cycle • Magma rises, cools, and hardens into igneous rock. • It rises to the surface breaks apart, forming sediment. • Sediment is carried to the ocean by rivers were it builds up and becomes sedimentary rock. • Heat and pressure change it into metamorphic rock. • The rock cycle can have m ...
... The Rock Cycle • Magma rises, cools, and hardens into igneous rock. • It rises to the surface breaks apart, forming sediment. • Sediment is carried to the ocean by rivers were it builds up and becomes sedimentary rock. • Heat and pressure change it into metamorphic rock. • The rock cycle can have m ...
From a new hydrogeological conceptual model for hard rock
... related to mineralogical weathering processes, the structure of the mother rock is lost, o in the underlying isalterite, the weathering processes only induce slight or no change in volume and preserve the original rock structure; in most of the cases this layer takes up half to two thirds of the ent ...
... related to mineralogical weathering processes, the structure of the mother rock is lost, o in the underlying isalterite, the weathering processes only induce slight or no change in volume and preserve the original rock structure; in most of the cases this layer takes up half to two thirds of the ent ...
Background
... the mineral quartz always consists of one part silicon (an element) to two parts oxygen (another element). Some minerals, like gold, copper, and sulfur, are made up of only one element. However, most minerals are combinations of several different elements. Gold found in Georgia is the same as gold f ...
... the mineral quartz always consists of one part silicon (an element) to two parts oxygen (another element). Some minerals, like gold, copper, and sulfur, are made up of only one element. However, most minerals are combinations of several different elements. Gold found in Georgia is the same as gold f ...
File
... Conditions like temperature and pressure under which the mineral forms. Minerals formed from the same elements in the same proportions can have very different internal structures, (ex)depending on pressure which packs atoms more dense. ...
... Conditions like temperature and pressure under which the mineral forms. Minerals formed from the same elements in the same proportions can have very different internal structures, (ex)depending on pressure which packs atoms more dense. ...
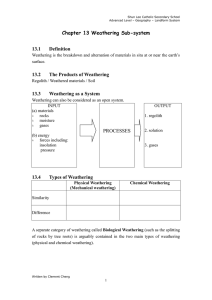
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
... and without roots, the soil will erode away. 2. Strip Mining – removing rock cover to get to the resources below, which causes the loose sediments to erode away. 3. Construction – the clearing of land to build buildings/houses also causes all loose soil to erode away. 4. Improper Farming – not plowi ...
... and without roots, the soil will erode away. 2. Strip Mining – removing rock cover to get to the resources below, which causes the loose sediments to erode away. 3. Construction – the clearing of land to build buildings/houses also causes all loose soil to erode away. 4. Improper Farming – not plowi ...
mineral properties
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS The Study of rocks allows geologist to understand the history of the Earth. Most Rocks are aggregates of minerals. One must therefore, be able to identify minerals, which are components of common rocks. MINERAL. Naturally occurring inorganic crystalline solid with def ...
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS The Study of rocks allows geologist to understand the history of the Earth. Most Rocks are aggregates of minerals. One must therefore, be able to identify minerals, which are components of common rocks. MINERAL. Naturally occurring inorganic crystalline solid with def ...
Economic Geology
... After the introductory lectures the students start on practicals during the third week. ...
... After the introductory lectures the students start on practicals during the third week. ...
Rocks & Minerals
... quick cooling doesn't allow the formation of large crystals so most extrusive rocks have small crystals or none at all. Also called ...
... quick cooling doesn't allow the formation of large crystals so most extrusive rocks have small crystals or none at all. Also called ...
Roberts Soil - Clydebank High School
... by physical and chemical weathering Largest component in terms of volume 45% in a typical topsoil ...
... by physical and chemical weathering Largest component in terms of volume 45% in a typical topsoil ...
processes
... The process is very important in initiating the decomposition of feldspar, a constituent of granite, which is broken down by water and is turned into a soft powdery mineral called kaolin, thus causing the solid rock to disintegrate (granular disintegration). In warm humid regions, hydrolysis may be ...
... The process is very important in initiating the decomposition of feldspar, a constituent of granite, which is broken down by water and is turned into a soft powdery mineral called kaolin, thus causing the solid rock to disintegrate (granular disintegration). In warm humid regions, hydrolysis may be ...
EXERCISE 5E METAMORPHIC ROCK IDENTIFICATION PURPOSE
... BANDED -‐ more than one mineral different minerals in parallel bands or "stripes" always foliated NONFOLIATED -‐ minerals in random arrangement, not parallel ...
... BANDED -‐ more than one mineral different minerals in parallel bands or "stripes" always foliated NONFOLIATED -‐ minerals in random arrangement, not parallel ...
How does Soil Form?
... of weathering, the nutrients that they supply, and the particle sizes that they contain. • A young soil is more influenced by the parent material characteristics than mature soils • Particle size has an impact on the properties of soil in the field. ...
... of weathering, the nutrients that they supply, and the particle sizes that they contain. • A young soil is more influenced by the parent material characteristics than mature soils • Particle size has an impact on the properties of soil in the field. ...
WED and Soil Formation 2014
... Temperate Forest and Grassland Climates Temperate forest and grassland climates get enough rain to cause a high level of chemical weathering, but not too much that nutrients are leached out. Arctic Climates In arctic climates, as in desert climates, chemical weathering occurs very slowly. Low temper ...
... Temperate Forest and Grassland Climates Temperate forest and grassland climates get enough rain to cause a high level of chemical weathering, but not too much that nutrients are leached out. Arctic Climates In arctic climates, as in desert climates, chemical weathering occurs very slowly. Low temper ...
Minerals
... The particles of the material line up in a regular, repeating pattern. Has flat sides called faces, that meet at sharp edges and corners. ...
... The particles of the material line up in a regular, repeating pattern. Has flat sides called faces, that meet at sharp edges and corners. ...
Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition: Trans Pecos/Chihuahuan
... a cause or agent of weathering, erosion, and deposition, is constant along the Texas coastline. The effects of wave action may happen slowly or very quickly. Sediments may be weathered and eroded along beaches and carried out into the ocean to form sand bars. Sediments may also be deposited along th ...
... a cause or agent of weathering, erosion, and deposition, is constant along the Texas coastline. The effects of wave action may happen slowly or very quickly. Sediments may be weathered and eroded along beaches and carried out into the ocean to form sand bars. Sediments may also be deposited along th ...
Day 16 (Geography)
... Chemical properties of Arid – Desert Soils: They are usually poor in organic matter. Some desert soils are alkaline with varying degree of soluble salts like calcium carbonate. Calcium content increases downwards and the subsoil has ten times more calcium. The phosphate content of these soils ...
... Chemical properties of Arid – Desert Soils: They are usually poor in organic matter. Some desert soils are alkaline with varying degree of soluble salts like calcium carbonate. Calcium content increases downwards and the subsoil has ten times more calcium. The phosphate content of these soils ...
Weathering and Soil Weathering - Natural earth processes that
... d. Effects- Mechanical weathering forces rock to break into smaller and smaller pieces allowing more rock to be exposed to more and more erosion and weathering. The cycle will continue forever. ii. Chemical Weathering 1. When chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them into diff ...
... d. Effects- Mechanical weathering forces rock to break into smaller and smaller pieces allowing more rock to be exposed to more and more erosion and weathering. The cycle will continue forever. ii. Chemical Weathering 1. When chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them into diff ...
and View
... around the field to catch the eroded soil. Soil erosions are caused when deforestation is plowed. The roots of trees holds the soil firmly underground to prevent soil erosion. But when people start to chop down trees erosion will follow up. People can prevent erosion by taking proper care of the soi ...
... around the field to catch the eroded soil. Soil erosions are caused when deforestation is plowed. The roots of trees holds the soil firmly underground to prevent soil erosion. But when people start to chop down trees erosion will follow up. People can prevent erosion by taking proper care of the soi ...
Economic Geology Course Name: Economic Geology Course Code
... After the introductory lectures the students start on practicals during the third week. ...
... After the introductory lectures the students start on practicals during the third week. ...
08_chapter 2
... Lichens are the association between fungus and a photosynthetic partner either green algae or cyanobacteria. Lichens which dwell on rocks are known as saxicolous species and fall under distinct groups such as (i) Crustose (ii) Fruticose and (iii) Foliose based on their mode of attachment to rocks (J ...
... Lichens are the association between fungus and a photosynthetic partner either green algae or cyanobacteria. Lichens which dwell on rocks are known as saxicolous species and fall under distinct groups such as (i) Crustose (ii) Fruticose and (iii) Foliose based on their mode of attachment to rocks (J ...
GEOG 123B Lec. #5
... set of processes to physical weathering. Chemical weathering is the actual decomposition of minerals in rock. Chemical weathering involves reactions between air and water and minerals in rock. Minerals may combine with water in chemical reactions (such as carbonation), or carbon dioxide and oxygen f ...
... set of processes to physical weathering. Chemical weathering is the actual decomposition of minerals in rock. Chemical weathering involves reactions between air and water and minerals in rock. Minerals may combine with water in chemical reactions (such as carbonation), or carbon dioxide and oxygen f ...
Grade: 3rd Activity #: 1 Activity Title: Studying Rocks and Minerals
... dissolving minerals where water has no effect. Of course, identification of minerals using solubility is a test that could destroy the specimen, if it is soluble. An unneeded fragment can be used for such tests. ...
... dissolving minerals where water has no effect. Of course, identification of minerals using solubility is a test that could destroy the specimen, if it is soluble. An unneeded fragment can be used for such tests. ...
Minerals - SchoolRack
... The particles of the material line up in a regular, repeating pattern. Has flat sides called faces, that meet at sharp edges and corners. ...
... The particles of the material line up in a regular, repeating pattern. Has flat sides called faces, that meet at sharp edges and corners. ...
a mineral is
... MINERALS ARE MADE UP OF SINGLE ELEMENTS OR COMPOUNDS ELEMENTS A SUBSTANCE THAT CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN TO ANY SIMPLER SUBSTANCE EIGHT MOST COMMON ELEMENTS IN THE EARTH’S CRUST: 1.) OXYGEN 46% ...
... MINERALS ARE MADE UP OF SINGLE ELEMENTS OR COMPOUNDS ELEMENTS A SUBSTANCE THAT CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN TO ANY SIMPLER SUBSTANCE EIGHT MOST COMMON ELEMENTS IN THE EARTH’S CRUST: 1.) OXYGEN 46% ...
Soil as a Resource
... the nutrients over time – In areas where climates are monsoonal, soil may form ‘brick’ hard surfaces – Lateritic soils are difficult to farm or work for people to grow food with ...
... the nutrients over time – In areas where climates are monsoonal, soil may form ‘brick’ hard surfaces – Lateritic soils are difficult to farm or work for people to grow food with ...
Laterite

Laterite is a soil and rock type rich in iron and aluminium, and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and long-lasting weathering of the underlying parent rock. Tropical weathering (laterization) is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned altogether. At least a few researchers specializing in regolith development have considered that hopeless confusion has evolved around the name. There is no likelihood, however, that the name will ever be abandoned; for material that looks highly similar to the Indian laterite occurs abundantly worldwide, and it is reasonable to call such material laterite.Historically, laterite was cut into brick-like shapes and used in monument-building. After 1000 CE, construction at Angkor Wat and other southeast Asian sites changed to rectangular temple enclosures made of laterite, brick and stone. Since the mid-1970s, some trial sections of bituminous-surfaced, low-volume roads have used laterite in place of stone as a base course. Thick laterite layers are porous and slightly permeable, so the layers can function as aquifers in rural areas. Locally available laterites have been used in an acid solution, followed by precipitation to remove phosphorus and heavy metals at sewage-treatment facilities.Laterites are a source of aluminium ore; the ore exists largely in clay minerals and the hydroxides, gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore, which resembles the composition of bauxite. In Northern Ireland they once provided a major source of iron and aluminium ores. Laterite ores also were the early major source of nickel.