The Biolog Plates Technique as a Tool in Ecological Studies of
... Microorganisms as an Important Component of Ecosystems and Objects of Environmental Studies Soil microorganisms play a crucial role in one of the most important ecological processes – the turnover of chemical elements in an ecosystem. Soil microbes break down complex organic molecules and release in ...
... Microorganisms as an Important Component of Ecosystems and Objects of Environmental Studies Soil microorganisms play a crucial role in one of the most important ecological processes – the turnover of chemical elements in an ecosystem. Soil microbes break down complex organic molecules and release in ...
Growing Carrots in Home Gardens
... Because carrots are a root crop, they grow best in soils that are well-drained, high in organic matter, and free of rocks. They are difficult to grow successfully in clay or rocky soils. Carrots prefer slightly acidic soil (pH 6 to 7), but will tolerate slightly alkaline soil (pH of 7 to 8). A soil ...
... Because carrots are a root crop, they grow best in soils that are well-drained, high in organic matter, and free of rocks. They are difficult to grow successfully in clay or rocky soils. Carrots prefer slightly acidic soil (pH 6 to 7), but will tolerate slightly alkaline soil (pH of 7 to 8). A soil ...
3.1 Introduction CHAPTER 3 MODELING ROTAVATOR TORQUE AND POWER REQUIREMENTS
... The changing location of the tip of a rotavator as it processes the soil is one of the key parameters that must to be considered when developing a mathematical model for its torque requirements. For a rotavator fitted with cutting blades of given a configuration, the instantaneous location of ...
... The changing location of the tip of a rotavator as it processes the soil is one of the key parameters that must to be considered when developing a mathematical model for its torque requirements. For a rotavator fitted with cutting blades of given a configuration, the instantaneous location of ...
Recent research with inoculants and N fertilizers for field pea has
... produced 22% higher biomass yield than the uninoculated check when Starter N was <20 kg N ha-1 (Clayton et al., 2004a). The biomass yield increase due to the granular soil inoculant was a mere 4% over the uninoculated pea when fertilizer N was applied at 40 to 80 kg ha-1. McConnell et al. (2002) fou ...
... produced 22% higher biomass yield than the uninoculated check when Starter N was <20 kg N ha-1 (Clayton et al., 2004a). The biomass yield increase due to the granular soil inoculant was a mere 4% over the uninoculated pea when fertilizer N was applied at 40 to 80 kg ha-1. McConnell et al. (2002) fou ...
Explicit Spatial Markov Chain
... While the recent developing trend in kriging geostatistics is focusing on incorporating multiplepoint statistics from various data sources such as training images (i.e., multiple-point geostatistics) (Journel, 2005), the recent progress in geostatistical development is seeing the emergence of Markov ...
... While the recent developing trend in kriging geostatistics is focusing on incorporating multiplepoint statistics from various data sources such as training images (i.e., multiple-point geostatistics) (Journel, 2005), the recent progress in geostatistical development is seeing the emergence of Markov ...
u>n 5 H fTiyc - Wageningen UR E
... observation points were established, at which points both the soil surveyor and the vegetation scientist recorded theirdata simultaneously. Apart from recording field data atthesepoints,vegetation and soils were viewed while travelling between points.Fig. 1 gives these locations and a reliability di ...
... observation points were established, at which points both the soil surveyor and the vegetation scientist recorded theirdata simultaneously. Apart from recording field data atthesepoints,vegetation and soils were viewed while travelling between points.Fig. 1 gives these locations and a reliability di ...
Presentation 11
... However, average salinity in soil not the same as ECdrainage. Determine average ECsoil by applying this procedure stepwise to a series of soil depths down to the bottom of the root zone. This approach requires an assumption on how much soil water is used in ET in each depth segment. ...
... However, average salinity in soil not the same as ECdrainage. Determine average ECsoil by applying this procedure stepwise to a series of soil depths down to the bottom of the root zone. This approach requires an assumption on how much soil water is used in ET in each depth segment. ...
THE SULFUR CYCLE
... ☺ Human action has had a major effect on the sulfur cycle. As farming techniques and practices of humans has developed throughout the years, more sulfur in the soil has been released into the atmosphere as dust due to grazing and plowing of land, and river diversion. Sulfur has also been released by ...
... ☺ Human action has had a major effect on the sulfur cycle. As farming techniques and practices of humans has developed throughout the years, more sulfur in the soil has been released into the atmosphere as dust due to grazing and plowing of land, and river diversion. Sulfur has also been released by ...
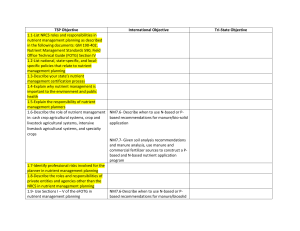
Specialty 4R Performance Objectives Comparison Version
... vulnerability of a site for P loss 4.11-Describe methods of reducing site vulnerability to soluble and sediment-bound phosphorus transport 4.12-Use individual site characteristics for the Leaching Index to characterize the vulnerability of a site for nitrate leaching 4.13-Describe methods of reducin ...
... vulnerability of a site for P loss 4.11-Describe methods of reducing site vulnerability to soluble and sediment-bound phosphorus transport 4.12-Use individual site characteristics for the Leaching Index to characterize the vulnerability of a site for nitrate leaching 4.13-Describe methods of reducin ...
Pausch J., Kramer S., Scharroba A., Scheunemann N
... within the soil food web is determined by ecosystem type. In particular, in arable systems, where plant biomass is harvested as crop, the internal terrestrial C cycle is strongly dependent on root-derived C rather than aboveground litter (Drigo et al. 2010). Surprisingly, only few studies using stab ...
... within the soil food web is determined by ecosystem type. In particular, in arable systems, where plant biomass is harvested as crop, the internal terrestrial C cycle is strongly dependent on root-derived C rather than aboveground litter (Drigo et al. 2010). Surprisingly, only few studies using stab ...
Community-weighted mean traits but not functional
... We used one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test the effect of different habitat types on plant taxonomic diversity (species richness), the CWM traits, functional diversity (FRic, FEve, and FDiv), and soil properties. Correlations between the CWM traits and soil properties were tested using Pear ...
... We used one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test the effect of different habitat types on plant taxonomic diversity (species richness), the CWM traits, functional diversity (FRic, FEve, and FDiv), and soil properties. Correlations between the CWM traits and soil properties were tested using Pear ...
MCEEE 105 –4 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOTECHNOLOGY (Elective I)
... (b) Briefly describe the failures of foundations due to pollutants. (5 marks) (c) Explain the environmental cycle and their interaction with the environment. (10 marks) 3) (a) What are the factors to be considered while selecting site for landfills? (5 marks) (b) Explain the different methods for an ...
... (b) Briefly describe the failures of foundations due to pollutants. (5 marks) (c) Explain the environmental cycle and their interaction with the environment. (10 marks) 3) (a) What are the factors to be considered while selecting site for landfills? (5 marks) (b) Explain the different methods for an ...
Chisel lourd de 2.50 - 5.90 m
... The load transfer on the tractor is made by accumulation pressure in a hydraulic accumulator when lowering the machine ...
... The load transfer on the tractor is made by accumulation pressure in a hydraulic accumulator when lowering the machine ...
Isolation and Characterization of Nitrogen
... be as a result of few media that was used (nitrogen f ree-media). Isolation of these organisms from soil samples were examined clearly and confirmed their ubiquity as noted by Skinner and Banfield (2005). Azospirillum and Azotobacter were grown under aerobic conditions while Clostridium was under an ...
... be as a result of few media that was used (nitrogen f ree-media). Isolation of these organisms from soil samples were examined clearly and confirmed their ubiquity as noted by Skinner and Banfield (2005). Azospirillum and Azotobacter were grown under aerobic conditions while Clostridium was under an ...
Topic 12: Soils of England and Wales - Soil
... near the soil surface in the winter time. This cause waterlogging and a lack of aeration. These soils occur on the floodplains of rivers. A gley soil is one that is periodically waterlogged during the year, mainly in winter and spring when there is the wettest weather, and this sets up chemical proce ...
... near the soil surface in the winter time. This cause waterlogging and a lack of aeration. These soils occur on the floodplains of rivers. A gley soil is one that is periodically waterlogged during the year, mainly in winter and spring when there is the wettest weather, and this sets up chemical proce ...
effect of fertigation on availability of nutrients (n, p
... Comparatively higher available nutrients were observed in Richfield water soluble fertilizer than straight fertilizer because Richfield water soluble fertilizer contains high soluble nutrients. Among the different levels of fertilizer, the treatment that received 125 per cent of recommended dose of ...
... Comparatively higher available nutrients were observed in Richfield water soluble fertilizer than straight fertilizer because Richfield water soluble fertilizer contains high soluble nutrients. Among the different levels of fertilizer, the treatment that received 125 per cent of recommended dose of ...
full text pdf
... whole mountain region and they can pull several spruce logs at the same time. Such activities lead to intensive erosion gully formation. Soil erosion involving gullies is one of the major causes of land degradation worldwide and a global threat to forestry productivity (Gyssels et al. 2005). The gul ...
... whole mountain region and they can pull several spruce logs at the same time. Such activities lead to intensive erosion gully formation. Soil erosion involving gullies is one of the major causes of land degradation worldwide and a global threat to forestry productivity (Gyssels et al. 2005). The gul ...
Chapter 12
... An investigation of groundwater conditions and recharge in a hard-rock basin in the Betwa basin in central India was undertaken from 1976 to 1980. The study was a joint research project between the Indian Central Groundwater Board and the British Geological Survey, and the Institute of Hydrology was ...
... An investigation of groundwater conditions and recharge in a hard-rock basin in the Betwa basin in central India was undertaken from 1976 to 1980. The study was a joint research project between the Indian Central Groundwater Board and the British Geological Survey, and the Institute of Hydrology was ...
effects of competition on resource availability and growth of a
... and duration of soil moisture reduction. For the shallowest soils and depths, soil moisture reduction occurred mainly during the first 5–10 wk of the growing season; for the lowest soil depths at the Agronomy Farm, no detectable period of reduction was observed and we used the last five data points ...
... and duration of soil moisture reduction. For the shallowest soils and depths, soil moisture reduction occurred mainly during the first 5–10 wk of the growing season; for the lowest soil depths at the Agronomy Farm, no detectable period of reduction was observed and we used the last five data points ...
Supplementary information
... rhizosphere fraction (SRS) of Phragmites australis and Cladium mariscus, as well as anoxic bulk soils (SBS) and water-soil interfaces (SWSI) in marsh sediment or salisodisol. ...
... rhizosphere fraction (SRS) of Phragmites australis and Cladium mariscus, as well as anoxic bulk soils (SBS) and water-soil interfaces (SWSI) in marsh sediment or salisodisol. ...
PDF
... Gut Wall Ecosystem:The common species of earthworm ecological groups foster the development of distinct gut wall-associated bacterial communities and that the relative abundance of specific bacteria within the gut wall, including Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and an actinobacterium, is ecological group ...
... Gut Wall Ecosystem:The common species of earthworm ecological groups foster the development of distinct gut wall-associated bacterial communities and that the relative abundance of specific bacteria within the gut wall, including Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and an actinobacterium, is ecological group ...
A Comparison of Landscape Mulches
... Thick layer can inhibit infiltration of water Easily transported via stormwater runoff Rapid decomposition requires frequent replenishment ...
... Thick layer can inhibit infiltration of water Easily transported via stormwater runoff Rapid decomposition requires frequent replenishment ...
nitrogen_cycle
... • Green plants absorb nitrogen in the form of ions: • ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ions via the roots. • Green plants use these ions to make amino acids and proteins, which are passed to consumers by feeding. ...
... • Green plants absorb nitrogen in the form of ions: • ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ions via the roots. • Green plants use these ions to make amino acids and proteins, which are passed to consumers by feeding. ...
- Wiley Online Library
... to soil conditioned by endophyte-free plants?, we used a general linear model that included the independent factors of tree species (nine species), treatment (five levels: E+ live, E+ sterile, E– live, E– sterile and No fescue), and tree species × treatment (proc glm, SAS Institute 2004, v. 9.1, Car ...
... to soil conditioned by endophyte-free plants?, we used a general linear model that included the independent factors of tree species (nine species), treatment (five levels: E+ live, E+ sterile, E– live, E– sterile and No fescue), and tree species × treatment (proc glm, SAS Institute 2004, v. 9.1, Car ...
D. Soil - Humble ISD
... each launch the number of pumps was recorded as well as the height reached by the rocket. If the pattern shown in the data continues, how many pumps would it take for the rocket to reach a height of 15 meters? ...
... each launch the number of pumps was recorded as well as the height reached by the rocket. If the pattern shown in the data continues, how many pumps would it take for the rocket to reach a height of 15 meters? ...