Agriculture and water
... Germany, Scotland and Estonia because there are no droughts or very high temperatures. But it can be caused by fertilizer and road salt ...
... Germany, Scotland and Estonia because there are no droughts or very high temperatures. But it can be caused by fertilizer and road salt ...
Compacted Zone In Soil - NRCS
... The size and continuity of pores controls whether larger microbes, such as protozoa, can prey upon bacteria and fungi. Smaller pores favor bacteria and smaller predators over fungi and larger predators. Arthropods are severely affected by compaction. The predatory species of nematodes is also affect ...
... The size and continuity of pores controls whether larger microbes, such as protozoa, can prey upon bacteria and fungi. Smaller pores favor bacteria and smaller predators over fungi and larger predators. Arthropods are severely affected by compaction. The predatory species of nematodes is also affect ...
Soil Erosion - University of Connecticut
... 1. Soil erosion is the process of weathering and transport of solids (sediment, soil, rock and other particles) in the natural environment or their source and deposits them elsewhere. 2. Soil erosion usually occurs due to transport by wind, water, or ice; by down-slope creeping of soil and other mat ...
... 1. Soil erosion is the process of weathering and transport of solids (sediment, soil, rock and other particles) in the natural environment or their source and deposits them elsewhere. 2. Soil erosion usually occurs due to transport by wind, water, or ice; by down-slope creeping of soil and other mat ...
verticillium soil assay for determination of colony forming units per
... For each sample: 1. Break up soil into an even consistency. 2. Shake soil to allow for mixing. 3. Take a subsample using a 30 ml beaker to transfer 4 full beakers to another bag. Or use whatever sub-sampling method you use normally. 4. Shake soil to allow for mixing. 5. Weigh 6 g of soil into a 125 ...
... For each sample: 1. Break up soil into an even consistency. 2. Shake soil to allow for mixing. 3. Take a subsample using a 30 ml beaker to transfer 4 full beakers to another bag. Or use whatever sub-sampling method you use normally. 4. Shake soil to allow for mixing. 5. Weigh 6 g of soil into a 125 ...
Lindsey`s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
Soil Study Guide
... plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of minerals. 5. Silt is fine particles of soil that are carried along by flowing water and settle at the bottom of a lake or river. 6. Loam is the best soil for plants to grow in, especially vegetables. 7. Sandy soil has large grains and does not hold water well ...
... plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of minerals. 5. Silt is fine particles of soil that are carried along by flowing water and settle at the bottom of a lake or river. 6. Loam is the best soil for plants to grow in, especially vegetables. 7. Sandy soil has large grains and does not hold water well ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... Why is soil one of Earth’s most valuable natural resources? Everything that lives on land, including humans, depends directly or indirectly on soil. Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
... Why is soil one of Earth’s most valuable natural resources? Everything that lives on land, including humans, depends directly or indirectly on soil. Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
Summative Assessment Questions on Soils (LCA Ag,Hort Basic Hort
... 1. A good fertile soil provides plants with what? 2. List the constituents of a fertile soil. 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime adde ...
... 1. A good fertile soil provides plants with what? 2. List the constituents of a fertile soil. 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime adde ...
soil and weathering
... and carries away minerals and nutrients in topsoil 13. the decaying organic matter in soil 15. weathering breakdown or decomposition of rock that takes place when minerals change through chemical processes 16. the process in which layers or sheets of rock gradually break off 17. the process in which ...
... and carries away minerals and nutrients in topsoil 13. the decaying organic matter in soil 15. weathering breakdown or decomposition of rock that takes place when minerals change through chemical processes 16. the process in which layers or sheets of rock gradually break off 17. the process in which ...
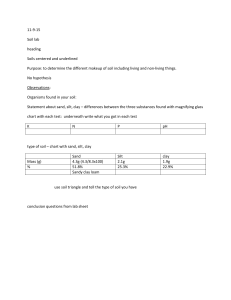
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
New soil test - Washtenaw County
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
Lecture 4
... land-resulting from sheet or overland flow occurring in thin layers. minute rilling takes place almost simultaneously with the first detachment and movement of soil particles. the constant meander and change of position of these microscopic rills. ...
... land-resulting from sheet or overland flow occurring in thin layers. minute rilling takes place almost simultaneously with the first detachment and movement of soil particles. the constant meander and change of position of these microscopic rills. ...
CRSC 6 – Introduction to Precision Agriculture
... be used to identify the locations where soil samples are taken. 2. _________________ are used to identify areas of the field which have different levels of nutrients. ...
... be used to identify the locations where soil samples are taken. 2. _________________ are used to identify areas of the field which have different levels of nutrients. ...
THE EFFECT OF AGRICULTURE
... surrounding the fields for large-scale farming lead to soil erosion easily due to the removal of the wind break, mechanical ploughing loosens soil and speed up erosion ...
... surrounding the fields for large-scale farming lead to soil erosion easily due to the removal of the wind break, mechanical ploughing loosens soil and speed up erosion ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
Teaching soil ecology in one lab session
... • Talk about variation among ecosystems, as well as within ecosystems. • Have students generate hypotheses about how soils might differ within their campus ecosystem (based on plant cover, management, etc.) ...
... • Talk about variation among ecosystems, as well as within ecosystems. • Have students generate hypotheses about how soils might differ within their campus ecosystem (based on plant cover, management, etc.) ...
limiting soil compaction
... Consider using low-impact machinery for equipment operations: small, rubber tracked machines are lighter and more precise than large machines. Work when the soil is dry if at all possible; wet soil is more susceptible to compaction. Walk the area with the equipment operators before work starts to cl ...
... Consider using low-impact machinery for equipment operations: small, rubber tracked machines are lighter and more precise than large machines. Work when the soil is dry if at all possible; wet soil is more susceptible to compaction. Walk the area with the equipment operators before work starts to cl ...