Tolerancing Optical Systems
... blemishes. In most cases these defects are small and they do not affect system performance. Hence they are often called “beauty specifications”. They indicate the level of workmanship in the part and face it, nobody wants their expensive optics to ...
... blemishes. In most cases these defects are small and they do not affect system performance. Hence they are often called “beauty specifications”. They indicate the level of workmanship in the part and face it, nobody wants their expensive optics to ...
Experimental method for reliably establishing the refractive index of
... and Miller’s values were “so far outside the range of refractive indices ever measured for insect cuticles (1.5 and 1.6) that they should be carefully checked”. However, Caveney later conducted experiments on the cuticle of an iridescent scarab beetle and determined the average refractive index of i ...
... and Miller’s values were “so far outside the range of refractive indices ever measured for insect cuticles (1.5 and 1.6) that they should be carefully checked”. However, Caveney later conducted experiments on the cuticle of an iridescent scarab beetle and determined the average refractive index of i ...
A single atom in free space as a quantum aperture
... various atomic quantities. As a simple starting point and in order to make contact with the work of Ref. [9], we assume that the atom reaches a stationary steady state. In this case, given the value of the electric field at the atom’s position αF~out (~r0 ), the various atomic expectation values can ...
... various atomic quantities. As a simple starting point and in order to make contact with the work of Ref. [9], we assume that the atom reaches a stationary steady state. In this case, given the value of the electric field at the atom’s position αF~out (~r0 ), the various atomic expectation values can ...
08-Michelson
... successive movements of distance /2 by M1 will also fulfill this condition. Parallel rays making an angle with the axis interfere constructively if 2dcos = m . The net result is concentric circular fringes corresponding to appropriate values of . "Localized fringes" which are virtually paralle ...
... successive movements of distance /2 by M1 will also fulfill this condition. Parallel rays making an angle with the axis interfere constructively if 2dcos = m . The net result is concentric circular fringes corresponding to appropriate values of . "Localized fringes" which are virtually paralle ...
Document
... Section 6.4.1, where we discussed Vander Lugt’s matched filter. If instead of the plane wave reference we had an arbitrary field interfering with the object field, the numerical reconstruction would yield the correlation between the Fourier transform of the two fields. Since the reference field is ...
... Section 6.4.1, where we discussed Vander Lugt’s matched filter. If instead of the plane wave reference we had an arbitrary field interfering with the object field, the numerical reconstruction would yield the correlation between the Fourier transform of the two fields. Since the reference field is ...
Microscope Project for Undergraduate Laboratories Abstract
... the parts are durable and basic, recycled or even 3D printed parts could be used.5,6 In this section, we justify some of the choices we made for components. The optical breadboard with 1/4”-20 tapped holes in a 1-inch square grid was used as a platform to build the microscope if an optical table is ...
... the parts are durable and basic, recycled or even 3D printed parts could be used.5,6 In this section, we justify some of the choices we made for components. The optical breadboard with 1/4”-20 tapped holes in a 1-inch square grid was used as a platform to build the microscope if an optical table is ...
The Research of Near-Infrared Electro-Optics
... (2) The light source and lens is fine tuned until the reflected beam from the plane mirror being focused on the position of the light source. (3) The photodiode is also calibrated and fine tunes as in step 1 & 2, but to achieve maximum signal receipt. plane mirror ...
... (2) The light source and lens is fine tuned until the reflected beam from the plane mirror being focused on the position of the light source. (3) The photodiode is also calibrated and fine tunes as in step 1 & 2, but to achieve maximum signal receipt. plane mirror ...
Experimental demonstration of a light-ray-direction
... confocal lenslet arrays (that is, confocal arrays of spherical microlenses) [11]. In the simplest case, namely if the two lenslet arrays have the same focal length and are aligned such that corresponding lenslets in the two arrays share the same optical axis, such confocal lenslet arrays act – ray-o ...
... confocal lenslet arrays (that is, confocal arrays of spherical microlenses) [11]. In the simplest case, namely if the two lenslet arrays have the same focal length and are aligned such that corresponding lenslets in the two arrays share the same optical axis, such confocal lenslet arrays act – ray-o ...
Problem 2
... Let us consider only the situation that the light wave travels along the direction perpendicular to the plates (the ray diagram depicted in Fig.2-4 is only a ...
... Let us consider only the situation that the light wave travels along the direction perpendicular to the plates (the ray diagram depicted in Fig.2-4 is only a ...
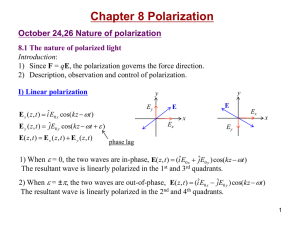
Chapter 8
... October 31 Scattering and polarization 8.5 Scattering and polarization Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directio ...
... October 31 Scattering and polarization 8.5 Scattering and polarization Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directio ...
Aberrations and retinal image quality of the normal human eye
... and interferometric techniques.12 The second set was made on nine other eyes with a slightly different procedure. For comparison with double-pass and interferometric MTF’s, measurements were made on the right eyes of RNB, DRW, and DHB, whose ages were 36, 40, and 34, respectively. These observers we ...
... and interferometric techniques.12 The second set was made on nine other eyes with a slightly different procedure. For comparison with double-pass and interferometric MTF’s, measurements were made on the right eyes of RNB, DRW, and DHB, whose ages were 36, 40, and 34, respectively. These observers we ...
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... Geometrical optics can’t tell how much is reflected and how much transmitted at an interface. This can be derived from Maxwell’s equations. These are described in terms of the reflection and transmission coefficients R and T, which are, respectively, the fraction of incident intensity reflected and ...
... Geometrical optics can’t tell how much is reflected and how much transmitted at an interface. This can be derived from Maxwell’s equations. These are described in terms of the reflection and transmission coefficients R and T, which are, respectively, the fraction of incident intensity reflected and ...
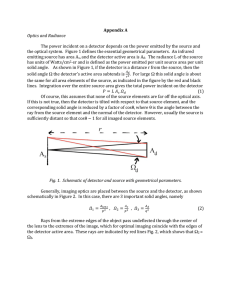
Appendix A Optics and Radiance The power incident on a
... corresponding solid angle is reduced by a factor of cosθ, where θ is the angle between the ray from the source element and the normal of the detector. However, usually the source is sufficiently ...
... corresponding solid angle is reduced by a factor of cosθ, where θ is the angle between the ray from the source element and the normal of the detector. However, usually the source is sufficiently ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.