Lasers and lenses - University of Toronto
... atom cloud to be trapped will be located approximately 3.75cm inside the cell. This means that the focusing lens must have a focal length of 4cm or greater. There should be space for this directly opposite the BEC imaging system. According to the rules of Gaussian optics, in order to obtain the smal ...
... atom cloud to be trapped will be located approximately 3.75cm inside the cell. This means that the focusing lens must have a focal length of 4cm or greater. There should be space for this directly opposite the BEC imaging system. According to the rules of Gaussian optics, in order to obtain the smal ...
What is a Fresnel Lens?
... These circular ridges give the Fresnel lens a zigzag or sawtooth cross-section. Each sawtooth creates a tiny prism. By choosing appropriate powers for these prisms, designers can define the focal length and control image quality. Fresnel lenses are molded from precision opticalgrade acrylic. Typical ...
... These circular ridges give the Fresnel lens a zigzag or sawtooth cross-section. Each sawtooth creates a tiny prism. By choosing appropriate powers for these prisms, designers can define the focal length and control image quality. Fresnel lenses are molded from precision opticalgrade acrylic. Typical ...
CC_A3_C2_photo2_old
... – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
... – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
Direct measurement of terahertz wavefront pulses using 2D electro
... Wavefront characterization of terahertz (THz) pulses is essential to optimize far-field intensity distribution or spot focalization, as well as increase the peak power of intense terahertz sources. In the visible spectral region, Hartmann masks, invented a century ago, are used to perform optical me ...
... Wavefront characterization of terahertz (THz) pulses is essential to optimize far-field intensity distribution or spot focalization, as well as increase the peak power of intense terahertz sources. In the visible spectral region, Hartmann masks, invented a century ago, are used to perform optical me ...
Geometrical Optics 101: Paraxial Ray Tracing
... If the location of the aperture stop is unknown, a trial ray, known as the pseudo marginal ray, must be propagated through the system. For an object not at infinity, this ray must begin at the axial position of the object and can have an arbitrary incident angle. For an object at infinity, the ray c ...
... If the location of the aperture stop is unknown, a trial ray, known as the pseudo marginal ray, must be propagated through the system. For an object not at infinity, this ray must begin at the axial position of the object and can have an arbitrary incident angle. For an object at infinity, the ray c ...
Optical aberrations of intraocular lenses measured in vivo and in vitro
... model cornea as a function of IOL power, as well as individual predictions of total spherical aberration by using individual corneal topography, anterior chamber depth, and IOL parameters. This modeling also allowed us to test the effects of IOL tilt and decentration. The computer simulations were p ...
... model cornea as a function of IOL power, as well as individual predictions of total spherical aberration by using individual corneal topography, anterior chamber depth, and IOL parameters. This modeling also allowed us to test the effects of IOL tilt and decentration. The computer simulations were p ...
Optical fibers - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... A single mode optical fiber consists of a core having a uniform refractive index n1 that abruptly decreases at the core-cladding interface to a lower value n2 the refractive index of the cladding. The diameter of the core is narrow (5-10m) generally a few times the wavelength of the light propagat ...
... A single mode optical fiber consists of a core having a uniform refractive index n1 that abruptly decreases at the core-cladding interface to a lower value n2 the refractive index of the cladding. The diameter of the core is narrow (5-10m) generally a few times the wavelength of the light propagat ...
outline21379
... 1) Determine by over-refracting the endpoint diagnostic contact lens and adding the vertexed equivalent diopter sphere to the power of the diagnostic lens 2) SAM-FAP 3) Residual astigmatism a. ...
... 1) Determine by over-refracting the endpoint diagnostic contact lens and adding the vertexed equivalent diopter sphere to the power of the diagnostic lens 2) SAM-FAP 3) Residual astigmatism a. ...
Ophthalmic lens
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
course objectives - Metropolitan Community College
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: light, white light, wavefront, a ray, a plane wave, parallel light, specular versus diffuse reflection, virtual versus real image, focal point, focal length, index of refraction, Snell’s law, total internal reflection, critical angle, con ...
... Define and explain the following terms, principles and ideas: light, white light, wavefront, a ray, a plane wave, parallel light, specular versus diffuse reflection, virtual versus real image, focal point, focal length, index of refraction, Snell’s law, total internal reflection, critical angle, con ...
Microscopy
... transistor in a square array of identical transistors on a silicon wafer. You may not use any lenses. 2) Review the ray-tracing diagram for the compound microscope of lab 3. ...
... transistor in a square array of identical transistors on a silicon wafer. You may not use any lenses. 2) Review the ray-tracing diagram for the compound microscope of lab 3. ...
IT19 Color Quick Response Codes for High Profile Security
... the Fraunhofer diffraction formula, the Fourier Transform operation is utilized to give the far field amplitude calculation required for calculating the interference pattern. The spectral estimation technique is introduced to the color digital holography to improve color reproduction Figure 2 shows ...
... the Fraunhofer diffraction formula, the Fourier Transform operation is utilized to give the far field amplitude calculation required for calculating the interference pattern. The spectral estimation technique is introduced to the color digital holography to improve color reproduction Figure 2 shows ...
PDF Format
... The wave plates operate on the principle that two orthogonally oriented polarization states experience two different indices of refraction. Consequently, one polarization of light travels faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in th ...
... The wave plates operate on the principle that two orthogonally oriented polarization states experience two different indices of refraction. Consequently, one polarization of light travels faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in th ...
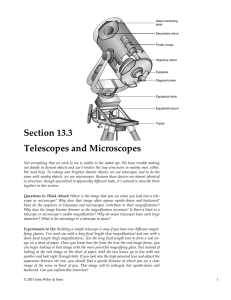
Section 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes
... actually the real image from the first part of the telescope. You use the magnifying glass—actually called the eyepiece or ocular lens—to enlarge the real image so that you can see its detail more clearly. You can focus the eyepiece, like any magnifying glass, by moving it back and forth. The farthe ...
... actually the real image from the first part of the telescope. You use the magnifying glass—actually called the eyepiece or ocular lens—to enlarge the real image so that you can see its detail more clearly. You can focus the eyepiece, like any magnifying glass, by moving it back and forth. The farthe ...
Computer-generated holograms of three
... heavy computational task. We propose and demonstrate a new algorithm for computing CGHs of 3D objects. In our scheme, many different angular projections of computer-designed 3D objects are numerically processed to yield a single two-dimensional complex matrix. This matrix is equivalent to the comple ...
... heavy computational task. We propose and demonstrate a new algorithm for computing CGHs of 3D objects. In our scheme, many different angular projections of computer-designed 3D objects are numerically processed to yield a single two-dimensional complex matrix. This matrix is equivalent to the comple ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.