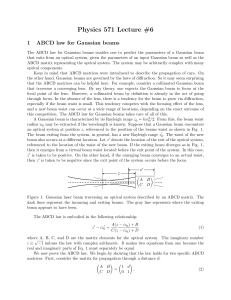
Manuscript2 - Open Research Exeter
... higher the concentration ratio of a solar concentrator system, the more dependent upon accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Je ...
... higher the concentration ratio of a solar concentrator system, the more dependent upon accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Je ...
Part 4 - MZA Associates Corporation
... where the phase (green waves, f) is equal to a particular value (r). • Light travels in a straight line (light blue arrows) normal to the wavefront. • 2p discontinuities, intensity variations, and interference complicate matters. ...
... where the phase (green waves, f) is equal to a particular value (r). • Light travels in a straight line (light blue arrows) normal to the wavefront. • 2p discontinuities, intensity variations, and interference complicate matters. ...
Note
... • The observed profile is the convolution of the true line profile with the instrument profile • For high S/N ratio data, Fourier techniques can be used to back out the IP from a spectrum to recover some of the resolution. ...
... • The observed profile is the convolution of the true line profile with the instrument profile • For high S/N ratio data, Fourier techniques can be used to back out the IP from a spectrum to recover some of the resolution. ...
The Critical Angle and Beyond - The Society of Vacuum Coaters
... and parallel to the first surface, it can intrude into the exponential tail of the fields. This surface will have the same pattern of intersections with the constant phase planes as the first surface. Suppose the other side of the second surface consists of material with refractive index n0. Since a ...
... and parallel to the first surface, it can intrude into the exponential tail of the fields. This surface will have the same pattern of intersections with the constant phase planes as the first surface. Suppose the other side of the second surface consists of material with refractive index n0. Since a ...
Analytic design method for optimal imaging: coupling three ray sets
... In contrast, direct optics design methods do not necessarily follow this design strategy. Usually, a key objective is to find a set of unrestricted free-form surfaces designed to have specific predefined characteristics. Where unrestricted means that the optical surfaces can have any shape to fulfil ...
... In contrast, direct optics design methods do not necessarily follow this design strategy. Usually, a key objective is to find a set of unrestricted free-form surfaces designed to have specific predefined characteristics. Where unrestricted means that the optical surfaces can have any shape to fulfil ...
Real-time digital holographic microscopy Ventseslav Sainov and Elena Stoykova
... of recent advances in laser sources, two dimensional photo sensors (CCD or CMOS cameras) and digital signal processing techniques [1-3]. Digital holography exhibits some exceptional features which makes it especially suitable for microscopy [4] as quantitative phase-contrast imaging of transparent b ...
... of recent advances in laser sources, two dimensional photo sensors (CCD or CMOS cameras) and digital signal processing techniques [1-3]. Digital holography exhibits some exceptional features which makes it especially suitable for microscopy [4] as quantitative phase-contrast imaging of transparent b ...
CHAPTER 15. LASER AND FIBER OPTICS The laser is essentially
... population of this level easily piles up to a value much larger than that of level E1 (lower laser level), which is an ordinary level that decays to the ground states quite rapidly (step 4). The population N1 cannot build to a large value. The required population inversion for the light amplificatio ...
... population of this level easily piles up to a value much larger than that of level E1 (lower laser level), which is an ordinary level that decays to the ground states quite rapidly (step 4). The population N1 cannot build to a large value. The required population inversion for the light amplificatio ...
Axial birefringence in high-numerical-aperture optical
... The effects of birefringence on the light distribution in the focal region of a high-NA optical system are investigated with use of the Debye approach to vector diffraction theory. The attention is limited to uniaxially birefringent media with symmetry axis along the optical axis of the imaging syst ...
... The effects of birefringence on the light distribution in the focal region of a high-NA optical system are investigated with use of the Debye approach to vector diffraction theory. The attention is limited to uniaxially birefringent media with symmetry axis along the optical axis of the imaging syst ...
Chapter 8
... November 7 Scattering and polarization 8.5 Scattering and polarization Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directio ...
... November 7 Scattering and polarization 8.5 Scattering and polarization Polarization by scattering: If the incident light is unpolarized, then 1) The scattered light in the forward direction is unpolarized. 2) The scattered light at 90º is linearly polarized. 3) The scattered light in other directio ...
Word - WM Keck Observatory
... on the right is measured to be nearly 3 pixels, rather than the one pixel of actual image shift. The “centroid gain” will hence always be less than one. It can be parameterized by the ratio of the slit width to the width of the actual image. For a very narrow slit, the centroid gain will be near uni ...
... on the right is measured to be nearly 3 pixels, rather than the one pixel of actual image shift. The “centroid gain” will hence always be less than one. It can be parameterized by the ratio of the slit width to the width of the actual image. For a very narrow slit, the centroid gain will be near uni ...
Refractive indexes of (Al,Ga,In)As epilayers on InP for optoelectronic
... We have minimized this error by performing the spectrophotometer background correction with a bare InP substrate (rather than a metal mirror). The fringe amplitude is the determined from a normalized reflectivity spectrum which oscillates around unity. The data of Pettit et al. [9] was used for the ...
... We have minimized this error by performing the spectrophotometer background correction with a bare InP substrate (rather than a metal mirror). The fringe amplitude is the determined from a normalized reflectivity spectrum which oscillates around unity. The data of Pettit et al. [9] was used for the ...
Measurement of spectacle lenses: A review
... suitable solution for the wearer of ophthalmic lenses, since they can be fabricated for the specific needs of the individual [5]. Free form lenses are irregular surfaces without a rotational axis, modeled with CAD software [6]. The precision of free form lenses is of 0.01 D, also they have a reduced ...
... suitable solution for the wearer of ophthalmic lenses, since they can be fabricated for the specific needs of the individual [5]. Free form lenses are irregular surfaces without a rotational axis, modeled with CAD software [6]. The precision of free form lenses is of 0.01 D, also they have a reduced ...
Slide
... principle, which can be stated as follows: Knowing the optical field over any given plane in vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, the field at any other plane can be expressed as a superposition of “secondary” spherical waves, known as Huygens wavelets, originating from each point in the first plan ...
... principle, which can be stated as follows: Knowing the optical field over any given plane in vacuum or an ideal dielectric medium, the field at any other plane can be expressed as a superposition of “secondary” spherical waves, known as Huygens wavelets, originating from each point in the first plan ...
The Compound Microscope
... • Finally, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) bombards a specimen with a beam of electrons instead of light to produce a highly magnified image from 100x to 100,0000x. • Its depth of focus is some 300 times better than optical systems at similar magnification. • The bombardment of the specimen’s ...
... • Finally, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) bombards a specimen with a beam of electrons instead of light to produce a highly magnified image from 100x to 100,0000x. • Its depth of focus is some 300 times better than optical systems at similar magnification. • The bombardment of the specimen’s ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.











![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852282_1-34a75f388cb1d60fa5a2254e9305255e-300x300.png)