Basic Biomechanics
... – Popliteal crease heights (low, high, level) – Trochanter heights (low, high, level) – Iliac crest heights (low on the right/left, normal) – Lumbar scoliosis (right/left, or no signs of) – Thoracic scoliosis (right/left, or no signs of) – Shoulder level (low on the right/left, or normal) – Cervical ...
... – Popliteal crease heights (low, high, level) – Trochanter heights (low, high, level) – Iliac crest heights (low on the right/left, normal) – Lumbar scoliosis (right/left, or no signs of) – Thoracic scoliosis (right/left, or no signs of) – Shoulder level (low on the right/left, or normal) – Cervical ...
Atlanto-occipital and Atlantoaxial joints
... • surround the joint • Thick posterolaterally and anteromedially 2.Anterior atlanto‐occipital membrane: • Anterior margin of foramen above to upper border of anterior arch of atlas below • Anteriorly strengthened by anterior longitudinal ligament • Laterally continuous with the anterior part of c ...
... • surround the joint • Thick posterolaterally and anteromedially 2.Anterior atlanto‐occipital membrane: • Anterior margin of foramen above to upper border of anterior arch of atlas below • Anteriorly strengthened by anterior longitudinal ligament • Laterally continuous with the anterior part of c ...
X-Ray - chiropractic National Boards
... Rib Fracture - Follow ribs two at a time checking for alteration in lines. Primary location lateral aspect of film where ribs curve from posterior to anterior. Do not assess ribs on a lateral thoracic. Compression fracture - Fracture of a vertebra by pressure along the long axis of the vertebral col ...
... Rib Fracture - Follow ribs two at a time checking for alteration in lines. Primary location lateral aspect of film where ribs curve from posterior to anterior. Do not assess ribs on a lateral thoracic. Compression fracture - Fracture of a vertebra by pressure along the long axis of the vertebral col ...
X-ray Part IV National Boards Know the synonyms for National
... Rib Fracture - Follow ribs two at a time checking for alteration in lines. Primary location lateral aspect of film where ribs curve from posterior to anterior. Do not assess ribs on a lateral thoracic. Compression fracture - Fracture of a vertebra by pressure along the long axis of the vertebral col ...
... Rib Fracture - Follow ribs two at a time checking for alteration in lines. Primary location lateral aspect of film where ribs curve from posterior to anterior. Do not assess ribs on a lateral thoracic. Compression fracture - Fracture of a vertebra by pressure along the long axis of the vertebral col ...
Muscles and movements of back
... - repeatedly do this while using laryngeal muscles to call for help ...
... - repeatedly do this while using laryngeal muscles to call for help ...
carnosaurs, allosaurids, sauropods, cetiosaurids
... processes, the 2 prootics, the laterosphenoids (incomplete anteriorly), the 2 parietals and the nearly complete supraoccipital. In posterior view, the occipital condyle is low and wide, with a neck that is well-marked on the ventral and lateral faces but does not extend beyond the dorsal edge of the ...
... processes, the 2 prootics, the laterosphenoids (incomplete anteriorly), the 2 parietals and the nearly complete supraoccipital. In posterior view, the occipital condyle is low and wide, with a neck that is well-marked on the ventral and lateral faces but does not extend beyond the dorsal edge of the ...
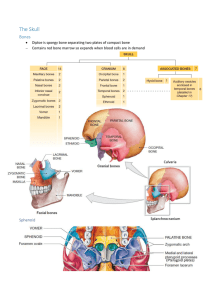
The Skull
... Neonate skulls Anterior and posterior fontanelles Frontal suture (under age of 5) Metopic suture (if present over age of 5) ...
... Neonate skulls Anterior and posterior fontanelles Frontal suture (under age of 5) Metopic suture (if present over age of 5) ...
Occipitalization of atlas with other associated anomalies of skull
... observed along the line of fusion. The left portion of the posterior arch was longer than the right one. The posterior tubercle of the posterior arch had lost its typical appearance. At the inferior margin, the posterior arch in the midline showed a notch. On both sides, the grooves for the vertebra ...
... observed along the line of fusion. The left portion of the posterior arch was longer than the right one. The posterior tubercle of the posterior arch had lost its typical appearance. At the inferior margin, the posterior arch in the midline showed a notch. On both sides, the grooves for the vertebra ...
Spinal Cord - mrsralston
... After passing through the intervertebral foramen a spinal nerve divides into several branches = plexus (cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral) ...
... After passing through the intervertebral foramen a spinal nerve divides into several branches = plexus (cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral) ...
Body Organization - Appoquinimink High School
... opposite of proximal; particular body part is farther from a point of attachment than another body part. (Fingers are distal to the wrist) ...
... opposite of proximal; particular body part is farther from a point of attachment than another body part. (Fingers are distal to the wrist) ...
Bone Markings
... Centrum – rounded central portion, which faces anteriorly in the human vertebral column Vertebral arch – composed of pedicles, laminae, and spinous process, it represents he junction of all posterior extensions from the vertebral body Vertebral (spinal) foramen – opening enclosed by the body and ver ...
... Centrum – rounded central portion, which faces anteriorly in the human vertebral column Vertebral arch – composed of pedicles, laminae, and spinous process, it represents he junction of all posterior extensions from the vertebral body Vertebral (spinal) foramen – opening enclosed by the body and ver ...
The Spine
... ribs o Body is intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae Lumbar – 5 vertebrae (L1-L5) o Has a large body o Does not have costal facets nor transverse process foramina Sacral – 5 (fused) vertebrae (S1-S5) Coccygeal – 4 (3-5) (fused) vertebrae (Tailbone) ...
... ribs o Body is intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae Lumbar – 5 vertebrae (L1-L5) o Has a large body o Does not have costal facets nor transverse process foramina Sacral – 5 (fused) vertebrae (S1-S5) Coccygeal – 4 (3-5) (fused) vertebrae (Tailbone) ...
L1: Organisation of ANS L2: Thoracic walls and breast
... Costal cartilage – attaches ribs to sternum anteriorly and contributes to mobility - Typical ribs (3-9) – curved and flat - Atypical rib (1,2,10-12) – different markings o Rib 1 is flatter, grooves for subclavian vessels and scalene tubercle - Costal groove – has intercostal nerves (protected) Stern ...
... Costal cartilage – attaches ribs to sternum anteriorly and contributes to mobility - Typical ribs (3-9) – curved and flat - Atypical rib (1,2,10-12) – different markings o Rib 1 is flatter, grooves for subclavian vessels and scalene tubercle - Costal groove – has intercostal nerves (protected) Stern ...
Chapter 9 Spine
... investigated with MRI or CT. Specific low back pain refers to back pain with associated clinical ...
... investigated with MRI or CT. Specific low back pain refers to back pain with associated clinical ...
Cervical)Plexus)Blocks)
... block and here the C4 level is marked and the transducer is placed laterally at this landmark and moved posteriorly =ll the transverse process of C4 is iden=fied • The needle is then introduced ...
... block and here the C4 level is marked and the transducer is placed laterally at this landmark and moved posteriorly =ll the transverse process of C4 is iden=fied • The needle is then introduced ...
Anth 480 HYOID Body - attachment for many muscle with the term
... Body - attachment for many muscle with the term "hyoid" in them (geniohyoid, stylohyoid, omohyoid, mylohyoid, sternohyoid) Greater cornu(a) VERTEBRAE Your garden variety vertebra has the following parts: vertebral body - not quite synonymous with centrum (which lacks portion made up by neural arch) ...
... Body - attachment for many muscle with the term "hyoid" in them (geniohyoid, stylohyoid, omohyoid, mylohyoid, sternohyoid) Greater cornu(a) VERTEBRAE Your garden variety vertebra has the following parts: vertebral body - not quite synonymous with centrum (which lacks portion made up by neural arch) ...
sirenomelia: sympus dipus (" mermaid ")
... (Fig. 1). The upper limbs appeared flattened antero-posteriorly, and the wrist, metacarpo-phalangeal and interphalangeal joints were readily hyperextended. The pelvic girdle was about two-thirds the expected diameter. A small, shallow dimple was present over the top of the coccyx, and another dimple ...
... (Fig. 1). The upper limbs appeared flattened antero-posteriorly, and the wrist, metacarpo-phalangeal and interphalangeal joints were readily hyperextended. The pelvic girdle was about two-thirds the expected diameter. A small, shallow dimple was present over the top of the coccyx, and another dimple ...
Orientation to Human Body PPT
... • Cavities and the organs (viscera) of the cavities are lined with membranes. Why do you think this is? – Dorsal cavities: Cranial, vertebral. • Dorsal membranes: meninges. – Ventral cavities: Thoracic, abdominopelvic. • Ventral membranes: pluera, pericardium, ...
... • Cavities and the organs (viscera) of the cavities are lined with membranes. Why do you think this is? – Dorsal cavities: Cranial, vertebral. • Dorsal membranes: meninges. – Ventral cavities: Thoracic, abdominopelvic. • Ventral membranes: pluera, pericardium, ...
The Lower Limbs
... – Forms the most inferior part of the coxa – Ischial tuberosity is roughened area of most inferior point that receives the body weight when sitting – Ischial spine is a projection on the posterior side of the ischium, above the ischial tuberosity – Greater sciatic notch is above the ischium, below t ...
... – Forms the most inferior part of the coxa – Ischial tuberosity is roughened area of most inferior point that receives the body weight when sitting – Ischial spine is a projection on the posterior side of the ischium, above the ischial tuberosity – Greater sciatic notch is above the ischium, below t ...
Spinal Cord and Nerves Notes
... It is a _______________________ cord that measures about ______ inches that extends from the _______________________ _______________________ of the skull to about the _______________________ _______________________ vertebra (just below the ribs) After the _______________________ vertebra, the spinal ...
... It is a _______________________ cord that measures about ______ inches that extends from the _______________________ _______________________ of the skull to about the _______________________ _______________________ vertebra (just below the ribs) After the _______________________ vertebra, the spinal ...
A new hero emerges: another exceptional mammalian spine and its
... S3. SPECIMEN DESCRIPTION External measurements and weight are provided in the main text. The specimen is an adult based on the fully fused suture between the basioccipital and basisphenoid bones (figure 1) and the presence of an embryo in the uterus. The vertebral column has eight corrugated, interl ...
... S3. SPECIMEN DESCRIPTION External measurements and weight are provided in the main text. The specimen is an adult based on the fully fused suture between the basioccipital and basisphenoid bones (figure 1) and the presence of an embryo in the uterus. The vertebral column has eight corrugated, interl ...
Upper Appendicular Skeleton1
... Head fits into the ??? Glenoid Cavity of the scapula 2 processes located just below the head 1. Greater Tubercle- lateral side 2. Lesser Tubercle- anterior side Intertubercular Groove- A narrow furrow located “between tubercles” ...
... Head fits into the ??? Glenoid Cavity of the scapula 2 processes located just below the head 1. Greater Tubercle- lateral side 2. Lesser Tubercle- anterior side Intertubercular Groove- A narrow furrow located “between tubercles” ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.