World War II Lecture Slides
... Germans began to drive the trapped Allied forces in Belgium toward the English Channel The only hope for the French and British troops was to escape by sea, but the Germans had captured every port except one, Dunkirk ...
... Germans began to drive the trapped Allied forces in Belgium toward the English Channel The only hope for the French and British troops was to escape by sea, but the Germans had captured every port except one, Dunkirk ...
File - In The Front Seat
... • Charles DeGaulle used guerilla tactics to fight the Germans • "France has lost a battle; she has not lost the war" ...
... • Charles DeGaulle used guerilla tactics to fight the Germans • "France has lost a battle; she has not lost the war" ...
Explain the importance of the battle of Britain as a
... France’s colonies to join in the war effort and started to organise the French Resistance which proved vital in Anglo-French operations. Operation Overlord, Commonly known as D-Day, was the invasion of Europe by Allied troops on the Normandy beaches in 1944. The operation was planned to shock German ...
... France’s colonies to join in the war effort and started to organise the French Resistance which proved vital in Anglo-French operations. Operation Overlord, Commonly known as D-Day, was the invasion of Europe by Allied troops on the Normandy beaches in 1944. The operation was planned to shock German ...
WWII - Barren County Schools
... Germans began to drive the trapped Allied forces in Belgium toward the English Channel The only hope for the French and British troops was to escape by sea, but the Germans had captured every port except one, Dunkirk ...
... Germans began to drive the trapped Allied forces in Belgium toward the English Channel The only hope for the French and British troops was to escape by sea, but the Germans had captured every port except one, Dunkirk ...
The Steady March Toward War in Europe
... Dictators Threaten the Peace of the World The “Peace” Following WWI Leads to Nationalism…and Dictators- The vengeful Treaty of Versailles set the board for a nationalistic rise of dictators in Europe and Asia. The “peace” brought by the war to end all wars was a farce. Germany and Russia were pawns ...
... Dictators Threaten the Peace of the World The “Peace” Following WWI Leads to Nationalism…and Dictators- The vengeful Treaty of Versailles set the board for a nationalistic rise of dictators in Europe and Asia. The “peace” brought by the war to end all wars was a farce. Germany and Russia were pawns ...
Operation Barbarossa * what went wrong?
... It is commonly believed that the invasion of Russia was one of Hitler's greatest strategic blunders. Up to that point the German war machine had conquered and subjugated all her enemies (except for Britain), while at the same time Russia had been providing her with much needed resources such as oil ...
... It is commonly believed that the invasion of Russia was one of Hitler's greatest strategic blunders. Up to that point the German war machine had conquered and subjugated all her enemies (except for Britain), while at the same time Russia had been providing her with much needed resources such as oil ...
Timeline for World War II — Germany
... 1941: June 4: Kaiser Wilhelm, once head of Germany and instigator of World War I, died in Holland. 1941: June 22: Germany invaded the Soviet Union with the aid of Finland, Hungary, Romania, and Slovakia. Romania invaded southern Russia on the side of Germany. 1941: July 4: Mass murder of Polish scie ...
... 1941: June 4: Kaiser Wilhelm, once head of Germany and instigator of World War I, died in Holland. 1941: June 22: Germany invaded the Soviet Union with the aid of Finland, Hungary, Romania, and Slovakia. Romania invaded southern Russia on the side of Germany. 1941: July 4: Mass murder of Polish scie ...
France and World War Two
... was that of the general who had defended Verdun in 1916 and restored morale in the army after mutinies of 1917. He was deputy leader of final war government in 1940 and argued for the Armistice, which was signed on 22 June. How inevitable was this decision? Continuation of the war from the colonies ...
... was that of the general who had defended Verdun in 1916 and restored morale in the army after mutinies of 1917. He was deputy leader of final war government in 1940 and argued for the Armistice, which was signed on 22 June. How inevitable was this decision? Continuation of the war from the colonies ...
CONTENTS - ORRHS Library Commons
... justified because the Japanese were determined to defend their homeland to the last man in order to raise the human cost for Allied victory and induce a negotiated peace. (Michael Perry May) No, although the atomic bombing of Hiroshima was justified and morally defensible, the attack on Nagasaki was ...
... justified because the Japanese were determined to defend their homeland to the last man in order to raise the human cost for Allied victory and induce a negotiated peace. (Michael Perry May) No, although the atomic bombing of Hiroshima was justified and morally defensible, the attack on Nagasaki was ...
Canadian Battles
... • seizing Iwo Jima would let sea/air blockades, power to conduct intense air bombardment and destroy the enemy’s air and navel capabilities. • Capturing Iwo Jima meant the battle for Okinawa, and the invasion of Japan was on its way to becoming reality. ...
... • seizing Iwo Jima would let sea/air blockades, power to conduct intense air bombardment and destroy the enemy’s air and navel capabilities. • Capturing Iwo Jima meant the battle for Okinawa, and the invasion of Japan was on its way to becoming reality. ...
Warfare 1917-1918 (USA) - 1914-1918
... own respective armies in order to make the quickest impact on the Western Front. Joffre, however, sensed the negative reaction this approach was having and quickly changed course. Thus began one of the most significant and recurring issues of the American war effort - the amalgamation controversy - ...
... own respective armies in order to make the quickest impact on the Western Front. Joffre, however, sensed the negative reaction this approach was having and quickly changed course. Thus began one of the most significant and recurring issues of the American war effort - the amalgamation controversy - ...
Occupation of France Influences Philosophy
... supplies and men to Germany. French citizens were conscripted by the Germans when they needed people to work in factories and the like. Many such draftees took to the hills in France and worked against the Germans. Other French citizens passed military intelligence to Great Britain and other Allies, ...
... supplies and men to Germany. French citizens were conscripted by the Germans when they needed people to work in factories and the like. Many such draftees took to the hills in France and worked against the Germans. Other French citizens passed military intelligence to Great Britain and other Allies, ...
French Belligerence in the Face of German Reconstruction: 1945
... Clay's recommendation was refused. As late as July, 1947, France was still delaying American efforts, this time regarding the setting of a level of indUStry, and of coal organization in the Ruhr. "It is well known we have receded in the face of French position," Clay told Washington, "Soviet propaga ...
... Clay's recommendation was refused. As late as July, 1947, France was still delaying American efforts, this time regarding the setting of a level of indUStry, and of coal organization in the Ruhr. "It is well known we have receded in the face of French position," Clay told Washington, "Soviet propaga ...
Ludendorff`s Spring Offensive and the Allied Counter
... Continuing Spring Offensive operations Despite Operation Michael not achieving its full strategic goals, Ludendorff was keen to launch further offensives. • Second Offensive – Operation Georgette: 9-29 April This offensive was launched in Flanders with the aim of taking back ground lost around Passc ...
... Continuing Spring Offensive operations Despite Operation Michael not achieving its full strategic goals, Ludendorff was keen to launch further offensives. • Second Offensive – Operation Georgette: 9-29 April This offensive was launched in Flanders with the aim of taking back ground lost around Passc ...
Nazi Invasion of Poland
... The period following would become known as the Phony War. From September 1939 to May 1940 Great Britain and France were officially at war with Germany, but there were no conflicts between the two sides. For eight months both sides began preparing for battle, waiting for the other side to make a move ...
... The period following would become known as the Phony War. From September 1939 to May 1940 Great Britain and France were officially at war with Germany, but there were no conflicts between the two sides. For eight months both sides began preparing for battle, waiting for the other side to make a move ...
File - Mr. Takos` Website
... -On September 1, 1939 Hitler launched his invasion into Poland using a new war technique he called a __________ or __________ war -______ softened the infrastructure of major ______ and ___ targets, while _____ and personnel carriers _______ occupied regions caught off guard -_______________ German ...
... -On September 1, 1939 Hitler launched his invasion into Poland using a new war technique he called a __________ or __________ war -______ softened the infrastructure of major ______ and ___ targets, while _____ and personnel carriers _______ occupied regions caught off guard -_______________ German ...
File - Campbell`s Web Soup
... Allied merchant supply ships sailed surrounded by destroyers for protection against U-Boats Royal Canadian Navy provided much of the protection with small warships called corvettes ...
... Allied merchant supply ships sailed surrounded by destroyers for protection against U-Boats Royal Canadian Navy provided much of the protection with small warships called corvettes ...
World War II in Europe
... Hitler wanted to own all of Europe. He planned to take Poland next. This time, both Great Britain and France told him that they would fight back if he tried. But, Hitler did not think that they would act. On September 1, 1939, he invaded Poland. This started World War II. On one side was the Axis. T ...
... Hitler wanted to own all of Europe. He planned to take Poland next. This time, both Great Britain and France told him that they would fight back if he tried. But, Hitler did not think that they would act. On September 1, 1939, he invaded Poland. This started World War II. On one side was the Axis. T ...
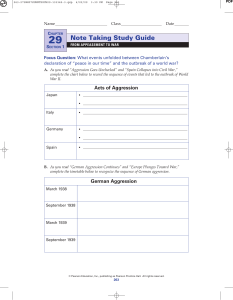
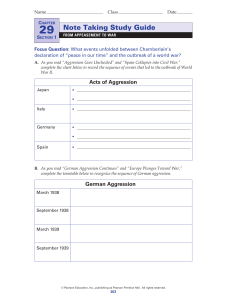
Note Taking Study Guide
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...
Road to world war ii
... 1941, FDR moved U.S. Pacific Fleet from West Coast to Pearl Harbor to demonstrate military readiness ► Embargo of 1941 July, Japan gained military control of southern Indochina U.S. froze Japanese assets in the U.S., closed the Panama Canal to Japan, placed embargo on export of oil to Japan ...
... 1941, FDR moved U.S. Pacific Fleet from West Coast to Pearl Harbor to demonstrate military readiness ► Embargo of 1941 July, Japan gained military control of southern Indochina U.S. froze Japanese assets in the U.S., closed the Panama Canal to Japan, placed embargo on export of oil to Japan ...
Outreach Educator Resource Guide
... formally signed the surrender on September 2 on the Battleship USS Missouri. f. World War II involved 61 countries with 1.7 billion people (three quarters of the World’s population at the time). G. Out of nearly 73,000,000 people killed in World War II, 61 million were allied people and 11 million w ...
... formally signed the surrender on September 2 on the Battleship USS Missouri. f. World War II involved 61 countries with 1.7 billion people (three quarters of the World’s population at the time). G. Out of nearly 73,000,000 people killed in World War II, 61 million were allied people and 11 million w ...
document
... -Both Britain and America agreed but differed on how to do it -Britain wanted to attack up from North Africa through Italy while America wanted to go through France -The Allies agreed to follow Britain's plan; General Eisenhower led the attack -Germany was pushed out of Africa by May 1943 -Roosevelt ...
... -Both Britain and America agreed but differed on how to do it -Britain wanted to attack up from North Africa through Italy while America wanted to go through France -The Allies agreed to follow Britain's plan; General Eisenhower led the attack -Germany was pushed out of Africa by May 1943 -Roosevelt ...
Reporting WWII - Centre for Journalism
... it might be widely replicated in the democratic nations of the world. ...
... it might be widely replicated in the democratic nations of the world. ...
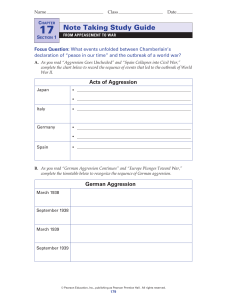
Note Taking Study Guide
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...
... Netherlands, and Belgium. By May, German forces had bypassed France’s Maginot Line. British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. However, in June, the French were forced to surrender. Germany occupied norther ...