* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Canadian Battles
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Canadian Battles
Juno Beach: Background and
Significance
On D-Day Canadians
landed on Juno Beach
They met severe German
opposition
After capturing many
towns they advanced
inland which secured a
stronghold for the allied
invasion
14000 attacked and 340
died and 574 wounded
Led to liberation of Europe
and the defeat of Nazi
Germany
www.6juin1944.com
Battle of Normandy: Description
Canadian Navy provided
109 vessels, 10,000 sailors
as help to the 7,000 Allied
vessels
Canadian minesweepers
helped clearing the English
Channel for the invasion
Allied paratroopers,
including 450 Canadians,
landed behind the German
coastal defences.Separated
they captured a German
headquarters, destroyed a
key bridge, and seized a
crossroads.
www.maxpower.ca
Battle of Normandy: Significance
Canadian troops had
progressed further
inland than any of
their Allies
340 Canadians were
killed, another 574
wounded and 47
prisoners
The Atlantic Wall had
been broken allowing
easy advancements
http://img236.imageshack.us/img236/7721/b1p17ruk0.jpg
Liberation of Netherlands - Intro
1939-1945
Previous assault across
the Rhine a success
Many troops
Made way to Germany
Russians approaching
Vienna
http://www.gazellebookservices.co.uk/Military/WW2/images/Canada%20and%20Liberation%20of%20the%20Netherlands.jpg
Liberation of Netherlands - Battle
TASK: Canadian army was
to open supply route
through Arnhem & clear
northeastern Netherlands
Two Canadian Army corps
would fight together for the
first time in history
#1: Deal with German’s in
Western Netherlands: √
#2: clear the northeastern
Netherlands: √
http://data2.collectionscanada.ca/ap/a/a134390-v6.jpg
Liberation of Netherlands Significance
Canadians big part of liberation
Allies pushing back Axis Powers
Liberation occurred at a vital moment (people were starving
Hunger Winter)
Contributed to end of war (Hitler’s suicide)
http://wwii.ca/photos/belgium_map.jpg
The Battle of St. Lawrence Background
• This battle took place
throughout the lower St.
Lawrence River and the
entire Gulf of St.
Lawrence, Strait of Belle
Isle and Cabot Strait
• Occurred from May to
Oct. 1942, Sept. 1943
and again in Oct. and
Nov. 1944
• It involved many
merchant marine ships
and 3 Canadian warships
during this time
http://www.qc.ec.gc.ca/CSL/INF/images/inf016_001_e.jpg
Battle of the St. LawrenceSummary
•
•
•
•
•
In 1939 Montreal exported more
tons of shipping than all other
Canadian east coast ports
combined
Therefore an attack on the Gulf
was a serious threat because of
the great amount of shipping that
passed through there and it’s
excellent access to Canada’s
industrial heartland
People in 1940 anticipated an
attack and wanted to establish a
Naval base at Gaspé, Quebec
On May , 1942 the base opened
and one week later the first
German U-boat attack occurred
Each tried to outsmart other,
fought over period of 2 yrs.
http://www.firstworldwar.com/photos/graphics/ww_uboat_camou_01.jpg
Battle of St. Lawrence- Significance
• This was only battle fought on
Canadian waters since war of
1812
• Death and shipping tolls rising
so government decided to
close the St. Lawrence to all
trans-Atlantic shipping on
Sept. 9, 1942. (this eventually
forced Germans to move on
somewhere else)
• This battle part of larger
conflict called the battle of the
Atlantic, between 1939-1945
http://jove.prohosting.com/~sinking/wwii/u-118.jpg
Defense of Hong Kong: Description
• Morning of Dec. 8th 1941 8 hours after Pearl
Harbor
• Japan attacked Hong Kong
• After 3 days of combat, defenders were pushed
away from the mainland into Hong Kong
• On the 13th and 17th Japan told the defenders to
surrender but Hong Kong didn’t
Image Showing Japanese lines of Attack
Defense of Hong Kong: Description
Con’t
• The allies surrendered on Christmas Day
• It was an 18 day battle
• The allies were outnumbered 3-1
Dongjiang Guerillas fighting in trenches.
Defense of Hong Kong: Outcome
• Hong Kong lost
• 2000 of 14 000 defenders were killed (over 550
Canadians)
• the rest suffered in Japanese POW camps for the rest of
the war
• Those who survived came home with bad health and
shortened lives
Prisoners of War
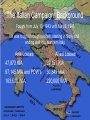
The Italian Campaign: Background
Fought from July 10, 1943 until May 8, 1945
It was fought through out Italy, starting in Sicily and
ending well into Northern Italy.
Axis Losses
47,873 KIA
97,145 MIA and POW’s
163,600 WIA
Allied Losses
59,151 KIA
30,849 MIA
220,000 WIA
What Happened
• Began with amphibious/airborne invasion
of Sicily on July 10, 1943
• Later they slowly Invaded main land Italy,
breaking through heavy opposition.
• They took towns and cities along the way,
at a very high price.
• Germany surrendered on May 2, 1945
after losing almost all their fighting force.
Significance
This battle was fought
before the battle of
Normandy quite
intentionally so as to draw
German troop away from
the French beaches. It
also allowed the allies to
capture Rome and gave
the Italians a chance to
separate from Germany
The Raid on Dieppe: Significance:
• A huge failure
• More Canadians died
in one hour in Dieppe
then in any other day
of the war
• Canadian troops
become more
experienced for the
D-Day invasion two
years later
• Also concentrated
German’s attention
more to the Eastern
Front
The Raid on Dieppe :Summary
• The object was to
attack and destroy
targets on the port of
Dieppe, France, to
make the English
channel defense
stronger at the expense
of other armed areas
• The element of surprise
was gone by morning
light
• The main attack on
Dieppe beach was
swept with machine
guns making a
successful raid
impossible
• The raid was
conquered by Germany
soldiers by the
afternoon
The Raid on Dieppe : Background
Information
• On August 19th, 1942
• The Dieppe Raid is also
known as The Operation
Jubilee
• 4,963 Canadians, 907
died including 56 officers
and 1,946 were captured
• the Royal Regiment of
Canada were on the
beaches of Puys, Dieppe
and Pourville
Home Front
• Kids at home had to take the place of
their parents who went to war and
some worked on farms
• Teens from 17 to 18 would go to war
• Sometimes teens would lie about
their age so there were some soldiers
who were only 13 years old
• Youth were constantly being
encouraged to go fight
• Age for getting a drivers license went
down to 14 years of age
Canadian Production of War
Materials
• The Second World War was highly mechanized.
• The industry in Canada produced 800,000 military transport vehicles, 50,000
tanks, 40,000 field, naval, and anti-aircraft guns, and 1,700,000 small arms.
• With this massive production there was a ratio of one vehicle for every three
soldiers.
http://www.vac-acc.gc.ca/remembers/sub.cfm?source=history/secondwar/fact_sheets/material
Canadian Production of War
Materials: Significance
• The sacrifices made by Canadians during the Second World War
were numerous and spanned a broad range of efforts.
• The contributions of the home front industry helped produce
essential material in the war.
Propaganda
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
There was a lot of propaganda used during the second world war.
Lord Kitchener struck his famous pose of pointing at the viewer and
saying “BRITONS want YOU to join the army” which worked so well
that the U.S. copied him using Uncle Sam.
Many different styles of posters were also used to sell war bonds,
which gave extra money to the war effort, and paid you more then you
spent when the war ended.
War stamps were sold to children, for less cost, as well as less return
Uncle Sam originated in the 1800’s and came into play during wars by
copying Lord Kitchener
Sources: http://www.wardsbookofdays.com/index_files/Kitchener2.JPG
http://www.sonofthesouth.net/uncle-sam/
http://italy.indymedia.org/uploads/2005/03/buy_war_bonds_01.jpg
http://www.redstone.army.mil/history/women_chron/images/warbond.jpg
Propaganda examples
Science and Technology: WWII
There were many
technological innovations in
the WWII era. Some include:
Anti-fog windshield fluid
Synthetic rubber
Use of nylon for parachutes
Study of magnetism to
protect the hulls of ships
from mines
Canadian Anti-Acoustic
Torpedo (CAT) gear
developed for the protection
from torpedoes.
http://www-ics.u-strasbg.fr/~etsp/lecture/mchem_poly/f/parachute.jpg
http://www.100.nist.gov/rubber.jpg
http://www.navweaps.com/Weapons/WTUS_Torpedo_pic.jpg
Science and Tech con’t…
One of the bigger
innovations was the
atomic bomb (fission
bomb).
This was done by
splitting the nucleus of
an atom into two
smaller nuclei.
This atomic bomb was
used in the last battle of
WWII, HiroshimaNagasaki.
http://blog.dreamhost.com/wp-content/uploads/2006/08/atomic-bomb.jpg
Wome at
{Description}
War;
Wome:
Worked i Factories
Drove taxies,
buses, streetcars
Built parts for air
plaes, subs ad
ships
worked o Air
fields
Took o their sos
jobs o farms
The role of
chaged
wome
Wome at War;
{Significance}
Proved they
had the skills
Prior to war
600,000 wome
held jobs,
after the war
1,200,000 did
Wome built a
reputatio for
fie precisio
work i optics,
etc.
The efforts of
both me ad
wome who
cotributed i
WW2, have
helped create
a lastig
legacy for
Caada.
International Battles
Battle for Berlin
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
One of the final battles of WW2
One of the “bloodiest battles in the world”
Start late April 1945 until early May
Russia out numbered Germany 5:1 in soldiers
Hitler committed suicide before the end of the battle
Germany surrender
Nearly a quarter of a million people died during the last
three weeks of World War Two
• 70,000 Russian soldiers lost their life
D – Day - Events
http://www.orbitcast.com/archives/d-day.jpg
June 6th 1944
Royal Canadian Air Force
pre bombed key points
Royal Canadian Navy
contributed 10 000 sailors
Stormy weather (English
channel: rough)
Only one Canadian unit
reached its D-Day objective
Element of surprise
D – Day – In relation to WWII
60th Anniversary of D-Day,
Omaha Beach, Normandy, France June
6, 2004
http://dallaspolicechoir.com/yahoo_site_admin/assets/images/P1030506.33570747_std.JPG
Huge success
Allies had landed as many as 155,000 troops in
France, 6,000 vehicles, 600 guns and about 4,000
tons of supplies
Sealed the Deal ( 1944: Nearing end of war)
Dunkirk, the definition
•
•
•
•
•
While fighting, many Allied troop divisions were trapped in the coastal
port of Dunkirk.
Of the 400 000 troops that were caught in Dunkirk, around 60 000 of
them were killed or wounded while fighting the 800 000 Germans, who
only lost 10 000 troops
338 000 Allied troops were evacuated over an 8 day period.
Due to the nature of the allied evacuation, the Allie’s had to leave
behind many machine guns and vehicles.
The Allies lost almost double troops and planes as the German army.
Sources: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Dunkirk
http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/2WWdunkirk.htm
Dunkirk, The significances
Large number of Allied soldiers lost in comparison to
Germans
Allies would have been at great disadvantage if soldiers
had not escaped
German army was strengthened by Allies loss of
machine guns, vehicles and other machinery that the
Allies left.
Hitler thought something was wrong, because it was so
easy.
El Alamein Summery
• fought in deserts of North Africa
• seen as one of the main victories of World
War Two
• mainly between two of the outstanding
commanders who were Montgomery and
Rommel
• allied victory lead to the Afrika Korpa
retreating and the Germans surrendering
on May 1943
Fall of France
Germany invaded France
The battle consisted of two main operations,
Case Yellow and Case Red
-German armored units cut off and
surrounded the Allies that had advanced into
Belgium
-German forces attacked a larger territory of
France using blitzkrieg
Fall of France con’t…
June 13th Paris was invaded
by German forces
-they were expecting an
invasion from the east
June 23rd France
surrendered, which meant:
Disarmament of the
French troops
Occupation of two-thirds
of France by Germany
France was occupied by
Germany until the Allied
landing in1944
http://www.ushmm.org/museum/exhibit/online/szyk/wartime/media/80491z.jpg
Hiroshima – What Happened
• August 6, 1945, 8:15am the US dropped an
atomic bomb over Hiroshima, Japan
• Happened under command of US President
Truman
• A 9 700 lb uranium bomb
• Nicknamed “Little Boy”
• Instantly killed 70 000
http://students.umf.maine.edu/~donoghtp/Hiroshima_aftermath.jpg
Hiroshima – What Happened
• The bodies of those close
to detonation were turned
to char
• Described as a blinding
light combined with an
overwhelming wave of
heat
• The detonation of fires
created a fire storm
• About 5 days later
radiation sickness
appeared
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/usaweb/Images/manhattanproject_w_bomb.jpg
Hiroshima – Related to the War
• Why the bomb was
dropped:
An attempt to end the war
Hiroshima was an
important military centre
Japan ignored the
ultimatum to surrender or
suffer the consequences
• This bomb along with a
second bomb in
Nagasaki, Japan, 3 days
later were the only two
Nuclear bombs dropped
in history of war
Little Boy
http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB162/little-boy-model.jpg
Big Boy
http://www.ufo-blog.com/images/hiroshima_and_nagasaki_bombs.jpg
Hiroshima – Related to the War
• Dropped by B-29 Super
fortress - Enola Gay
• August 15 1945 Japan
announced its surrender
to the Allied Powers
• Even though the bombs
killed many innocent
civilians, it is said to have
saved the lives of millions
of Japanese and
American troops because
of the Japanese
surrender
http://www.commondreams.org/headlines03/images/1110-02.jpg
Invasion Of Sicily:
Background
•The plan was to land the two armies side
by side in southern Sicily, and advance
directly across the island.
•A corpse disguised as a British officer was
sent to drift ashore in Spain, carrying a
briefcase containing fake allied documents.
These documents revealed that the Allies
were planning to invade Greece and not
Sicily.
Invasion Of Sicily: Battle And
Outcome
• The Allies landed in strong winds which
ensured the element of surprise
• The Allies only met minor opposition
• After a week of fighting the Allies took
over the capitol of Sicily (Palermo)
which signaled the loss of Sicily to the
Germans and Italians
Iwo Jima
• Date: Feb16 – March 26, 1945
• Location: Iwo Jima
• Description: capture would make emergency landing
strip for damaged B-29s during the bombing runs.
• Iwo Jima had 3 airfields which made it ideal for
fighting.
• Tokyo thought if there were enough American
casualties, Washington wouldn’t dare launch an
attack.
• Japanese strategy: no Japanese survivors (heroic in
their eyes).
Significance of Iwo Jima
• Important air base for fighter escorts
supporting long-range bombing missions
against mainland Japan.
• seizing Iwo Jima would let sea/air
blockades, power to conduct intense air
bombardment and destroy the enemy’s air
and navel capabilities.
• Capturing Iwo Jima meant the battle for
Okinawa, and the invasion of Japan was on
its way to becoming reality.
Normandy Description
• The battle of Normandy lasted 3
months
• After the Allies took the beach
they needed to expand quickly
to give them more of a foothold
• It took the allies 10 days to
make a significant foothold in
France
Normandy What
Happened
• Canadians, British and
Americans attacked the coast
of Normandy
• 1074 casualties 359 deaths
• July 8 1944 Canadians captured
Buron and Authie
• July 10 1944 Canadians
captured Caen
Normandy Significance
• It gave the allies a foot hold in
Europe to ultimately push the
Germans back into Germany
Operation Barbarossa:Description
Germany invaded Soviet Union,
June 22, 1941
117 German divisions, 132
Russian
Armies: North(von Leeb), Centre
(von Bock) and South(von
Rundstedt)
Objectives: Moscow, Leningrad
300,000 Russian infantry, 2,500
tanks, 1,400 artillery, 250 aircraft
captured
Hitler delayed army’s advance
moving troops
Winter weakened Germans and
Russia defeated them
Operation Barbarossa:Significance
Germany invaded Russia after
saying they wouldn’t
Largest military attack in WW2
Opened up Eastern Front
Battles: Moscow, Smolensk,
Brody, Bialystok-Minsk, Raseiniai
One of most lethal attacks in
WW2
Germans lost because of
overdeployment and
underestimation of the Soviets
Siege of Leningrad
Some say “ General Winter”
helped Soviets
Pearl
Harbor;
agaist the
{Description}
Uited
States' base
at Pearl
Harbor i
Hawaii by
the
Japaese
avy
December
7th, 1941
The aerial
attack
cosisted of
355 plaes-took off
form 6
Japaese
carriers
*Two of the
The battle of Pearl
Harbor;
{Significance}
Resulted in the United
States becoming
involved in World War
two.
Modernized the US
navy in less than two
hours
Stalingrad: Description
• Germany used the Blitzkrieg technique against
the USSR
• Between July 17 1942 and February 2 1943
• Casualties estimated to be above 1.5 million
• Soviet victory
The city of Salingrad being bombed.
Stalingrad: Importance
• Important to Hitler for two reasons
• First: it was a vital transport route between the
Caspian Sea and Northern Russia
• Second: it would secure the left flank of the
Germans
• A goal of cutting off the fuel to Stalin’s war
machines
Image on next page.