* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - In The Front Seat
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
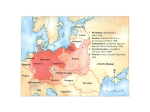
Causes of World War II 1933 to June 1940 By Mr. Woodmansee Good Shepherd Catholic School Causes of WWII A N T I Appeasement Nationalism Totalitarianism Imperialism The Fuhrer Commander-in-Chief Conrad Hommel 1940 The Flag Bearer Hubert Lanzigner after 1933 The Baby Fritz Markensen Two Men Looking at the Moon Casper David Frederick Men Looking Out Workers Soldiers Farmers by Hans Schmitz-Wiednbruck Plowing by Julius Paul Junghanns Harvest by Karl Alexander, 1938 Youth Volunteers in the Reich Labor Service 1936 Berlin Olympics • Promoted the Nazi State • Only Aryan participated – Anti-Semitic posters were removed – Gypsies were arrested Nazi Germany Keeping Control: Terror State “Terror is the best political weapon for nothing drives people harder than a fear of sudden death.” The Terror State • Both the Gestapo (Secret Police) and the SS (Storm Troopers – Hitler’s private soldiers) were run by Heinrich Himmler • The Gestapo employed an army of spies who would inform on people Enemies of the State • Communists • Social Democrats • Jews • Trade Unionists. • Work Shy • Homosexuals • Gypsies • Germans who bought from Jews • Pacifists • Radical Christian Organisation • Anyone who criticised Hitler or the Nazi Party. Enemies of the State • Scare tactics were used to ensure Germans did as they were told • A list of German women who were still purchasing goods from Jewish shops How did the Terror State Work? You are imprisoned for up to six months doing hard physical labor. You are handed over to the SS who run the concentration camps. By signing this form you are giving your consent to be put into a concentration camp. When you are released you tell everybody what has happened to you Fear Days or maybe weeks later you are interviewed and asked to sign form D11 Gestapo Spies inform on you You are woken up by the Gestapo at 1 am in the morning and told that you have 5 minutes to pack your bags. You are arrested and thrown into a cell at the police station Key Quote: Martin Niemollen, 1945 • When the Nazis came for the Communists I was silent, I was not a Communist. • When the Nazis came for the Social Democrats I was silent, I was not a Social Democrat. • When the Nazis came for the Jews I was silent, I was not a Jew. • When the Nazis came for me there was nobody left to protest. Totalitarian State • The government control the population by fear • The NAZIs removed opposition • Used citizens to spy on each other – especially the youth – Hitler Jugen (Hitler Youth) A Weak League of Nations German Foreign Policy 1933 - 1939 Presentation by Mr Young Your Task You are an expert in foreign policy It is your job to advise the new leaders of Germany You will be told about various problems and given a choice of three policies to follow. Choose wisely. Your success will be rewarded. Failure will be punished! Mein Kampf Your policy has very clear aims: Destroy the Treaty of Versailles Gain ‘Lebensraum’ (living space) in the east Bring all Germans into one Reich Make Germany strong again Crisis: Austria 1934 The Depression has made Austria weak Taking over Austria will be very popular in Germany It will bring many Germans into the Reich However other countries might oppose you Crisis: Austria 1934 Try to take over Austria by sending troops to Vienna Try to take over Austria by political pressure Do nothing, its not worth annoying France, Britain and Italy Crisis: Austria 1934 30 Points 10 Points 20 Points Crisis: Rhineland 1936 Italy has invaded Ethiopia The league of Nations is divided While the League is divided you could send troops to the Rhineland Be careful! Any opposition and you’ll have to withdraw Crisis: Rhineland 1936 Send in the troops. France is divided and Britain wants peace Ask permission from the Allies before doing anything Do nothing, you can’t risk war with France. Germany is too weak Crisis: Rhineland 1936 10 Points 20 Points 30 Points Crisis: Austria 1938 Austria is even weaker than in 1934 Italy is now your ally You have many supporters in Austria, who can help you Union with Austria is forbidden by the Treaty of Versailles Crisis: Austria 1938 Try to take over Austria by sending troops to Vienna Try to take over Austria by political pressure Do nothing, its not worth annoying France, Britain and Italy Crisis: Austria 1938 20 Points 10 Points 30 Points Crisis: Czechoslovakia 1938 Three million German speakers live in Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia has a strong army and alliances with Britain, France and the Soviet Union Victory over the Czechs will finally destroy the Treaty of Versailles The army is unwilling to fight over the Sudetenland Crisis: Czechoslovakia 1938 Invade Czechoslovakia and hope the army follows your orders Make a deal with Russia and hope Britain and France ignore your actions Threaten the Czechs and make a deal with Britain and France Crisis: Czechoslovakia 1938 30 Points 20 Points 10 Points Crisis: Poland 1939 After victory over the Czechs you can’t do wrong Poland splits German land and holds the German city of Danzig Poland has an alliance with Britain and France The Soviet Union could be a threat, the Red Army could easily help the Poles Crisis: Poland 1939 Do a Deal with Russia to split Poland between you Invade Poland without any agreements no-one can stop you now Stop now, you’ve already achieved most of your aims Crisis: Poland 1939 10 Points 30 Points 20 Points Add up your scores How did you do? 120 - 150 Points Your advice has been superb for the outside world as war has been avoided However, your advice has not been good for you. The Gestapo have arrested you and you are never seen again How did you do? 90 – 110 Points You’re not the expert the Nazi party thought you were. You’ve missed many opportunities to expand Germany’s population and resources You have been demoted but you still have a comfortable life in Berlin How did you do? 50 – 80 Points Fantastic! you have made Germany strong again, the Treaty is a thing of the past and Germany is well prepared in case war comes. You have been rewarded with promotion in the Nazi party and all the privileges of power What did Hitler do? Austria 1934 Rhineland 1936 Austria 1938 Czechoslovakia 1938 Poland 1939 What did Hitler do? Crisis: Austria 1934 Try to take over Austria by sending troops to Vienna Try to take over Austria by political pressure Do nothing, its not worth annoying France, Britain and Italy What did Hitler do? Crisis: Rhineland 1936 Sent troops in the Rhineland. France was divided and Britain wants peace Ask permission from the Allies before doing anything Do nothing, you can’t risk war with France. Germany is too weak What did Hitler do? Crisis: Austria 1938 Took over Austria by sending troops to Vienna Try to take over Austria by political pressure Do nothing, its not worth annoying France, Britain and Italy What did Hitler do? Crisis: Czechoslovakia 1938 Invaded Czechoslovakia Make a deal with Russia and hope Britain and France ignore your actions Threaten the Czechs and make a deal with Britain and France What did Hitler do? Crisis: Poland 1939 Made a non – aggression pact with Russia to divided Poland Invade Poland without any agreements no-one can stop you now Stop now, you’ve already achieved most of your aims Appeasement • March 1938 Ger. took control of Austria – GB and Fr took no serious action • September 1938 Ger. demanded Czechoslovakia cede (give) the Sudetenland – Munich Conference – Chamberlin gave in • Hitler agreed not to take any more European land... Sudetenland Now we have “peace in our time!” Herr Hitler is a man we can do business with. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain Czech woman “welcoming a German army division, 1938 German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact • August 23, 1938 by foreign ministers von Ribbentop (Germany) and Molotov (USSR) signed a non-Aggression Pact • Both countries publicly agreed not to attack each other Shhhh! Secretly they agreed to invade Poland On September 1, 1939 Germany unleashed a blitzkrieg (lightning war) against Poland. The goal was to destroy communication, transportation and shock the enemy into submission. It worked. Poland (cont’d) • Wehrmarcht (main German Army) easily defeated Polish forces in days • The Soviets invaded Sept. 17, 1939 – The Poles ran to the Russian Army who they thought were there to protect them Poland (cont’d) • Totenkoph (Death’s Head) Squadrons hunted down and executed “racially inferior” people • Many Jews were rounded up and forced into the Warsaw Ghetto Sitzkrieg • September 3, 1939 GB and France declared war on Germany • GB evacuated some Poles but offered no military resistance to Ger. – “Confetti War” • Allies waited for Ger. to attack Belgium and France Western Front • April 9, 1940 Germany attacked Copenhagen and landed in Norway – Denmark fell – Oslo, Norway fell but with British supplies the Norwegians resistance held the mountains Western Front • May 10, 1940 Germany attacked France, Belgium, Luxemburg and the Netherlands • By May 13 The Allied forces were trapped in northern France • May 14 the Netherlands surrendered Miracle at Dunkirk • May 27 the BEF evacuated across the English Channel from France at Dunkirk – “Operation Dynamo” • Churchill became fully committed to the war Fall of France – June 22, 1940 Vichy France A puppet French state was organized to administer southern France Marshall Henri Petain Pres. Vichy France Free French Forces • Charles DeGaulle used guerilla tactics to fight the Germans • "France has lost a battle; she has not lost the war" Fall of France Examined • It is a mistake to believe that French forces were weak, in fact they were more advanced and larger in number then German forces – Many German leaders were apprehensive about war with France • The quick fall of France is attributed to Germany’s unexpected attack though the Ardennes Forest Causes of WWII Examined • World War II started with the rise of a totalitarian German state under the leadership of Adolf Hitler who sought to create a new continental empire for the German people at the expense of their neighbors • The invasion of Poland revealed Hitler’s sinister plans and preludes what will happen in Russia • With the fall of France only Great Britain stands to oppose Nazi Germany and Italy