Recent advances in diffuse optical imaging
... Measurements of the intensity of light transmitted between two points on the surface of tissue are not only relatively straightforward and inexpensive to obtain, but also contain a remarkable amount of useful information, as demonstrated by the clinical successes of NIRS (Obrig and Villringer 2003). ...
... Measurements of the intensity of light transmitted between two points on the surface of tissue are not only relatively straightforward and inexpensive to obtain, but also contain a remarkable amount of useful information, as demonstrated by the clinical successes of NIRS (Obrig and Villringer 2003). ...
Resolution enhancement techniques in microscopy
... explore the foundations of resolution as expounded by the astronomers and the physicists and describe the conditions for which they apply. Then we elucidate Ernst Abbe’s theory of optical formation in the microscope, and its experimental verification and dissemination to the world wide microscope com ...
... explore the foundations of resolution as expounded by the astronomers and the physicists and describe the conditions for which they apply. Then we elucidate Ernst Abbe’s theory of optical formation in the microscope, and its experimental verification and dissemination to the world wide microscope com ...
Fresnel at the Observatory
... In September 1815, François Arago received at the Observatory a letter from someone unknown to him : the letter included the following words : I think that I have found the explanation and the theory of the colored fringes which can be seen in the shade of bodies illuminated by a point source of lig ...
... In September 1815, François Arago received at the Observatory a letter from someone unknown to him : the letter included the following words : I think that I have found the explanation and the theory of the colored fringes which can be seen in the shade of bodies illuminated by a point source of lig ...
polarization 3
... So This explanation was based on the following assumptions: 1. A plane polarized light falling on an optically active medium along its optic axis splits up into two circularly polarized vibrations of equal amplitudes and rotating in opposite directions –one clockwise and other anticlockwise. 2. In ...
... So This explanation was based on the following assumptions: 1. A plane polarized light falling on an optically active medium along its optic axis splits up into two circularly polarized vibrations of equal amplitudes and rotating in opposite directions –one clockwise and other anticlockwise. 2. In ...
Radially and azimuthally polarized beams generated by space
... one can obtain any desired continuous polarization. Furthermore, the continuity of our grating ensures the continuity of the transmitted field, thus suppressing diffraction effects that may arise from discontinuity. Our gratings are compact, lightweight, and f lexible in design and have high transmi ...
... one can obtain any desired continuous polarization. Furthermore, the continuity of our grating ensures the continuity of the transmitted field, thus suppressing diffraction effects that may arise from discontinuity. Our gratings are compact, lightweight, and f lexible in design and have high transmi ...
Absorption of low-loss optical materials measured at 1064 nm by a
... nm and continues to decrease. Detection of such a low absorption level is difficult because the thickness of the silica substrates shaped to become optical components is usually not larger than a few centimeters, so the total absorption integrated over the sample thickness never exceeds a few ppm. T ...
... nm and continues to decrease. Detection of such a low absorption level is difficult because the thickness of the silica substrates shaped to become optical components is usually not larger than a few centimeters, so the total absorption integrated over the sample thickness never exceeds a few ppm. T ...
Optical Stochastic CooLing
... distribution of cooling rates. In particular, an increase of horizontal damping can allow a reduction of the optical amplifier wavelength, but at the same time it makes more difficult to handle an increase of beta-function in the cooling area required to keep sufficiently large value for the horizon ...
... distribution of cooling rates. In particular, an increase of horizontal damping can allow a reduction of the optical amplifier wavelength, but at the same time it makes more difficult to handle an increase of beta-function in the cooling area required to keep sufficiently large value for the horizon ...
Encircled energy factor in impulse response functions of
... dispersion factor in the diffraction pattern of circular apertures. LUNEBERG [12] proposed four apodisations problems and suggested a method to solve them by using the calculus of variations. The third Lunenburg problem is to find the optimum pupil function which gives maximum energy in a given area ...
... dispersion factor in the diffraction pattern of circular apertures. LUNEBERG [12] proposed four apodisations problems and suggested a method to solve them by using the calculus of variations. The third Lunenburg problem is to find the optimum pupil function which gives maximum energy in a given area ...
Highly transmissive luminescent down
... optical simulator CROWM (Combined Ray Optics / Wave Optics Model), developed by Lipovšek et al. [22]. The optical simulator is based on the combination of three-dimensional ray tracing and one-dimensional transfer matrix methods. They are used together to analyze light propagation through thick and ...
... optical simulator CROWM (Combined Ray Optics / Wave Optics Model), developed by Lipovšek et al. [22]. The optical simulator is based on the combination of three-dimensional ray tracing and one-dimensional transfer matrix methods. They are used together to analyze light propagation through thick and ...
Optics - Filter Properties & manipulation of light in flow cytometry
... • Reducing reliance on the in line arrangement PMTs • Placing a second fluorescence collection lens at 180o from the first one (this is more difficult in most instruments) ...
... • Reducing reliance on the in line arrangement PMTs • Placing a second fluorescence collection lens at 180o from the first one (this is more difficult in most instruments) ...
Detection of Fluorescence from Single Molecules
... You will learn how to manipulate laser light using lenses. Specifically, you will measure the focal length of a lens. Using the light source and lens, you will verify the thin lens relation. Day 2: Alignment of the excitation pathway – Part 1 You will direct collimated laser light into the microscop ...
... You will learn how to manipulate laser light using lenses. Specifically, you will measure the focal length of a lens. Using the light source and lens, you will verify the thin lens relation. Day 2: Alignment of the excitation pathway – Part 1 You will direct collimated laser light into the microscop ...
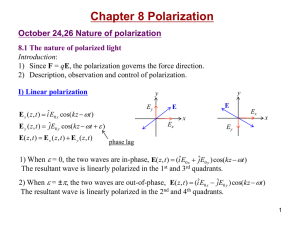
Chapter 8
... Anisotropy of the binding force of an electron cloud causes the anisotropy in the refractive indexes for different light polarizations. 8.4.1 Calcite (CaCO3) Optic axis: Inside the (uniaxial) crystal there is a special direction along which when light is propagating there is no birefringence occurs. ...
... Anisotropy of the binding force of an electron cloud causes the anisotropy in the refractive indexes for different light polarizations. 8.4.1 Calcite (CaCO3) Optic axis: Inside the (uniaxial) crystal there is a special direction along which when light is propagating there is no birefringence occurs. ...
Chapter 35
... two waves of the same wavelength, frequency, and amplitude are added up together. It all depends on the relative phase of the two waves. This phenomenon is called interference. Thus for waves, 1 + 1 can equal to any number between 0 and 4! This is, of course, because waves are not simply numbers, bu ...
... two waves of the same wavelength, frequency, and amplitude are added up together. It all depends on the relative phase of the two waves. This phenomenon is called interference. Thus for waves, 1 + 1 can equal to any number between 0 and 4! This is, of course, because waves are not simply numbers, bu ...
P approximation for reflectance imaging with an oblique beam of arbitrary profile 1
... Instead of solving the RTE based boundary-value problems directly, one can obtain light distributions with a MC method by sampling a large number of photons undergoing stochastic processes of absorption and scattering. These processes are characterized by the probability distribution functions based ...
... Instead of solving the RTE based boundary-value problems directly, one can obtain light distributions with a MC method by sampling a large number of photons undergoing stochastic processes of absorption and scattering. These processes are characterized by the probability distribution functions based ...
Evolutionary optimization of layouts for high density free space
... But the angles and folding intervals are not the only parameters that can be set. It is also possible to change the arrangement of the connectors, thus influencing the value of LAB , the geometric distance between the in- and output fiber, for a beam. We ran the EA with a lot of different arrangements ...
... But the angles and folding intervals are not the only parameters that can be set. It is also possible to change the arrangement of the connectors, thus influencing the value of LAB , the geometric distance between the in- and output fiber, for a beam. We ran the EA with a lot of different arrangements ...
Physicists realize an atom laser, a source of coherent matter waves
... An atom laser based on BEC is a special case of macroscopic occupation of a quantum state. In this case, the atoms accumulate in the ground state and are in thermal equilibrium. More generally, atom lasers can operate in higher order modes and also as a driven system which is not in thermal equilibr ...
... An atom laser based on BEC is a special case of macroscopic occupation of a quantum state. In this case, the atoms accumulate in the ground state and are in thermal equilibrium. More generally, atom lasers can operate in higher order modes and also as a driven system which is not in thermal equilibr ...
Coatings - CVI Laser Optics
... with different optical properties (most notably refractive index), part of the light is reflected and part of the light is transmitted. The intensity ratio of the reflected and transmitted light is primarily a function of the change in refractive index between the two media, and the angle of inciden ...
... with different optical properties (most notably refractive index), part of the light is reflected and part of the light is transmitted. The intensity ratio of the reflected and transmitted light is primarily a function of the change in refractive index between the two media, and the angle of inciden ...
Click
... It was designed by William Nicol in 1820. A calcite crystal whose length is three times as its width The end faces of this crystals are grounded in such a way that the angles in the principal section becomes 680 and 1120 instead of 710 and 1090 The crystal is cut in two pieces by a plane perpendic ...
... It was designed by William Nicol in 1820. A calcite crystal whose length is three times as its width The end faces of this crystals are grounded in such a way that the angles in the principal section becomes 680 and 1120 instead of 710 and 1090 The crystal is cut in two pieces by a plane perpendic ...
... SPM leads to symmetric spectral broadening around ωo, whereas the self steepening term that leads to optical shock results in asymmetric spectral broadening of the pulse. Selfsteepening can be explained by the intensity-dependence of the group velocity [1]. As the intensity of a pulse increases from ...
Modeling phase microscopy of transparent three
... [1–8]. These objects are visualized well by techniques such as differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, but standard DIC systems are qualitative in nature and do not provide quantitative phase information [9]. Several modalities have been developed to obtain quantitative complex field im ...
... [1–8]. These objects are visualized well by techniques such as differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, but standard DIC systems are qualitative in nature and do not provide quantitative phase information [9]. Several modalities have been developed to obtain quantitative complex field im ...