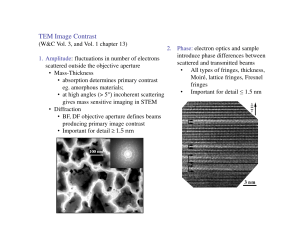
Covalent Crystals in molecules)
... - in liquid these bonds continuously break and reform - in ice water molecules crystallize into structures with only four nearest neighbors (see figure) resulting in the low density observed in ice - hydrogen bonds are also important in biological settings (e.g. DNA replication) ...
... - in liquid these bonds continuously break and reform - in ice water molecules crystallize into structures with only four nearest neighbors (see figure) resulting in the low density observed in ice - hydrogen bonds are also important in biological settings (e.g. DNA replication) ...
Free electron theory of metals
... Heat capacities and Hall effect of many metals are wrong Hall effect can be positive Does not explain why mean free paths can be so long Does not explain why some materials are metals, some insulators and some are semiconductors ...
... Heat capacities and Hall effect of many metals are wrong Hall effect can be positive Does not explain why mean free paths can be so long Does not explain why some materials are metals, some insulators and some are semiconductors ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
Modelling Mass Transfer in Nitrification Processes Using
... Our understanding of selective oxidation processes has been gradual and often the biggest problem was reconciliation of kinetic data with mechanistic information. The surface chemical and physical phenomena models were the seeds of most current research activities in the field - Imagine - Test - Fit ...
... Our understanding of selective oxidation processes has been gradual and often the biggest problem was reconciliation of kinetic data with mechanistic information. The surface chemical and physical phenomena models were the seeds of most current research activities in the field - Imagine - Test - Fit ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
File - Science With BLT
... the octet rule? a. 1 c. 5 b. 3 d. 8 ____ 30. The elements of the ____ group satisfy the octet rule without forming compounds. a. main c. alkali metal b. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal ____ 31. When the octet rule is satisfied, the outermost ____ are filled. a. d and f orbitals c. s and d orbitals ...
... the octet rule? a. 1 c. 5 b. 3 d. 8 ____ 30. The elements of the ____ group satisfy the octet rule without forming compounds. a. main c. alkali metal b. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal ____ 31. When the octet rule is satisfied, the outermost ____ are filled. a. d and f orbitals c. s and d orbitals ...
Pure Substances and Mixtures
... • Valence electrons is the name given to electrons in the last energy level of the atom. There will NEVER be more than 8 valence electrons • Elements in columns 1A through VIIIA: the number of valence electrons can be determined by the column number; 1A has 1 valence electron, IIA has 2 valence elec ...
... • Valence electrons is the name given to electrons in the last energy level of the atom. There will NEVER be more than 8 valence electrons • Elements in columns 1A through VIIIA: the number of valence electrons can be determined by the column number; 1A has 1 valence electron, IIA has 2 valence elec ...
Minerals * Chemistry Review
... • The number of protons plus neutrons gives the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
... • The number of protons plus neutrons gives the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
Electrons_Holes
... In this E-k diagram, the lowest point in the conduction band is not directly above the highest point on the valence band. The difference between these two points is still the bandgap energy, Eg. If the free electron drops down from the lowest point in the conduction band in the highest point in the ...
... In this E-k diagram, the lowest point in the conduction band is not directly above the highest point on the valence band. The difference between these two points is still the bandgap energy, Eg. If the free electron drops down from the lowest point in the conduction band in the highest point in the ...
Conduction electrons
... • Low resistivity => “conductor” • High resistivity => “insulator” • Intermediate resistivity => “semiconductor” – conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators – generally crystalline in structure for IC devices • In recent years, however, non-crystalline semiconductors have become co ...
... • Low resistivity => “conductor” • High resistivity => “insulator” • Intermediate resistivity => “semiconductor” – conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators – generally crystalline in structure for IC devices • In recent years, however, non-crystalline semiconductors have become co ...
Ch. 3
... going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
... going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
ARPES experiments on 3D topological insulators
... ‘hydrogen atoms’ of topological insulators • Lots of circumstantial evidence that these materials are likely 3D Tis • Dirac-like surface state at TRIM • Surface state has spin texture (spin-momentum locking) • Surface states are robust, except when they are subjected to magnetic impurities ...
... ‘hydrogen atoms’ of topological insulators • Lots of circumstantial evidence that these materials are likely 3D Tis • Dirac-like surface state at TRIM • Surface state has spin texture (spin-momentum locking) • Surface states are robust, except when they are subjected to magnetic impurities ...
History of the Atom
... with cathode rays (originates for the cathode). - Cathode rays move toward the anode, pass through hole to form beam - Beams bends away from the negatively charged plate and toward the positively charged plate. Concluded that a cathode ray consists of a beam of negatively charged particles (electron ...
... with cathode rays (originates for the cathode). - Cathode rays move toward the anode, pass through hole to form beam - Beams bends away from the negatively charged plate and toward the positively charged plate. Concluded that a cathode ray consists of a beam of negatively charged particles (electron ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... (1) electrons, only (2) neutrons, only (3) protons and electrons (4) protons and neutrons 3. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom of sulfur in the ground state? ...
... (1) electrons, only (2) neutrons, only (3) protons and electrons (4) protons and neutrons 3. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom of sulfur in the ground state? ...
Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons
... 3. The electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 4. A chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they share 5. Type of bond that forms between two atoms of similar electronegativity when electrons are equally shared 6. ...
... 3. The electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 4. A chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two electrons they share 5. Type of bond that forms between two atoms of similar electronegativity when electrons are equally shared 6. ...
Nearly Free Electron Approximation
... This is largely brought on by the lattice of positively charged nuclei that can interact with the electrons, so essentially the electrons are not free ie (nearly free approximation), but periodically disrupted by an attractive potential. The wavefunction for an electron in a periodic potential is gi ...
... This is largely brought on by the lattice of positively charged nuclei that can interact with the electrons, so essentially the electrons are not free ie (nearly free approximation), but periodically disrupted by an attractive potential. The wavefunction for an electron in a periodic potential is gi ...
3. atomic structure
... usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
... usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
Atomic Structure
... neutral atom in its ground state in order to form a cation. • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
... neutral atom in its ground state in order to form a cation. • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
Exam #2
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
What is matter made of?
... in half again & again until it became too small that it could no longer be divided. ...
... in half again & again until it became too small that it could no longer be divided. ...
Low-energy electron diffraction

Low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) is a technique for the determination of the surface structure of single-crystalline materials by bombardment with a collimated beam of low energy electrons (20–200 eV) and observation of diffracted electrons as spots on a fluorescent screen.LEED may be used in one of two ways: Qualitatively, where the diffraction pattern is recorded and analysis of the spot positions gives information on the symmetry of the surface structure. In the presence of an adsorbate the qualitative analysis may reveal information about the size and rotational alignment of the adsorbate unit cell with respect to the substrate unit cell. Quantitatively, where the intensities of diffracted beams are recorded as a function of incident electron beam energy to generate the so-called I-V curves. By comparison with theoretical curves, these may provide accurate information on atomic positions on the surface at hand.↑