Unit 2
... A. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. B. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. C. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. D. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. 26. The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it _____ A. contains nearly all of t ...
... A. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. B. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. C. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. D. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. 26. The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it _____ A. contains nearly all of t ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
document
... element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reactio ...
... element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reactio ...
Microbial Metabolism
... • To determine which direction the reactions go, see which is “higher” on the electron tower • Note the position of important electron carriers (NAD, FAD, cytochrome a) and external electron donors/acceptors (H2, organic compounds, O2) ...
... • To determine which direction the reactions go, see which is “higher” on the electron tower • Note the position of important electron carriers (NAD, FAD, cytochrome a) and external electron donors/acceptors (H2, organic compounds, O2) ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... can unite chemically to form compounds when conditions are ...
... can unite chemically to form compounds when conditions are ...
speckling in diffraction patterns and optical images formed with the
... expected provided only that the area of the object employed is large enough to include a representative sample of its random structure. The above physical considerations serve to establish reasons for some of the general features of the speckled diffraction patterns observed from rough objects. They ...
... expected provided only that the area of the object employed is large enough to include a representative sample of its random structure. The above physical considerations serve to establish reasons for some of the general features of the speckled diffraction patterns observed from rough objects. They ...
Infoscience
... This is known as the equilibrium Volta potential difference. Under equilibrium, the ionization energies, eq S5, of the conductors also become equal as the conductor with lower work function becomes positively charged with respect to that with higher work function,S3 and this makes equally difficult ...
... This is known as the equilibrium Volta potential difference. Under equilibrium, the ionization energies, eq S5, of the conductors also become equal as the conductor with lower work function becomes positively charged with respect to that with higher work function,S3 and this makes equally difficult ...
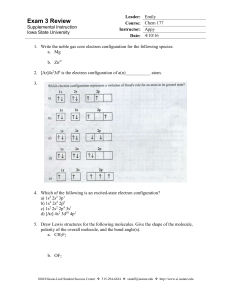
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydrogen 18. Give the correct order of increasing radii for the isoelectronic series: Rb+, Sr2+, Se2-, Br – ...
... b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydrogen 18. Give the correct order of increasing radii for the isoelectronic series: Rb+, Sr2+, Se2-, Br – ...
Chemistry for Bio 11
... • Compounds- different elements in a molecule, in exact, whole-number ratios, joined by a chemical bond • 2 major means of intramolecular chemical bonding: Covalent (incl. polar and nonpolar) and Ionic ...
... • Compounds- different elements in a molecule, in exact, whole-number ratios, joined by a chemical bond • 2 major means of intramolecular chemical bonding: Covalent (incl. polar and nonpolar) and Ionic ...
Atoms and Elements
... For a NEUTRAL atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. For an anion, add electrons. For a cation, subtract electrons. ...
... For a NEUTRAL atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. For an anion, add electrons. For a cation, subtract electrons. ...
ch04_sec3_as - LCMR School District
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
Section 3: Modern Atomic Theory Atoms Section 3
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
... Electron Energy Levels 〉 How are the energy levels of an atom filled? 〉 The number of energy levels that are filled in an atom depends on the number of electrons. • valence electron: an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
O 95: Metal Substrates: Adsorption of Atoms and Inorganic Molecules
... Surfaces - Structure, Properties and Reactivity from Density Functional Theory — ∙Wolfgang Hieringer — Theoretical Chemistry, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Transition metal coordination compounds adsorbed on metal surfaces have received increasing attention in recent years. Not only do they appear ...
... Surfaces - Structure, Properties and Reactivity from Density Functional Theory — ∙Wolfgang Hieringer — Theoretical Chemistry, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Transition metal coordination compounds adsorbed on metal surfaces have received increasing attention in recent years. Not only do they appear ...
lecture 6
... it shares with the hydrogen atoms towards it. The hydrogen atoms are left with a net positive charge and the oxygen is negative. This results in the water molecule having a large dipole moment. Two water molecules can therefore form a strong electrostatic interaction ...
... it shares with the hydrogen atoms towards it. The hydrogen atoms are left with a net positive charge and the oxygen is negative. This results in the water molecule having a large dipole moment. Two water molecules can therefore form a strong electrostatic interaction ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... ______10. When atoms share electrons, the electrical attraction of an atom for the shared electrons is called the atom's a. electron affinity. b. resonance. c. electronegativity. d. hybridization. ______11. If the atoms that share electrons have an unequal attraction for the electrons, the bond is c ...
... ______10. When atoms share electrons, the electrical attraction of an atom for the shared electrons is called the atom's a. electron affinity. b. resonance. c. electronegativity. d. hybridization. ______11. If the atoms that share electrons have an unequal attraction for the electrons, the bond is c ...
Biol 1441
... Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Element is a substance that cannot be broken down chemically to other substances by chemical reactions. A compound is a substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio. Essential Elements of Life: Carbon, oxygen, h ...
... Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Element is a substance that cannot be broken down chemically to other substances by chemical reactions. A compound is a substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio. Essential Elements of Life: Carbon, oxygen, h ...
Low-energy electron diffraction

Low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) is a technique for the determination of the surface structure of single-crystalline materials by bombardment with a collimated beam of low energy electrons (20–200 eV) and observation of diffracted electrons as spots on a fluorescent screen.LEED may be used in one of two ways: Qualitatively, where the diffraction pattern is recorded and analysis of the spot positions gives information on the symmetry of the surface structure. In the presence of an adsorbate the qualitative analysis may reveal information about the size and rotational alignment of the adsorbate unit cell with respect to the substrate unit cell. Quantitatively, where the intensities of diffracted beams are recorded as a function of incident electron beam energy to generate the so-called I-V curves. By comparison with theoretical curves, these may provide accurate information on atomic positions on the surface at hand.↑