Advanced Microscopy
... 4.1.3 photothermal microscopy 4.1.4 STED microscopy below the diffraction limit 4.1.5 PALM/STORM detection techniques for super-resolution ...
... 4.1.3 photothermal microscopy 4.1.4 STED microscopy below the diffraction limit 4.1.5 PALM/STORM detection techniques for super-resolution ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
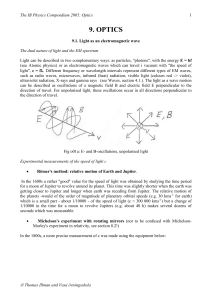
... by a light ray in going from one point to another through any set of media is such as to render its optical path equal, in the first approximation, to other paths closely adjacent to the actual one” (i.e., the path will be the one with the minimum time: a concept much in vogue at the time following i ...
... by a light ray in going from one point to another through any set of media is such as to render its optical path equal, in the first approximation, to other paths closely adjacent to the actual one” (i.e., the path will be the one with the minimum time: a concept much in vogue at the time following i ...
Optics - Jnoodle
... shape such that light entering from above will be totally internally reflected back up only if the material really is diamond, and not fake materials with n-values of around 1.5 or 1.6. This makes it possible for a jeweller to quickly determine if a diamond is genuine. Note II: The n-values for wate ...
... shape such that light entering from above will be totally internally reflected back up only if the material really is diamond, and not fake materials with n-values of around 1.5 or 1.6. This makes it possible for a jeweller to quickly determine if a diamond is genuine. Note II: The n-values for wate ...
Lecture 21 - Lehigh University
... The main factor which reduces image quality of an objective lens is the double dependence of its parameters on wavelength and temperature. Thus, in addition to spherical aberrations, both chromatic and temperature aberrations need to be carefully corrected in high performance optical systems. For e ...
... The main factor which reduces image quality of an objective lens is the double dependence of its parameters on wavelength and temperature. Thus, in addition to spherical aberrations, both chromatic and temperature aberrations need to be carefully corrected in high performance optical systems. For e ...
134_2010_1897_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... reaction in the expanded volume (2 L), there is an equivalent net consumption of H+-ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) and OH-- ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) – incorrect sign, used in Table S1 – to form 1.55E-07 mol/L H2O. Therefore, at initial state before chemical reaction, the concentrations of 0.140 mol/L NaOH an ...
... reaction in the expanded volume (2 L), there is an equivalent net consumption of H+-ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) and OH-- ions (-1.55E-07 mol/L) – incorrect sign, used in Table S1 – to form 1.55E-07 mol/L H2O. Therefore, at initial state before chemical reaction, the concentrations of 0.140 mol/L NaOH an ...
Ligand Conformation Enforces Trigonal
... 1084 and 619 cm-1. The solid-state ligand field spectrum of 1 shows a low-energy absorption band at 838 nm with a high-energy shoulder at 710 nm, characteristic for trigonalbipyramidal copper(II) complexes, corresponding to the d-d transition of Cu(II) ions. In acetonitrile solution, a weak band at ...
... 1084 and 619 cm-1. The solid-state ligand field spectrum of 1 shows a low-energy absorption band at 838 nm with a high-energy shoulder at 710 nm, characteristic for trigonalbipyramidal copper(II) complexes, corresponding to the d-d transition of Cu(II) ions. In acetonitrile solution, a weak band at ...
Helium Neon Laser - Abbe School of Photonics
... with a wavelength λ incides normally on the grating, each slit acts as a line of point sources. The light in a particular direction, ϕ, is made up of the interfering components from each slit (Fig. 8). Due to the difference in phase the waves from different slits mainly cancel one ...
... with a wavelength λ incides normally on the grating, each slit acts as a line of point sources. The light in a particular direction, ϕ, is made up of the interfering components from each slit (Fig. 8). Due to the difference in phase the waves from different slits mainly cancel one ...
Self-collimation and focusing effects in zero
... emulate negative-index materials [6], [7]. Transmission pikes lying in the zero-n̄ gap have in addition been theoretically predicted when a resonant optical condition similar to Fabry-Perot (FP) condition is satisfied [3]. Although these resonant states have not yet been experimentally observed, the ...
... emulate negative-index materials [6], [7]. Transmission pikes lying in the zero-n̄ gap have in addition been theoretically predicted when a resonant optical condition similar to Fabry-Perot (FP) condition is satisfied [3]. Although these resonant states have not yet been experimentally observed, the ...
High spatial resolution performance of a triple Fabry–Pérot filtergraph
... Cavallini 1998; Kentischer et al. 1998). The spectral passband of an FPI varies with the angle of incidence of a plane wave which transverses the interferometer. In all designs except the one by Bendlin et al. (1992), the FPIs are operated in a telecentric configuration – i.e., with a collimated pup ...
... Cavallini 1998; Kentischer et al. 1998). The spectral passband of an FPI varies with the angle of incidence of a plane wave which transverses the interferometer. In all designs except the one by Bendlin et al. (1992), the FPIs are operated in a telecentric configuration – i.e., with a collimated pup ...
Padgett, M. (2014) Light`s twist. Proceedings of the Royal Society of
... OAM-carrying beam into its various OAM components depends upon the choice of measurement axis [27], whereas a description of its polarization state does not. Another early study of beams carrying OAM centred around nonlinear optics. When an intense infrared laser is focused into a range of exotic ma ...
... OAM-carrying beam into its various OAM components depends upon the choice of measurement axis [27], whereas a description of its polarization state does not. Another early study of beams carrying OAM centred around nonlinear optics. When an intense infrared laser is focused into a range of exotic ma ...
Excitation Energy Dependence of Fluorescence Intermittency Nanocrystals in
... Hoheisel et al. [14] and Knappenberger et al. [15], that certain sets of trap states become energetically accessible above certain thresholds. This leads to an observable change in blinking dynamics. We these models further in Chapter 3. In order to explore the energy level structure of the quantum ...
... Hoheisel et al. [14] and Knappenberger et al. [15], that certain sets of trap states become energetically accessible above certain thresholds. This leads to an observable change in blinking dynamics. We these models further in Chapter 3. In order to explore the energy level structure of the quantum ...
Total internal reflection holography for optical interconnections
... Equation (8) shows that for a given NA, the aberrations induced by the wavelength shift are proportional to the focal length Pd of the optical element. Recording with spherical and plane waves under the conditions given in Eqs. (6a) and ...
... Equation (8) shows that for a given NA, the aberrations induced by the wavelength shift are proportional to the focal length Pd of the optical element. Recording with spherical and plane waves under the conditions given in Eqs. (6a) and ...
Disorder-Enhanced Imaging with Spatially Controlled Light
... In chapter 4 we experimentally show that spatial wave front shaping can be used to focus and concentrate light to an optimal small spot inside a turbid material. Chapter 5 is dedicated to a non-imaging approach of displacement metrology for disordered materials that opens the way for high speed nano ...
... In chapter 4 we experimentally show that spatial wave front shaping can be used to focus and concentrate light to an optimal small spot inside a turbid material. Chapter 5 is dedicated to a non-imaging approach of displacement metrology for disordered materials that opens the way for high speed nano ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.