PDF
... and the envelope, Aðt;zÞ; moves at a group velocity given by 1=b1 : A GVD term, which governs temporal spreading of the envelope, is given by b2 : Higherorder b terms are usually negligible for propagation of pulses of $1 ps duration in optical fibers and are lumped into the category of ‘higher-orde ...
... and the envelope, Aðt;zÞ; moves at a group velocity given by 1=b1 : A GVD term, which governs temporal spreading of the envelope, is given by b2 : Higherorder b terms are usually negligible for propagation of pulses of $1 ps duration in optical fibers and are lumped into the category of ‘higher-orde ...
Polarimeter - ScholarWorks@UNO
... late the elements of the Mueller matrix with relatively 65 out of the optical characteristics of the substance, thus simple arithmetic operations such as adding and sub enabling it to serve as an ellipsometer for characteriza tracting and multiplying or dividing by constants. This tion of surfaces a ...
... late the elements of the Mueller matrix with relatively 65 out of the optical characteristics of the substance, thus simple arithmetic operations such as adding and sub enabling it to serve as an ellipsometer for characteriza tracting and multiplying or dividing by constants. This tion of surfaces a ...
Biochemistry I Laboratory Chem 4401
... “Molarity” is a concentration term. It refers to the number of moles of a substance per liter of solution. It you recall, a “mole” is the quantity of substance that contains 6.02 x 1023 (Avogadro’s number) items. You may also recall that the atomic or formula weight of a substance, in grams, contain ...
... “Molarity” is a concentration term. It refers to the number of moles of a substance per liter of solution. It you recall, a “mole” is the quantity of substance that contains 6.02 x 1023 (Avogadro’s number) items. You may also recall that the atomic or formula weight of a substance, in grams, contain ...
Tapered Fiber Fabrication
... confining the light into a small space. This increases the intensity of the field in the core of the fiber and results in more light being guided outside of the core. Then, light can be coupled into objects such as microresonators by means of frustrated total internal reflection. Tapered optical fib ...
... confining the light into a small space. This increases the intensity of the field in the core of the fiber and results in more light being guided outside of the core. Then, light can be coupled into objects such as microresonators by means of frustrated total internal reflection. Tapered optical fib ...
Diamagnetic Raman Optical Activity of Chlorine, Bromine, and
... and overtone vibrations arise as the strongest ones amidst many fluorescence signals and a broad fluorescence background (the latter was subtracted from the spectrum shown). The fluorescence signal is very complex, depends on the excitations wavelength and other experimental conditions,[13] and can ...
... and overtone vibrations arise as the strongest ones amidst many fluorescence signals and a broad fluorescence background (the latter was subtracted from the spectrum shown). The fluorescence signal is very complex, depends on the excitations wavelength and other experimental conditions,[13] and can ...
Collision-induced Raman scattering by rare-gas atoms: The
... out at small values of ν, which makes the extraction of isotropic Ne–Ne intensities an unreliable operation below 100 cm−1. Only measurements taken above 100 cm−1 are numerically meaningful and are reported below. Figure 1 shows the isotropic Ne–Ne spectrum as a function of ν. Measurements are depic ...
... out at small values of ν, which makes the extraction of isotropic Ne–Ne intensities an unreliable operation below 100 cm−1. Only measurements taken above 100 cm−1 are numerically meaningful and are reported below. Figure 1 shows the isotropic Ne–Ne spectrum as a function of ν. Measurements are depic ...
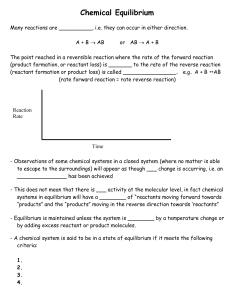
Chapter 17 Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria I. Solubility
... So, [H+] =( Ka)[HA]/[A-] Taking negative logs we get -log [H+] = -logKa - log [HA]/[A-] pH = pKa-log [HA]/[A-] Or pH pKa+log [base]/[acid] Henderson-Hasselbalch equation Addition of Strong acids or Bases to Buffers We break the calculation into two parts: stoichiometric and equilibrium The amount of ...
... So, [H+] =( Ka)[HA]/[A-] Taking negative logs we get -log [H+] = -logKa - log [HA]/[A-] pH = pKa-log [HA]/[A-] Or pH pKa+log [base]/[acid] Henderson-Hasselbalch equation Addition of Strong acids or Bases to Buffers We break the calculation into two parts: stoichiometric and equilibrium The amount of ...
Solvent effects on excited state relaxation phenomena
... In pure solvents effects of electrostatic forces and of specific short range interactions on the spectral position or photophysical properties are not easily distinguished. Shifts attributed to either of these two categories could add up or cancle dependent on the structure of the soluteaolvent clus ...
... In pure solvents effects of electrostatic forces and of specific short range interactions on the spectral position or photophysical properties are not easily distinguished. Shifts attributed to either of these two categories could add up or cancle dependent on the structure of the soluteaolvent clus ...
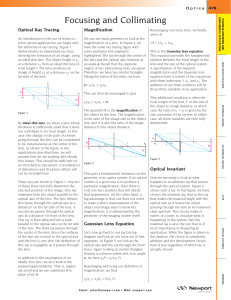
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
Microscopy Overview
... For S = 0 the illumination is purely coherent, while for S → ∞ imaging becomes purely incoherent, thus corresponding to the Rayleigh criterion. (So S should really be called an incoherence parameter.) An important in-between case is when S = 1, when the apertures of objective and condenser are equal ...
... For S = 0 the illumination is purely coherent, while for S → ∞ imaging becomes purely incoherent, thus corresponding to the Rayleigh criterion. (So S should really be called an incoherence parameter.) An important in-between case is when S = 1, when the apertures of objective and condenser are equal ...
File
... To determine if an approximation can be used follow the steps below: i) If [initial] / Kc > _____, use the approximation. Let the [initial] represent the [equilibrium] ii) If [initial] / Kc < 500, do _____ use the approximation. [Most likely QUADRATIC!] Let the [initial] - [change] represent the [eq ...
... To determine if an approximation can be used follow the steps below: i) If [initial] / Kc > _____, use the approximation. Let the [initial] represent the [equilibrium] ii) If [initial] / Kc < 500, do _____ use the approximation. [Most likely QUADRATIC!] Let the [initial] - [change] represent the [eq ...
Sample Exercise 19.1 Identifying Spontaneous Processes
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.