PPT - Tensors for Tots
... and emitted only discretely in quants (What we now call photons). The exchange of energy between the oscillators and the electromagnetic radiation field occurs in tiny energy packets rather than continuously as in the classical view. Planck's Radiation Law describes the distribution of intensities ...
... and emitted only discretely in quants (What we now call photons). The exchange of energy between the oscillators and the electromagnetic radiation field occurs in tiny energy packets rather than continuously as in the classical view. Planck's Radiation Law describes the distribution of intensities ...
The petrographic microscope
... Light is a form of radiant energy, and although its precise nature involves very complex Physics theories, all the phenomena relating to minerals can be explained by exclusively considering the oscillating theory, i.e. for our purposes, light is propagated as a consequence of a vibration of particl ...
... Light is a form of radiant energy, and although its precise nature involves very complex Physics theories, all the phenomena relating to minerals can be explained by exclusively considering the oscillating theory, i.e. for our purposes, light is propagated as a consequence of a vibration of particl ...
Section 9.4: Light: Wave or Particle?
... baseline array are combined to form interference patterns, which reveal information about the object under study. Another wave-like property used in interferometry is reflection. The electromagnetic radiation from the object reaches the large, parabolic radio telescope dishes, and the radio waves ar ...
... baseline array are combined to form interference patterns, which reveal information about the object under study. Another wave-like property used in interferometry is reflection. The electromagnetic radiation from the object reaches the large, parabolic radio telescope dishes, and the radio waves ar ...
11. Electro
... How a laser Works Electrons can have different energy levels or states We can raise the energy level of the electrons by energising the atom When an electron falls back from a higher to a lower energy level, it releases a photon (a light bundle) The photon will have a specific wavelength tha ...
... How a laser Works Electrons can have different energy levels or states We can raise the energy level of the electrons by energising the atom When an electron falls back from a higher to a lower energy level, it releases a photon (a light bundle) The photon will have a specific wavelength tha ...
BJ - Faculty Web Pages
... needs to be qualitative (don’t go too far with that- maybe semi-quantitative?), but it should be as informative as possible. ...
... needs to be qualitative (don’t go too far with that- maybe semi-quantitative?), but it should be as informative as possible. ...
03-02BohrAtom
... R(1/12 - 1/n2), n = 2, 3, ...(Lyman) (UV) R(1/32 - 1/n2), n = 4, 5, ...(Paschen) (IR) (R = 1.097 x 10-7 m-1) ...
... R(1/12 - 1/n2), n = 2, 3, ...(Lyman) (UV) R(1/32 - 1/n2), n = 4, 5, ...(Paschen) (IR) (R = 1.097 x 10-7 m-1) ...
The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The
... nucleus and it motion is governed by the ordinary laws of mechanics and electrostatics, with the restriction that the angular momentum of the electron is quantized (can only have certain ...
... nucleus and it motion is governed by the ordinary laws of mechanics and electrostatics, with the restriction that the angular momentum of the electron is quantized (can only have certain ...
Midterm 1 2009 (PDF format)
... d) H is the value of q measured under conditions of constant volume. e) The enthalpy change of a reaction is the reciprocal of the ∆H of the reverse reaction. ...
... d) H is the value of q measured under conditions of constant volume. e) The enthalpy change of a reaction is the reciprocal of the ∆H of the reverse reaction. ...
Nonlinear photoacoustic spectroscopy of hemoglobin
... fluence, the measured PA spectrum correlated well with the theoretical absorption spectrum of deoxygenated whole blood (R ¼ 0.999) with sO2 ¼ 8% (Fig. 3(a)). A typical second-order coefficient of deoxygenated lysed blood is shown in Fig. 3(b). To analyze the wavelength-dependent effects of optical s ...
... fluence, the measured PA spectrum correlated well with the theoretical absorption spectrum of deoxygenated whole blood (R ¼ 0.999) with sO2 ¼ 8% (Fig. 3(a)). A typical second-order coefficient of deoxygenated lysed blood is shown in Fig. 3(b). To analyze the wavelength-dependent effects of optical s ...
1 - 嘉義大學
... 10. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.00 liter to a volume of 10.00 liters against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. How much work (in joules) is performed on the surroundings? (T = 300 K; 1 L atm = 101.3 J) (A) 456 J (B) 912 J (C) 2740 J (D) none of these 11. What is t ...
... 10. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.00 liter to a volume of 10.00 liters against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. How much work (in joules) is performed on the surroundings? (T = 300 K; 1 L atm = 101.3 J) (A) 456 J (B) 912 J (C) 2740 J (D) none of these 11. What is t ...
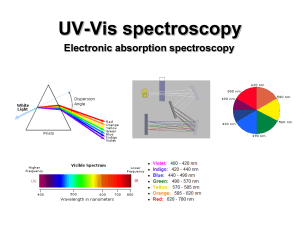
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.