Two Quick Light Experiments
... We will send laser light through a pattern of slits. According to Huygens' Principle, the light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic ...
... We will send laser light through a pattern of slits. According to Huygens' Principle, the light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic ...
Development of a New Atomic Model
... The Particle Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by matter only in whole numbers of photons. In order for an electron to be ejected from the metal surface, it must be struck by a single photon possessing the minimum amount of energy required to knock the electron loose. This ...
... The Particle Description of Light Electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by matter only in whole numbers of photons. In order for an electron to be ejected from the metal surface, it must be struck by a single photon possessing the minimum amount of energy required to knock the electron loose. This ...
Atomic Spectroscopy
... Beer's Law states that the light absorption is proportional to the number of absorbing species in the sample. Effectively for AA, this means that the amount of energy (light) absorbed is proportional to the concentration of atoms in the atomizer. Thus if a concentration of atoms 'c' produced an abso ...
... Beer's Law states that the light absorption is proportional to the number of absorbing species in the sample. Effectively for AA, this means that the amount of energy (light) absorbed is proportional to the concentration of atoms in the atomizer. Thus if a concentration of atoms 'c' produced an abso ...
Invisibility Cup - Purdue Engineering
... is that metals absorb light more strongly than microwaves, because they have a much greater electrical resistance at visible light frequencies. Cai et al.2 get round this problem by designing their wires to have as little resistance as possible. The wires resemble the structures they applied in thei ...
... is that metals absorb light more strongly than microwaves, because they have a much greater electrical resistance at visible light frequencies. Cai et al.2 get round this problem by designing their wires to have as little resistance as possible. The wires resemble the structures they applied in thei ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
The retrieval of ozone`s absorption coefficient in the stratosphere
... comes to multiple scattering environments with complex geometric configurations [7]. Ultimately, the Fourier series depicts another attempt to solve the ETR. Although it is mathematically complicated, it only concludes that it is possible to apply Fourier series in the radiative transfer calculation ...
... comes to multiple scattering environments with complex geometric configurations [7]. Ultimately, the Fourier series depicts another attempt to solve the ETR. Although it is mathematically complicated, it only concludes that it is possible to apply Fourier series in the radiative transfer calculation ...
39 Steps
... Unloading refers to dye that was in the cell but has now been pumped out or otherwise inactivated. The substrate-reaction rate applies to dyes with fluorescent properties that are related to their interaction with ions or other molecules in the cell. The pixel-dwell is in the order of microseconds, ...
... Unloading refers to dye that was in the cell but has now been pumped out or otherwise inactivated. The substrate-reaction rate applies to dyes with fluorescent properties that are related to their interaction with ions or other molecules in the cell. The pixel-dwell is in the order of microseconds, ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... voltage, or resistance) vary when light is incident upon it. The most common type consists of two electrodes separated by a light-sensitive semiconductor material. A battery or other voltage source connected to the electrodes sets up a current even in the absence of light; when light strikes the sem ...
... voltage, or resistance) vary when light is incident upon it. The most common type consists of two electrodes separated by a light-sensitive semiconductor material. A battery or other voltage source connected to the electrodes sets up a current even in the absence of light; when light strikes the sem ...
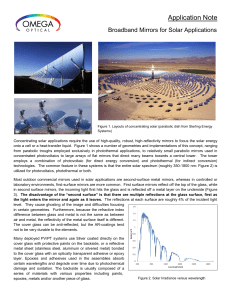
Broadband Mirrors for Solar Applications
... Concentrating solar applications require the use of high-quality, robust, high-reflectivity mirrors to focus the solar energy onto a cell or a heat-transfer liquid. Figure 1 shows a number of geometries and implementations of this concept, ranging from parabolic troughs employed exclusively in photo ...
... Concentrating solar applications require the use of high-quality, robust, high-reflectivity mirrors to focus the solar energy onto a cell or a heat-transfer liquid. Figure 1 shows a number of geometries and implementations of this concept, ranging from parabolic troughs employed exclusively in photo ...
12Sept_Synergist Solutions article
... factor. By performing a side-by-side comparison between a photometer and gravimetric analysis, the photometer response can be adjusted to match gravimetric concentration. This correction factor, or calibration factor, is valid as long as the dust being sampled does not change much in terms of size d ...
... factor. By performing a side-by-side comparison between a photometer and gravimetric analysis, the photometer response can be adjusted to match gravimetric concentration. This correction factor, or calibration factor, is valid as long as the dust being sampled does not change much in terms of size d ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.