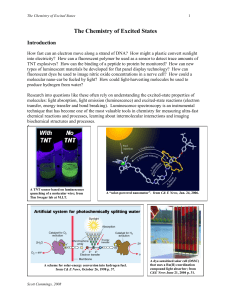
The Chemistry of Excited States
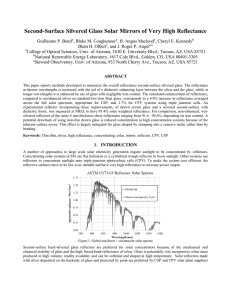
... usually observed in room-temperature fluid solution, but can be observed (at = 670 nm) in the solid-state or when the compound is dissolved in a solid-state host medium. Excitation of an [Ru(bpy)3]2+ solution using ex = 450 nm results in intense red phosphorescence centered at ~610 nm, originatin ...
... usually observed in room-temperature fluid solution, but can be observed (at = 670 nm) in the solid-state or when the compound is dissolved in a solid-state host medium. Excitation of an [Ru(bpy)3]2+ solution using ex = 450 nm results in intense red phosphorescence centered at ~610 nm, originatin ...
Solution - ZOMUedu
... ■ The moles of solute stay the same ■ M1V1 = M2V2 ○ Stock solution = a solution of known concentration that is used to make more dilute solutions Precipitation ○ Precipitation = when aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are poured together and a solid forms (solid = precipitate) ○ We can predict the ...
... ■ The moles of solute stay the same ■ M1V1 = M2V2 ○ Stock solution = a solution of known concentration that is used to make more dilute solutions Precipitation ○ Precipitation = when aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are poured together and a solid forms (solid = precipitate) ○ We can predict the ...
Download PDF
... optical fields undergo modifications in terms of irradiance, phase, spectrum, direction, polarization, and coherence, which can reveal information about the sample of interest. Light scattering by cells and tissues evolved as a dynamic area of study, especially because this type of investigation can ...
... optical fields undergo modifications in terms of irradiance, phase, spectrum, direction, polarization, and coherence, which can reveal information about the sample of interest. Light scattering by cells and tissues evolved as a dynamic area of study, especially because this type of investigation can ...
My Research about the silicon photonics
... 1. macrochip: interconnecting microchips electrically by stacking them edge to edge on a big silicon wafer, making larger chips on a single wafer of silicon 2. silicon photonics: optical networking by connecting chips via laser beam Usually electric wires connect computers and chips. Even within a c ...
... 1. macrochip: interconnecting microchips electrically by stacking them edge to edge on a big silicon wafer, making larger chips on a single wafer of silicon 2. silicon photonics: optical networking by connecting chips via laser beam Usually electric wires connect computers and chips. Even within a c ...
12. CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY • Confocal microscopy can render
... Aberrations, both chromatic and geometrical, lower the resolving power of the confocal microscope. Aberration correction, adaptive optics, is a critical issue especially when operating at very high NA (current research) However, even with an instrument that is capable in principle of producing ...
... Aberrations, both chromatic and geometrical, lower the resolving power of the confocal microscope. Aberration correction, adaptive optics, is a critical issue especially when operating at very high NA (current research) However, even with an instrument that is capable in principle of producing ...
PH4027 - Optoelectronics & Nonlinear Optics
... a large number of everyday applications, ranging from the ubiquitous LED, televisions and computer displays, as well as lasers in CD players, to sophisticated equipment for high-speed telecommunications applications that form the backbone of the internet. While classical optics is concerned with lin ...
... a large number of everyday applications, ranging from the ubiquitous LED, televisions and computer displays, as well as lasers in CD players, to sophisticated equipment for high-speed telecommunications applications that form the backbone of the internet. While classical optics is concerned with lin ...
KEMS448 Physical Chemistry Advanced Laboratory Work
... In this laboratory work, the surface tension of an anionic tenside molecule, sodium dodecyl sulphate (NDS), is measured as a function of concentration. From the results, the critical micelle concentration is determined and the behaviour of surface excess as a function of the concentration is examine ...
... In this laboratory work, the surface tension of an anionic tenside molecule, sodium dodecyl sulphate (NDS), is measured as a function of concentration. From the results, the critical micelle concentration is determined and the behaviour of surface excess as a function of the concentration is examine ...
here - TCD Maths home - Trinity College Dublin
... passed through a sample, then diffraction occurred at many angles, giving a 3D representation of the material being examined. This was a revolution in electron microscopy, allowing crystallographers and solid state physicists access to more data than ever before. ...
... passed through a sample, then diffraction occurred at many angles, giving a 3D representation of the material being examined. This was a revolution in electron microscopy, allowing crystallographers and solid state physicists access to more data than ever before. ...
Achromatic Polarization-Preserving Beam Displacer
... In many applications it is necessary to displace an optical beam. The widespread use of lasers for research and technology demands the steering of collimated beams from one spatial region in which the optical beams are prepared to another in which they are applied. In many of these situations the pr ...
... In many applications it is necessary to displace an optical beam. The widespread use of lasers for research and technology demands the steering of collimated beams from one spatial region in which the optical beams are prepared to another in which they are applied. In many of these situations the pr ...
Part One Time: 50 minutes Value: 50 % Instructions : Shade in the
... The actual yield of a precipitate during a chemical reaction was found to be 85.0 g. The chemist that performed the experiment had calculated that she should have produced 95.6 g of precipitate. What was the percentage yield of this reaction? A. ...
... The actual yield of a precipitate during a chemical reaction was found to be 85.0 g. The chemist that performed the experiment had calculated that she should have produced 95.6 g of precipitate. What was the percentage yield of this reaction? A. ...
Research on the Design of an Optical Information Storage Sensing
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
laser - SlideBoom
... Semiconducting lasers are multilayer semiconductor devices that generates a coherent beam of monochromatic light by laser action. A coherent beam resulted which all of the photons are in phase. ...
... Semiconducting lasers are multilayer semiconductor devices that generates a coherent beam of monochromatic light by laser action. A coherent beam resulted which all of the photons are in phase. ...
GGN PUBLIC SCHOOL, LUDHIANA XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT
... 13. The total magnification produced by a compound microscope is 20, while that produced by the eyepiece alone is 5. when the microscope is focused on a certain object, the distance between objective and eyepiece is 14 cm. Find the focal length of objective and eyepiece, if distance of distinct visi ...
... 13. The total magnification produced by a compound microscope is 20, while that produced by the eyepiece alone is 5. when the microscope is focused on a certain object, the distance between objective and eyepiece is 14 cm. Find the focal length of objective and eyepiece, if distance of distinct visi ...
Study on high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) silicon p
... SNR can be over 104 within the wavelength range of 500–600 nm and the peak of spectral responsivity is 0.48 A/W at about 520 nm. 3.1. Optimizing the p-n junction depth xj The 1/α is penetration depth of light wavelength λ, where α is photoabsorption coefficient. For the devices whose junction depth ...
... SNR can be over 104 within the wavelength range of 500–600 nm and the peak of spectral responsivity is 0.48 A/W at about 520 nm. 3.1. Optimizing the p-n junction depth xj The 1/α is penetration depth of light wavelength λ, where α is photoabsorption coefficient. For the devices whose junction depth ...
Regents Chemistry
... o rule of thumb: ‘like dissolves like’ o know that alcohols have characteristics of both polar & non-polar liquids but do not dissolve ionic compounds Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much w ...
... o rule of thumb: ‘like dissolves like’ o know that alcohols have characteristics of both polar & non-polar liquids but do not dissolve ionic compounds Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much w ...
Questions 3-4 from AP exam 2006
... 2006 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 3. Answer the following questions that relate to the analysis of chemical compounds. (a) A compound containing the elements C , H , N , and O is analyzed. When a 1.2359 g sample is burned in excess oxygen, 2.241 g of CO2(g) is formed. The combustion analys ...
... 2006 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 3. Answer the following questions that relate to the analysis of chemical compounds. (a) A compound containing the elements C , H , N , and O is analyzed. When a 1.2359 g sample is burned in excess oxygen, 2.241 g of CO2(g) is formed. The combustion analys ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.