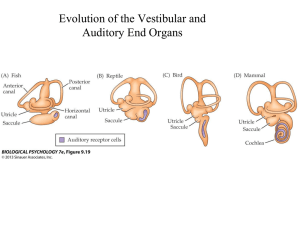
The peripheral auditory system
... loud sinusoids (140dB) at low frequencies in recently deceased humans using stroboscopic illumination • Bekesy found a relative bandwidth of 0.6 – e.g., 600 Hz 10dB bandwidth when CF is 1000 Hz – Too high to account for sharp frequency resolution of ear and auditory neurons! ...
... loud sinusoids (140dB) at low frequencies in recently deceased humans using stroboscopic illumination • Bekesy found a relative bandwidth of 0.6 – e.g., 600 Hz 10dB bandwidth when CF is 1000 Hz – Too high to account for sharp frequency resolution of ear and auditory neurons! ...
The Nonvisual Sensory Systems
... Pitch Perception Theories of Pitch Perception Frequency theory-the basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with a sound, causing auditory nerve axons to produce action potentials at the same frequency Place theory-the basilar membrane resembles the strings of a piano in that each area along the memb ...
... Pitch Perception Theories of Pitch Perception Frequency theory-the basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with a sound, causing auditory nerve axons to produce action potentials at the same frequency Place theory-the basilar membrane resembles the strings of a piano in that each area along the memb ...
P312Ch11_Auditory III (Coding Frequency And Intensity
... Main problem with this theory: We can perceive sounds whose frequencies are as high as 20,000 Hz, but neurons cannot respond at rates higher than 1000 action potentials per second, if that high. So the theory, unaltered, cannot account for our ability to hear sounds above 1000 Hz. One attempt to sal ...
... Main problem with this theory: We can perceive sounds whose frequencies are as high as 20,000 Hz, but neurons cannot respond at rates higher than 1000 action potentials per second, if that high. So the theory, unaltered, cannot account for our ability to hear sounds above 1000 Hz. One attempt to sal ...
The Auditory and Vestibular System
... One cycle is the distance between the waves of compression Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) Hearing range is 20 to 20,000 Hz. Most sensitive to frequencies ranging from 1,500 to 4,000 Hz. Decreases with age or exposure to loud sounds. There are high and low sounds that our ears cannot hear. ...
... One cycle is the distance between the waves of compression Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) Hearing range is 20 to 20,000 Hz. Most sensitive to frequencies ranging from 1,500 to 4,000 Hz. Decreases with age or exposure to loud sounds. There are high and low sounds that our ears cannot hear. ...
Hearing
... Code for the brain 1. Sensory neurons produce spikes 2. Spike rate increases with an increase in the stimulus intensity (here it was a weight on a muscle) ...
... Code for the brain 1. Sensory neurons produce spikes 2. Spike rate increases with an increase in the stimulus intensity (here it was a weight on a muscle) ...
HUMAN INFORMATION PROCESSING
... representation was emerging; the volunteers said they could visualize their own hands in two ways and could even choose between the two images. Brain scans associated activity with these new hand images in a region called 'Broca's area' that creates mental pictures of movement. These imagined images ...
... representation was emerging; the volunteers said they could visualize their own hands in two ways and could even choose between the two images. Brain scans associated activity with these new hand images in a region called 'Broca's area' that creates mental pictures of movement. These imagined images ...
Three-dimensional auditory localization in the
... discrimination task (Figure 2a) and range jitter discrimination task (Figure 2c), changes in echo amplitude affect the distance estimation of big brown bats in predictable ways (Figure 2f) [27,28]. Behaviorally, it has been demonstrated that sonar ranging in big brown bats is robust to changes in ec ...
... discrimination task (Figure 2a) and range jitter discrimination task (Figure 2c), changes in echo amplitude affect the distance estimation of big brown bats in predictable ways (Figure 2f) [27,28]. Behaviorally, it has been demonstrated that sonar ranging in big brown bats is robust to changes in ec ...
Cellular Neuroscience
... output should contain only the input frequency F0. • Fourier analysis is performed on the post stimulus time histogram to measure the amplitude ratio of the fundamental (1st harmonic, F1) to the “zero frequency” (i.e. sustained, “DC” response) F0. • Some complex cells have “on” and “off” responses w ...
... output should contain only the input frequency F0. • Fourier analysis is performed on the post stimulus time histogram to measure the amplitude ratio of the fundamental (1st harmonic, F1) to the “zero frequency” (i.e. sustained, “DC” response) F0. • Some complex cells have “on” and “off” responses w ...
Relationships between bat occupancy and habitat and landscape
... vegetative structure and insect abundance and thus bat activity is lower in these sites. Site occupancy was significantly reduced for northern long-eared, evening, and tri-colored bats with increasingly urban areas. Increasing forest cover at a 16 km radius positively affected big brown, eastern red ...
... vegetative structure and insect abundance and thus bat activity is lower in these sites. Site occupancy was significantly reduced for northern long-eared, evening, and tri-colored bats with increasingly urban areas. Increasing forest cover at a 16 km radius positively affected big brown, eastern red ...
vocabulary - Secret Garden and Dolphin Habitat
... with the light from the sky above. CREPUSCULAR Active during twilight hours like dawn and dusk. DORSAL FIN The fin on the back of the whale, dolphin or porpoise, which helps with balance and to regulate their body temperature. ECHOLOCATION The ability to locate objects by emitting sound waves and in ...
... with the light from the sky above. CREPUSCULAR Active during twilight hours like dawn and dusk. DORSAL FIN The fin on the back of the whale, dolphin or porpoise, which helps with balance and to regulate their body temperature. ECHOLOCATION The ability to locate objects by emitting sound waves and in ...
Ecology and Echolocation of Bats and Toothed Whales
... can be highly evolved to focus sonar pulses, or the mouth. Returning echoes are received in the ears, and pinna can be highly developed and moveable to optimally receive signals (Altringham 1996). Several species of the genus Rousettus, megachiropterans, emit sonar pulses not by their larynx, but by ...
... can be highly evolved to focus sonar pulses, or the mouth. Returning echoes are received in the ears, and pinna can be highly developed and moveable to optimally receive signals (Altringham 1996). Several species of the genus Rousettus, megachiropterans, emit sonar pulses not by their larynx, but by ...
The Auditory System
... Acoustic input typically comes from many different sources; they have different combinations of frequencies, their amplitudes change independently and they have different locations. But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system ...
... Acoustic input typically comes from many different sources; they have different combinations of frequencies, their amplitudes change independently and they have different locations. But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system ...
Tours - mzsdocents.org
... Large eyes, wide pupils to collect more light May have large ears Some rely on asymmetrical ears to locate prey (owls) Some rely more on sense of smell (badgers, moths) Many have sensitive whiskers Many use scents and calls to locate each other Some have developed additional senses (ba ...
... Large eyes, wide pupils to collect more light May have large ears Some rely on asymmetrical ears to locate prey (owls) Some rely more on sense of smell (badgers, moths) Many have sensitive whiskers Many use scents and calls to locate each other Some have developed additional senses (ba ...
Audition and Equilibrium
... Pitch (frequency) & Intensity • Base .... high pitch (treble) • Apex .... low pitch (bass) • Pitch coded by location of vibrations of Organ of Corti : Which hair cells are stimulated…which set of sensory axons have action potentials • Intensity coded by degree of displacement of stereocilia of hair ...
... Pitch (frequency) & Intensity • Base .... high pitch (treble) • Apex .... low pitch (bass) • Pitch coded by location of vibrations of Organ of Corti : Which hair cells are stimulated…which set of sensory axons have action potentials • Intensity coded by degree of displacement of stereocilia of hair ...
Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
... External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 1) ...
... External and Internal Structures of the Human Ear (Part 1) ...
Cortical Representation
... – Coefficient for F(t) shows the correlation (a measure of similarity) between the signal and F(t) ...
... – Coefficient for F(t) shows the correlation (a measure of similarity) between the signal and F(t) ...
Time-frequency computational model for echo
... environment from processing echoes of these sounds (Neuweiler, 2000; Popper and Fay, 1995). The images these bats perceive incorporate the shapes of objects at their correct locations over the operating range of their sonar (e.g., ~5 m for big brown bats; Kick, 1982). Experimental evidence indicates ...
... environment from processing echoes of these sounds (Neuweiler, 2000; Popper and Fay, 1995). The images these bats perceive incorporate the shapes of objects at their correct locations over the operating range of their sonar (e.g., ~5 m for big brown bats; Kick, 1982). Experimental evidence indicates ...
Slide ()
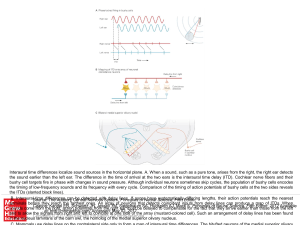
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
Remarkable Bats - Indiana County Parks and Trails
... insects. The little brown bat makes several feeding flights each night. In October and November, bats leave their summer roosts and move to tunnels, mine shafts, and caves. Here, clinging to the ceilings and clustered against one another, they hibernate. In spring, they emerge in April and May. They ...
... insects. The little brown bat makes several feeding flights each night. In October and November, bats leave their summer roosts and move to tunnels, mine shafts, and caves. Here, clinging to the ceilings and clustered against one another, they hibernate. In spring, they emerge in April and May. They ...
Animal echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is the biological sonar used by several kinds of animals. Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for navigation and for foraging (or hunting) in various environments. Some blind humans have learned to find their way using clicks produced by a device or by mouth.Echolocating animals include some mammals and a few birds; most notably microchiropteran bats and odontocetes (toothed whales and dolphins), but also in simpler form in other groups such as shrews, one genus of megachiropteran bats (Rousettus) and two cave dwelling bird groups, the so-called cave swiftlets in the genus Aerodramus (formerly Collocalia) and the unrelated Oilbird Steatornis caripensis.