2 Notes (Phylogeny II)
... Name for the gastrulation pattern shown by certain types of animals, including humans. Anatomical name referring to an animal’s head. Term for an animal that has only two tissue types (ectoderm and endoderm). A pattern of development where the blastopore becomes the mouth in the adult animal. A ball ...
... Name for the gastrulation pattern shown by certain types of animals, including humans. Anatomical name referring to an animal’s head. Term for an animal that has only two tissue types (ectoderm and endoderm). A pattern of development where the blastopore becomes the mouth in the adult animal. A ball ...
- Danville High School
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... 7. The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues 8. Many animals have at least one larval stage 9. A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis ...
... 7. The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues 8. Many animals have at least one larval stage 9. A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis ...
unit 7 –animal kingdom (invertebrates)
... 8. What three characteristics help determine how animals are classified? ...
... 8. What three characteristics help determine how animals are classified? ...
Animal Phyla Lab - Biology Junction
... Of all the phyla in the animal kingdom, Arthropoda is by far the largest and most diverse. All arthropods have segmented bodies and are covered in a hard, yet flexible, protective armor called an exoskeleton. Their body muscles attach to the inside of the exoskeleton. The name Arthropoda means “join ...
... Of all the phyla in the animal kingdom, Arthropoda is by far the largest and most diverse. All arthropods have segmented bodies and are covered in a hard, yet flexible, protective armor called an exoskeleton. Their body muscles attach to the inside of the exoskeleton. The name Arthropoda means “join ...
ZOO 261
... and Lugworms used by marine fishermen and the much smaller Tubifex or Red worms used by aquarists to feed their fish. In many countries people are still familiar with Medicinal leeches, and people who live closer to nature are naturally more familiar with a much wider range of Annelids than those wh ...
... and Lugworms used by marine fishermen and the much smaller Tubifex or Red worms used by aquarists to feed their fish. In many countries people are still familiar with Medicinal leeches, and people who live closer to nature are naturally more familiar with a much wider range of Annelids than those wh ...
Bonobo apes
... classified as endangered, there is no concrete data on population numbers, but the estimate is between 29,500 and 50,000 individuals. These apes are frugivores (fruit makes up half of their ...
... classified as endangered, there is no concrete data on population numbers, but the estimate is between 29,500 and 50,000 individuals. These apes are frugivores (fruit makes up half of their ...
Chapter 7: Animals and Infection Control
... Pets may enhance the experience of pupils in schools. However, some animals including exotic species such as reptiles, fish or birds that are often kept as pets can be a source of human infection. Infections that are passed from animals to humans are known as zoonoses. Some people such as pregnant w ...
... Pets may enhance the experience of pupils in schools. However, some animals including exotic species such as reptiles, fish or birds that are often kept as pets can be a source of human infection. Infections that are passed from animals to humans are known as zoonoses. Some people such as pregnant w ...
basics - Sakshi Education
... • Study of the set of morphological and anatomical features which are useful indentifying the organisms is called Identification • Naming of organisms is called - Nomenclature • Arrangement of organisms on the basis of their interrelationship- Classification Morphology : it is the study of the exter ...
... • Study of the set of morphological and anatomical features which are useful indentifying the organisms is called Identification • Naming of organisms is called - Nomenclature • Arrangement of organisms on the basis of their interrelationship- Classification Morphology : it is the study of the exter ...
document
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
DNA Technology - Loyalsock Township School District
... • Gametes –Produced by meiosis; haploid –Sperm small and flagellated –Egg large and nonmotile ...
... • Gametes –Produced by meiosis; haploid –Sperm small and flagellated –Egg large and nonmotile ...
Animal Body Systems
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
animals
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
Content Area: Zoology
... Explain how animals’ behavior (e.g., parental care, division of labor, niche, innate hive behavior in insects) may enhance the species' chances of survival ...
... Explain how animals’ behavior (e.g., parental care, division of labor, niche, innate hive behavior in insects) may enhance the species' chances of survival ...
Biology: Getting to know Idaho Reptiles ANSWER KEY
... 7. Of all the families in the family tree, which one is most closely related to Viperidae? Colubridae is the most related to Viperidae because they have the fewest number of branch points between each other according to the family tree. 8. What is the name of the only species of turtle found in Idah ...
... 7. Of all the families in the family tree, which one is most closely related to Viperidae? Colubridae is the most related to Viperidae because they have the fewest number of branch points between each other according to the family tree. 8. What is the name of the only species of turtle found in Idah ...
Animal Kingdom Webquest
... Why would this have been an evolutionary benefit? (http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20100414181920AAi7FdZ) ___________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ ...
... Why would this have been an evolutionary benefit? (http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20100414181920AAi7FdZ) ___________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ ...
Document
... d. a coelom that is not completely lined with mesoderm. e. a solid body without a cavity surrounding internal organs. 3. Which of the following subdivisions of the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? a. Protostomes b. Bilaterians c. Radians d. Eumetazoans (those with true tissues) ...
... d. a coelom that is not completely lined with mesoderm. e. a solid body without a cavity surrounding internal organs. 3. Which of the following subdivisions of the animal kingdom encompasses all the others in the list? a. Protostomes b. Bilaterians c. Radians d. Eumetazoans (those with true tissues) ...
p •ot - wwphs
... Animalia. Review those evolutionary branch points and then add the major phyla included in each group. Include common examples of animals in each phylum. ...
... Animalia. Review those evolutionary branch points and then add the major phyla included in each group. Include common examples of animals in each phylum. ...
Animal Kingdom
... 4. Simpler organisms may reproduce sexually and asexually. As complexity increases, organisms reproduce only sexually. ...
... 4. Simpler organisms may reproduce sexually and asexually. As complexity increases, organisms reproduce only sexually. ...
Kingdom Animalia - Corner Brook Regional High
... 4. Simpler organisms may reproduce sexually and asexually. As complexity increases, organisms reproduce only sexually. ...
... 4. Simpler organisms may reproduce sexually and asexually. As complexity increases, organisms reproduce only sexually. ...
evolutionary view
... ◦ If the organism carries a “small-scale model” of external reality and of its own possible actions within its head, it is able to try out various alternatives, conclude which are the best of them, react to future situations before they arise, utilize the knowledge of past events in dealing with the ...
... ◦ If the organism carries a “small-scale model” of external reality and of its own possible actions within its head, it is able to try out various alternatives, conclude which are the best of them, react to future situations before they arise, utilize the knowledge of past events in dealing with the ...
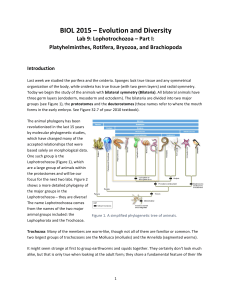
BIOL 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... their larvae hatch, each is a microscopic swimmer known as a trochophore larva. The larva has two bands of cilia around the middle that are used for swimming and for gathering food, and at the "top" is a cluster of longer flagellae. So the larvae of these groups are nearly identical, even though t ...
... their larvae hatch, each is a microscopic swimmer known as a trochophore larva. The larva has two bands of cilia around the middle that are used for swimming and for gathering food, and at the "top" is a cluster of longer flagellae. So the larvae of these groups are nearly identical, even though t ...
page 1 Chapter 7 Marine Animals without a Backbone CHAPTER
... (7) Molluscs have a circulatory system that transports nutrients and oxygen. Most molluscs have an open circulatory system in which blood flows out of vessels into open blood spaces. Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system. b) Nervous System and Behavior (1) Gastropods and bivalves do not have ...
... (7) Molluscs have a circulatory system that transports nutrients and oxygen. Most molluscs have an open circulatory system in which blood flows out of vessels into open blood spaces. Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system. b) Nervous System and Behavior (1) Gastropods and bivalves do not have ...