Flora and Fauna - Hotel Le Fontanelle
... they eat roots, nuts, and many other vegetable based foods, but also insects and small animals - they have even been known to eat small deer and lambs. Boars are known to be the only hoofed animals to dig burrows, which the female camouflages with twigs, leaves and other vegetation. A sow’s litter c ...
... they eat roots, nuts, and many other vegetable based foods, but also insects and small animals - they have even been known to eat small deer and lambs. Boars are known to be the only hoofed animals to dig burrows, which the female camouflages with twigs, leaves and other vegetation. A sow’s litter c ...
e1c15775504dd48
... Invertebrate Zoology Study of invertebrate animals Inverts make up at least 99% of all extant (living) ...
... Invertebrate Zoology Study of invertebrate animals Inverts make up at least 99% of all extant (living) ...
Sometimes Snakes - Indiana County Parks and Trails
... most frequently find while searching for salamanders. This small, non-venomous snake is found in and around salamander habitat since salamanders are its primary food source. The distinctive yellow-orange band around its neck is easy to pick out. When I find NorthernRingnecked snakes it seems that th ...
... most frequently find while searching for salamanders. This small, non-venomous snake is found in and around salamander habitat since salamanders are its primary food source. The distinctive yellow-orange band around its neck is easy to pick out. When I find NorthernRingnecked snakes it seems that th ...
Animals - Johnston Community College
... The fluid-filled interior forms a hydrostatic skeleton. Most species of roundworms have separate males and females. ...
... The fluid-filled interior forms a hydrostatic skeleton. Most species of roundworms have separate males and females. ...
You`re Such an Animal!
... Multicellular heterotrophs – take in food, digest it, distribute nutrients to cells Eukaryotes, cells lack cell walls Maintain homeostasis Divided into 2 groups: invertebrates and chordates Characteristics of Animals ...
... Multicellular heterotrophs – take in food, digest it, distribute nutrients to cells Eukaryotes, cells lack cell walls Maintain homeostasis Divided into 2 groups: invertebrates and chordates Characteristics of Animals ...
Outline of: Bryja, J., Patzenhauerova, H., Albrecht, T., Mosansky, L
... compared with each other to see which had higher rates of promiscuity and testes size, yet the results are never discussed in relation to the environment each sub species came from. For example, A. uralensis was found to be the least promiscuous. But what is it about their environment that makes the ...
... compared with each other to see which had higher rates of promiscuity and testes size, yet the results are never discussed in relation to the environment each sub species came from. For example, A. uralensis was found to be the least promiscuous. But what is it about their environment that makes the ...
introduction to foraging and environmental
... food based enrichment to stimulate the sense of taste by offering a variety of foods in a variety of shapes, sizes, and textures. Novel object enrichment is the use of items not normally found in the animal’s natural habitat. For example, small pieces of PVC pipe and baby toys can provide EE for gui ...
... food based enrichment to stimulate the sense of taste by offering a variety of foods in a variety of shapes, sizes, and textures. Novel object enrichment is the use of items not normally found in the animal’s natural habitat. For example, small pieces of PVC pipe and baby toys can provide EE for gui ...
Reptiles - Raise Your Confidence on Husbandry and Health
... animal’s needs. Arboreal reptiles like the iguana and chameleon need branches and foliage while terrestrial animals like tortoises and geckos need shelters. Secretive animals like the royal python need hidey holes as they like to eat in dark privacy. It is essential that tanks for snakes are secured ...
... animal’s needs. Arboreal reptiles like the iguana and chameleon need branches and foliage while terrestrial animals like tortoises and geckos need shelters. Secretive animals like the royal python need hidey holes as they like to eat in dark privacy. It is essential that tanks for snakes are secured ...
19 EVOLUTION OF THE ANIMAL PHYLA
... A. General Characteristics of Chordates 1. The chordates are deuterostome coelomates that developed after the echinoderms and possess an even more advanced endoskeleton. 2. Chordates have a dorsal notochord that allows for back and forth swimming motions. 3. A nerve cord follows this notochord and b ...
... A. General Characteristics of Chordates 1. The chordates are deuterostome coelomates that developed after the echinoderms and possess an even more advanced endoskeleton. 2. Chordates have a dorsal notochord that allows for back and forth swimming motions. 3. A nerve cord follows this notochord and b ...
Amazing Adaptations! - The Living Rainforest
... Sometimes however it rains very hard in the rainforests. Why can this be problem for plants? ...
... Sometimes however it rains very hard in the rainforests. Why can this be problem for plants? ...
Pseudocoelomate animals
... organs are held in place loosely, they are not as well organized as in a eucoelomate. (true coelomate) ...
... organs are held in place loosely, they are not as well organized as in a eucoelomate. (true coelomate) ...
Chapter 26: Animals – The Invertebrates
... Look like bells or upside-down saucers Mouth centered under bell May have extensions to help with feeding and capture prey Polyps Tubelike body with a tentacle-fringed mouth at one end Other end attached to substrate Epithelium – a tissue having a free surface that faces the environmen ...
... Look like bells or upside-down saucers Mouth centered under bell May have extensions to help with feeding and capture prey Polyps Tubelike body with a tentacle-fringed mouth at one end Other end attached to substrate Epithelium – a tissue having a free surface that faces the environmen ...
Evolution of functional morphology
... What is an Animal? 1. We often think of mammals or any vertebrate (= backbone), but these represent only a small fraction of the animal kingdom. 2. Although nearly 1.5 million species of animals have been described, 95% of them are invertebrates - animals without backbones. A. The characteristics sh ...
... What is an Animal? 1. We often think of mammals or any vertebrate (= backbone), but these represent only a small fraction of the animal kingdom. 2. Although nearly 1.5 million species of animals have been described, 95% of them are invertebrates - animals without backbones. A. The characteristics sh ...
Are animals smart? Things we can learn from animals.
... ■ Evidence suggests NOT necessarily random ■ Set of similar characteristics that most superstitious behaviors share – Responses are almost innate responses or previously learned responses – Responses are related to the Reinforcer ■ Looks like biology may be important! ...
... ■ Evidence suggests NOT necessarily random ■ Set of similar characteristics that most superstitious behaviors share – Responses are almost innate responses or previously learned responses – Responses are related to the Reinforcer ■ Looks like biology may be important! ...
Section 25.1 Summary – pages 673
... • The two cells that result from cleavage then divide to form four cells and so on, until a cell-covered, fluid-filled ball called a blastula is formed. • The blastula is formed early in the development of an animal ...
... • The two cells that result from cleavage then divide to form four cells and so on, until a cell-covered, fluid-filled ball called a blastula is formed. • The blastula is formed early in the development of an animal ...
File - Ms. Cash Science
... Coral What do they eat? * Tiny animals called zooplankton * Some catch larger food such as fish * They also get energy from special algae that live inside their body ...
... Coral What do they eat? * Tiny animals called zooplankton * Some catch larger food such as fish * They also get energy from special algae that live inside their body ...
Chapter 4 The Chemical Basis of Life
... Definition: specialized cell in cnidarians that functions in defense and capturing prey The tentacles of a hydra are armed with numerous cnidocytes and each cnidocyte holds a stinging capsule called a nematocyst when triggered by touch, the fine, coiled tubule within the nematocyst shoots out to ...
... Definition: specialized cell in cnidarians that functions in defense and capturing prey The tentacles of a hydra are armed with numerous cnidocytes and each cnidocyte holds a stinging capsule called a nematocyst when triggered by touch, the fine, coiled tubule within the nematocyst shoots out to ...
to the PDF file
... 1> Troop - Did you know that apes are considered to be the most intelligent of all the animals on earth? 2> Mess - Iguanas can stay underwater for approximately 28 minutes! 3> Owls - A herd is the collective noun for both Giraffes and Ibexes! Owls, however, are called a parliament! 4> Wolves - Wolve ...
... 1> Troop - Did you know that apes are considered to be the most intelligent of all the animals on earth? 2> Mess - Iguanas can stay underwater for approximately 28 minutes! 3> Owls - A herd is the collective noun for both Giraffes and Ibexes! Owls, however, are called a parliament! 4> Wolves - Wolve ...
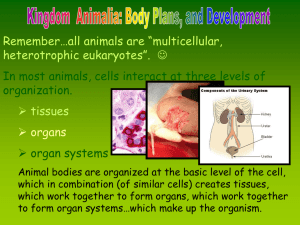
25.2 Animal Body Plans and Evolution
... Features of Body Plans Each animal phylum has a unique organization of body structures called its “body plan.” The features of a body plan include ▶ levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ▶ body symmetry: • radial symmetry: body parts extend from a central point • bilateral sy ...
... Features of Body Plans Each animal phylum has a unique organization of body structures called its “body plan.” The features of a body plan include ▶ levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ▶ body symmetry: • radial symmetry: body parts extend from a central point • bilateral sy ...
25.2 Animal Body Plans and Evolution
... Features of Body Plans Each animal phylum has a unique organization of body structures called its “body plan.” The features of a body plan include ▶ levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ▶ body symmetry: • radial symmetry: body parts extend from a central point • bilateral sy ...
... Features of Body Plans Each animal phylum has a unique organization of body structures called its “body plan.” The features of a body plan include ▶ levels of organization: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems ▶ body symmetry: • radial symmetry: body parts extend from a central point • bilateral sy ...
2 Notes (Phylogeny II)
... Name for the gastrulation pattern shown by certain types of animals, including humans. Anatomical name referring to an animal’s head. Term for an animal that has only two tissue types (ectoderm and endoderm). A pattern of development where the blastopore becomes the mouth in the adult animal. A ball ...
... Name for the gastrulation pattern shown by certain types of animals, including humans. Anatomical name referring to an animal’s head. Term for an animal that has only two tissue types (ectoderm and endoderm). A pattern of development where the blastopore becomes the mouth in the adult animal. A ball ...
Ch. 17 (word) - Ltcconline.net
... 1). have shells divided into 2 halves, hinged together 2). sedentary, live in sand or mud 3). muscular foot used for digging/anchoring 4). mucus coated gills to trap fine food particles 5). scallop - many eyes around mantle edges. can clap its shell shut and squirt water from its mantle cavity, jett ...
... 1). have shells divided into 2 halves, hinged together 2). sedentary, live in sand or mud 3). muscular foot used for digging/anchoring 4). mucus coated gills to trap fine food particles 5). scallop - many eyes around mantle edges. can clap its shell shut and squirt water from its mantle cavity, jett ...