Organizing Life`s Diversity
... nested-hierarchal system. Each category is contained within another, and they are arranged from broadest to most specific. ...
... nested-hierarchal system. Each category is contained within another, and they are arranged from broadest to most specific. ...
Dipsas trinitatis (Trinidad Snail-eating Snake)
... BEHAVIOUR. Snakes that are arboreal such as Dipsas trinitatis, often use immobility to avoid detection by any predators. Dipsas trinitatis has been known to mimic the venomous to Bothrops atrox perhaps in an effort to defend against its predators. Other methods used by Dipsadidae can also include th ...
... BEHAVIOUR. Snakes that are arboreal such as Dipsas trinitatis, often use immobility to avoid detection by any predators. Dipsas trinitatis has been known to mimic the venomous to Bothrops atrox perhaps in an effort to defend against its predators. Other methods used by Dipsadidae can also include th ...
Class - askIITians
... Ammoniotelic animals – These animals excrete ammonia. They include most aquatic invertebrates (Hydra) and some aquatic vertebrates (bony fishes, tailed amphibians). Ureotelic animals – These animals excrete urea. They include cartilaginous fishes (sharks, rays), tail-less amphibians (frog, toad) and ...
... Ammoniotelic animals – These animals excrete ammonia. They include most aquatic invertebrates (Hydra) and some aquatic vertebrates (bony fishes, tailed amphibians). Ureotelic animals – These animals excrete urea. They include cartilaginous fishes (sharks, rays), tail-less amphibians (frog, toad) and ...
Characteristics to Classify Animals
... posterior), front and back (dorsal vs. ventral), and right and left sides 2 equal halves(not always mirror image) through only ONE vertical plane For animals that swim, creep, run or move forward Bilateral symmetry enables effective movement in purposeful and intentional directions for the anima ...
... posterior), front and back (dorsal vs. ventral), and right and left sides 2 equal halves(not always mirror image) through only ONE vertical plane For animals that swim, creep, run or move forward Bilateral symmetry enables effective movement in purposeful and intentional directions for the anima ...
An Introduction to Invertebrates I Chapter 33A: 1. Porifera 2. Cnidaria
... called a proctostome (“anal mouth”) through which food enters the ...
... called a proctostome (“anal mouth”) through which food enters the ...
Chapter 31 - Mr. Krall
... is correct? A. Protostomes are animals in which the mouth develops from the blastopore. The anus or anal pore of protostomes develops from the second opening. Deuterostomes are animals in which the anus develops from the blastopore and the mouth develops secondarily later in their development. B. Pr ...
... is correct? A. Protostomes are animals in which the mouth develops from the blastopore. The anus or anal pore of protostomes develops from the second opening. Deuterostomes are animals in which the anus develops from the blastopore and the mouth develops secondarily later in their development. B. Pr ...
Chapter 33
... 7) Excretory system consists of protonephridia with flame cells. 8) Some species consist only of females that produce more females from unfertilized eggs in what is called parthenogenesis. Other species produce two kinds of eggs, one kind develops, diploid, into females; the other kind of egg is hap ...
... 7) Excretory system consists of protonephridia with flame cells. 8) Some species consist only of females that produce more females from unfertilized eggs in what is called parthenogenesis. Other species produce two kinds of eggs, one kind develops, diploid, into females; the other kind of egg is hap ...
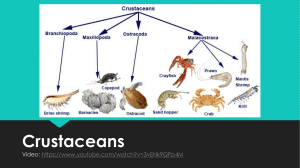
Crustaceans - Denton ISD
... Females lay the eggs and crawls into a hiding place to protect them When the eggs hatch, they stay stuck to the mother’s tail until ready to swim of their own ...
... Females lay the eggs and crawls into a hiding place to protect them When the eggs hatch, they stay stuck to the mother’s tail until ready to swim of their own ...
1 Name: ______ __ Date: ______ Block: ______ Classification
... percent of all animals are classified into eight of them. To get even more specific, seven of the eight phyla are invertebrates. Invertebrates comprise most of the animal kingdom, with almost 75 percent of all animals on earth being insects. They out number humans by a million to one! From Phylum, a ...
... percent of all animals are classified into eight of them. To get even more specific, seven of the eight phyla are invertebrates. Invertebrates comprise most of the animal kingdom, with almost 75 percent of all animals on earth being insects. They out number humans by a million to one! From Phylum, a ...
Mini-beasts and microhabitats
... 3. Gather a few handfuls of leaves and put them in the tray. 4. Gentle search in the leaves for mini-beasts such as: centipedes, woodlouse and beetles. 5. To search under decaying logs, make sure the log is carefully rolled to reveal the mini-beasts underneath. 6. Remember to return any mini-beasts ...
... 3. Gather a few handfuls of leaves and put them in the tray. 4. Gentle search in the leaves for mini-beasts such as: centipedes, woodlouse and beetles. 5. To search under decaying logs, make sure the log is carefully rolled to reveal the mini-beasts underneath. 6. Remember to return any mini-beasts ...
CHEETAH FACTS - Cheetah Conservation Fund
... leopards, lions, hyaenas and baboons. By 18 months of age, the mother leaves the cubs, which then form a sibling group staying together for another 6 months. At about 2 years, the female siblings l ...
... leopards, lions, hyaenas and baboons. By 18 months of age, the mother leaves the cubs, which then form a sibling group staying together for another 6 months. At about 2 years, the female siblings l ...
cheetah facts - Cheetah Conservation Fund
... leopards, lions, hyenas and baboons. By 18 months of age, the mother leaves the cubs, which then form a sibling group, staying together for another 6 months. At about 2 years, the female siblings leave the group, and the young males remain together for life. Males live alone or in coalitions made up ...
... leopards, lions, hyenas and baboons. By 18 months of age, the mother leaves the cubs, which then form a sibling group, staying together for another 6 months. At about 2 years, the female siblings leave the group, and the young males remain together for life. Males live alone or in coalitions made up ...
Document
... Animals respond to their environment using: Receptor cells = sound, light, external stimuli Nerve cells => nervous system ...
... Animals respond to their environment using: Receptor cells = sound, light, external stimuli Nerve cells => nervous system ...
Detailed information about common Alaska marine invertebrates.
... plankton until they molt several times, change form, and settle to the sea floor to become adults. The female crab’s abdominal flap is broader and larger than that of the male, because it covers and protects the eggs she carries for much of the year. Shrimps are not common intertidally in Alaska, bu ...
... plankton until they molt several times, change form, and settle to the sea floor to become adults. The female crab’s abdominal flap is broader and larger than that of the male, because it covers and protects the eggs she carries for much of the year. Shrimps are not common intertidally in Alaska, bu ...
Eight-cell stage
... - Only 1 central axis cut provides a mirror image - Has top, bottom, left & right - Triploblastic – 3 cell layers - Ectoderm & endoderm - Mesoderm – in between ecto- & endoderm - Cephalization – movement of sensory equipment towards the anterior end of the organism – associated with movement ...
... - Only 1 central axis cut provides a mirror image - Has top, bottom, left & right - Triploblastic – 3 cell layers - Ectoderm & endoderm - Mesoderm – in between ecto- & endoderm - Cephalization – movement of sensory equipment towards the anterior end of the organism – associated with movement ...
You`ve probably heard of stick insects, but did you know these
... I imagine that many escaped my view. But tonight I spot one under a pepper leaf. It’s just hatched from its egg and is one of the commoner species on the island, Metriophasma diocles – the subject of my scientific studies. This species is a good example of why phasmids play hide-and-seek. They face ...
... I imagine that many escaped my view. But tonight I spot one under a pepper leaf. It’s just hatched from its egg and is one of the commoner species on the island, Metriophasma diocles – the subject of my scientific studies. This species is a good example of why phasmids play hide-and-seek. They face ...
tissues
... Cells make up separate tissues. Tissues make up separate organs. And organs make up separate organ systems. ...
... Cells make up separate tissues. Tissues make up separate organs. And organs make up separate organ systems. ...
Anim Overview key
... Some animals are sessile which means they live their entire adult lives attached to one spot, but many animals are motile, which means that they move around. •To move, most animals use tissues called musclesthat generate force by contraction. •In the most successful groups of animals, muscles work ...
... Some animals are sessile which means they live their entire adult lives attached to one spot, but many animals are motile, which means that they move around. •To move, most animals use tissues called musclesthat generate force by contraction. •In the most successful groups of animals, muscles work ...
BSc_ ZOOA_Part-I
... -Torsions in Gastropods (Pechenik, p217-218) -Cyclomorphosis in Rotifers (Pechenik, p194-195) -Excretion in invertebrates with special reference to flame cells, nephridia, coelomoducts and malpighian tubules (in chapters on Platyhelminths, Annelids, Arthropods in Rupert et al. and in Pechenik) -Gas ...
... -Torsions in Gastropods (Pechenik, p217-218) -Cyclomorphosis in Rotifers (Pechenik, p194-195) -Excretion in invertebrates with special reference to flame cells, nephridia, coelomoducts and malpighian tubules (in chapters on Platyhelminths, Annelids, Arthropods in Rupert et al. and in Pechenik) -Gas ...
Chapter 33 PowerPoint
... • Have an excretory and osmoregulatory system – Network of fine tubules runs through body – Flame cells located on the side branches • Flagella move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then to pores located between the epidermal cells through which the liquid is expelled ...
... • Have an excretory and osmoregulatory system – Network of fine tubules runs through body – Flame cells located on the side branches • Flagella move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then to pores located between the epidermal cells through which the liquid is expelled ...
animal evolution
... Fossils from the Ediacara Hills of Australia (565 to 543 million years ago) and other sites around the world consist primarily of cnidarians, but soft-bodied mollusks were also present, and numerous fossilized burrows and tracks indicate the presence of worms. ...
... Fossils from the Ediacara Hills of Australia (565 to 543 million years ago) and other sites around the world consist primarily of cnidarians, but soft-bodied mollusks were also present, and numerous fossilized burrows and tracks indicate the presence of worms. ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
... Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
What Our Common Native Critters Eat
... somewhat for Hill Country conditions. This does not mean that any of the critters above won’t also take advantage of things humans put out, including pet food, deer food, and bird food. With the exception of feeding birds, most all wildlife specialists advise against putting out food for the other a ...
... somewhat for Hill Country conditions. This does not mean that any of the critters above won’t also take advantage of things humans put out, including pet food, deer food, and bird food. With the exception of feeding birds, most all wildlife specialists advise against putting out food for the other a ...