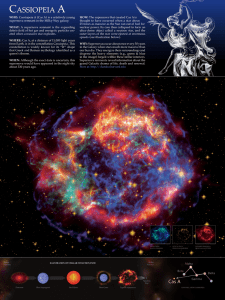
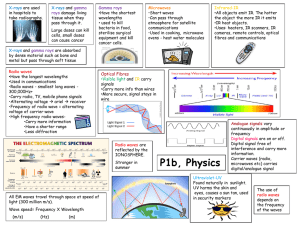
Astronomy Test Objective 1: Origins of the Universe Multiple Choice
... b. end up with a smaller mass. c. continue to fuse iron in its core. d. become a neutron star. Matching Match each item with the correct phrase below. a. black hole b. fusion c. main sequence d. nebula e. spectrum 4. Combining of lightweight nuclei into heavier nuclei, such as four hydrogen nuclei c ...
... b. end up with a smaller mass. c. continue to fuse iron in its core. d. become a neutron star. Matching Match each item with the correct phrase below. a. black hole b. fusion c. main sequence d. nebula e. spectrum 4. Combining of lightweight nuclei into heavier nuclei, such as four hydrogen nuclei c ...
Stars presentation by lauren
... brighter than our sun! It is over 45,000 light years away from Earth, and is at least 150 times bigger than the sun! ...
... brighter than our sun! It is over 45,000 light years away from Earth, and is at least 150 times bigger than the sun! ...
Stellar Evolution
... that supernova produce a neutron star. All that mass would be squished down to a tiny size from the enormous gravity, becoming very dense. 1 cm3 of it would weigh 10 million tons. Spinning neutron stars are called pulsars. ...
... that supernova produce a neutron star. All that mass would be squished down to a tiny size from the enormous gravity, becoming very dense. 1 cm3 of it would weigh 10 million tons. Spinning neutron stars are called pulsars. ...
BAS - Monthly Sky Guide
... Ophiuchus translates to “he who holds the serpent”. The adjoining constellation Serpens is the snake that Ophiuchus is carrying. ...
... Ophiuchus translates to “he who holds the serpent”. The adjoining constellation Serpens is the snake that Ophiuchus is carrying. ...
ASTRONOMY - Frost Middle School
... distributed throughout the universe to form galaxies • The mutual attraction between galaxies caused galaxies to cluster • Even though the distances between galaxy clusters are very large, gravity still acts between them • Because gravity acts over such great distances, gravity controls the size and ...
... distributed throughout the universe to form galaxies • The mutual attraction between galaxies caused galaxies to cluster • Even though the distances between galaxy clusters are very large, gravity still acts between them • Because gravity acts over such great distances, gravity controls the size and ...
Energy Levels in Atoms
... The spectra from two different atoms are observed. A spectral line in the first atom has exactly one-half the wavelength of a spectral line in the second atom. Which of the below is TRUE? • The spacing between 2 levels in the first atom must be twice the spacing between 2 levels in the second atom. ...
... The spectra from two different atoms are observed. A spectral line in the first atom has exactly one-half the wavelength of a spectral line in the second atom. Which of the below is TRUE? • The spacing between 2 levels in the first atom must be twice the spacing between 2 levels in the second atom. ...
More stellar evolution…bloated stars and compact cores
... We know the white dwarfs must have the properties as described (we’re not making this up) • We know the mass of Sirius B (1.02 versus 2.40 solar masses for Sirius A) • Even though it is hotter than Sirius A, it is much fainter (look at difference in absolute magnitudes • The only way to do this is ...
... We know the white dwarfs must have the properties as described (we’re not making this up) • We know the mass of Sirius B (1.02 versus 2.40 solar masses for Sirius A) • Even though it is hotter than Sirius A, it is much fainter (look at difference in absolute magnitudes • The only way to do this is ...
Distances in space ppt
... A Light Year is a standard unit of measurement for interstellar distances beyond the solar system. Milky Way Galaxy is approx. 100,000 LY across in distance ...
... A Light Year is a standard unit of measurement for interstellar distances beyond the solar system. Milky Way Galaxy is approx. 100,000 LY across in distance ...
Distances in Space Vocabulary
... A Light Year is a standard unit of measurement for interstellar distances beyond the solar system. Milky Way Galaxy is approx. 100,000 LY across in distance ...
... A Light Year is a standard unit of measurement for interstellar distances beyond the solar system. Milky Way Galaxy is approx. 100,000 LY across in distance ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Faulkes Telescope Project
... The life span of a star depends on its initial size. Smaller stars will exist for billions of years as they burn their fuel very slowly. When a star begins to run out of fuel, it expands into a Red Giant and will exist in this phase until the rest of its fuel is gone. At this point, the outward pres ...
... The life span of a star depends on its initial size. Smaller stars will exist for billions of years as they burn their fuel very slowly. When a star begins to run out of fuel, it expands into a Red Giant and will exist in this phase until the rest of its fuel is gone. At this point, the outward pres ...
Stars Answers - Science Skool!
... the elements throughout space. The core left behind forms a neutron star or black hole if sufficient mass is left behind 9. Why do scientists believe the Solar System was formed from the material produced when earlier stars exploded? Solar System contains elements heavier than hydrogen and helium wh ...
... the elements throughout space. The core left behind forms a neutron star or black hole if sufficient mass is left behind 9. Why do scientists believe the Solar System was formed from the material produced when earlier stars exploded? Solar System contains elements heavier than hydrogen and helium wh ...
The Lives of Stars
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
No Slide Title
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
4B-Astronomer-Notes
... He made important contributions by devising the most precise instruments available before the invention of the telescope for observing the heavens He charted over 1000 stars in the sky. His observations of planetary motion, particularly that of Mars, provided the crucial data for later astronomers l ...
... He made important contributions by devising the most precise instruments available before the invention of the telescope for observing the heavens He charted over 1000 stars in the sky. His observations of planetary motion, particularly that of Mars, provided the crucial data for later astronomers l ...
File
... few cm of air Beta Radiation– Stopped by thin aluminium or about 1m of air Gamma radiation- Stopped by thick lead or concrete and has an unlimited range in air ...
... few cm of air Beta Radiation– Stopped by thin aluminium or about 1m of air Gamma radiation- Stopped by thick lead or concrete and has an unlimited range in air ...
Elec Structure of Atom
... The lowest energy level is achieved in the ground state where n=1. Other n values correspond to excited states. Light is emitted when the electron drops from a high energy state to a low energy state; light can be absorbed to excite the electron from a low energy state to a high energy state. The fr ...
... The lowest energy level is achieved in the ground state where n=1. Other n values correspond to excited states. Light is emitted when the electron drops from a high energy state to a low energy state; light can be absorbed to excite the electron from a low energy state to a high energy state. The fr ...
Mark scheme for Support Worksheet – Topic E, Worksheet 1
... A and B have the same luminosity and A has a higher temperature; from L AT 4 B must then have the larger surface area and hence larger radius. ...
... A and B have the same luminosity and A has a higher temperature; from L AT 4 B must then have the larger surface area and hence larger radius. ...
Cosmology - RHIG - Wayne State University
... The stars and gas in most galaxies move much quicker than expected from the luminosity of the galaxies. In spiral galaxies, the rotation curve remains at about the same value at great distances from the center (it is said to be ``flat''). This means that the enclosed mass continues to increase even ...
... The stars and gas in most galaxies move much quicker than expected from the luminosity of the galaxies. In spiral galaxies, the rotation curve remains at about the same value at great distances from the center (it is said to be ``flat''). This means that the enclosed mass continues to increase even ...
Review for Midterm—Chapter 1
... • Temperature – relation to the motions of a large collection of particles • Thermal radiation – Relationship between apparent color and temperature – How do we measure temperature of distant objects? • Particle and wave properties of light – Photons: energy per photon – Waves: wavelength, frequency ...
... • Temperature – relation to the motions of a large collection of particles • Thermal radiation – Relationship between apparent color and temperature – How do we measure temperature of distant objects? • Particle and wave properties of light – Photons: energy per photon – Waves: wavelength, frequency ...
PH607lec12-10agn2
... strong radio, highly variable, mainly ellipticals OVV quasars: powerful BL Lacs but with emission lines Radio Galaxies BLRG: Broad/narrow lines, strong radio emission, FR II, weak polarisation, elliptical variable, variable Radio Galaxies NLRG: narrow lines only, strong radio, FR I/II, no polarisati ...
... strong radio, highly variable, mainly ellipticals OVV quasars: powerful BL Lacs but with emission lines Radio Galaxies BLRG: Broad/narrow lines, strong radio emission, FR II, weak polarisation, elliptical variable, variable Radio Galaxies NLRG: narrow lines only, strong radio, FR I/II, no polarisati ...
Lecture 5, Infrared Astronomy
... - transparency of dust to IR radiation, longer wavelengths not scattered like visible radiation • Cool objects - small cool stars, red giants, brown dwarfs - planets, comets, asteroids - nebulae, interstellar dust, protoplanetary disks Cool stars energy peak ~ 1µm Giant planets ~ 6-15µm Dust re-radi ...
... - transparency of dust to IR radiation, longer wavelengths not scattered like visible radiation • Cool objects - small cool stars, red giants, brown dwarfs - planets, comets, asteroids - nebulae, interstellar dust, protoplanetary disks Cool stars energy peak ~ 1µm Giant planets ~ 6-15µm Dust re-radi ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.