The Milky Way Galaxy
... Shapley found the distance to the globulars and plotted their positions He found: ...
... Shapley found the distance to the globulars and plotted their positions He found: ...
5. Electromagnetic Waves – Tutorial 5
... In 1926, Albert Michelson measured the speed of light with a technique similar to that used by Fizeau. Michelson used an eight-sided mirror rotating at 528 rev/s in place of the toothed wheel, as illustrated in Figure 5.8. The distance from the rotating mirror to a distant reflector was 35.5 km. If ...
... In 1926, Albert Michelson measured the speed of light with a technique similar to that used by Fizeau. Michelson used an eight-sided mirror rotating at 528 rev/s in place of the toothed wheel, as illustrated in Figure 5.8. The distance from the rotating mirror to a distant reflector was 35.5 km. If ...
Document
... So all objects are moving away from us Are we at the center of the universe? Raisin bread model Hubble constant - rate of recession/distance The further away galaxies are, the faster they are receding – This means the universe is expanding exponentially! ...
... So all objects are moving away from us Are we at the center of the universe? Raisin bread model Hubble constant - rate of recession/distance The further away galaxies are, the faster they are receding – This means the universe is expanding exponentially! ...
Solar Cells
... Speed of light c= frequency (f)* wavelength (l) c=f l =3 ×108 m/s Frequency f: # of cycles per second that pass a given point Wavelength l : Length of a single cycle of the wave Good website on EM waves ...
... Speed of light c= frequency (f)* wavelength (l) c=f l =3 ×108 m/s Frequency f: # of cycles per second that pass a given point Wavelength l : Length of a single cycle of the wave Good website on EM waves ...
Origin of the Universe
... more massive than our Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstellar space where they enrich clouds of Hydrogen and Helium that are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead ...
... more massive than our Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstellar space where they enrich clouds of Hydrogen and Helium that are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead ...
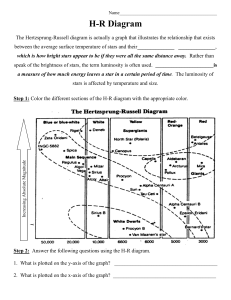
AnwerkeyTypes-of-stars-and-HR-diagram
... 2. How does surface temperature of White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors fro ...
... 2. How does surface temperature of White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors fro ...
June - San Bernardino Valley Amateur Astronomers
... nursery, a giant patch of gas, dust and young stars that is the most active star-forming region in the Local Group of galaxies we call home. Researchers calculated it was far more luminous than before thought, ranking among the brightest stars known. This super-bright star is also extraordinarily ho ...
... nursery, a giant patch of gas, dust and young stars that is the most active star-forming region in the Local Group of galaxies we call home. Researchers calculated it was far more luminous than before thought, ranking among the brightest stars known. This super-bright star is also extraordinarily ho ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... 1. How can one measure the mass of a star other than the Sun? (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnitude of a star tells its mass (c) the gravitational force on a companion star in a double star (d) the mass of a star is determined by its locat ...
... 1. How can one measure the mass of a star other than the Sun? (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnitude of a star tells its mass (c) the gravitational force on a companion star in a double star (d) the mass of a star is determined by its locat ...
Define density as the mass of an object divided by its volume
... 5. Atomic mass units (AMUs) are used to measure what types of particles? 6. How many neutrons are in sodium-24? 7. What process causes light to be emitted from an atom? 8. What happens to white light when it passes through a prism? 9. What property or properties are different between the different c ...
... 5. Atomic mass units (AMUs) are used to measure what types of particles? 6. How many neutrons are in sodium-24? 7. What process causes light to be emitted from an atom? 8. What happens to white light when it passes through a prism? 9. What property or properties are different between the different c ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 4. What happens that similates the birth of a star? 5. Explain what happens in nuclear fusion? 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature wh ...
... 4. What happens that similates the birth of a star? 5. Explain what happens in nuclear fusion? 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature wh ...
1 milles million 93 km810 1.496 1AU = × = 63,240AU ly1 km 12 10
... Planet is a cosmic object of significant size that orbits a star and does not produce its own light. We can see the nearby planets because they reflect the light of the Sun. The Earth is one of nine planets that revolve around the Sun. These planets, along with their satellites and other small bodie ...
... Planet is a cosmic object of significant size that orbits a star and does not produce its own light. We can see the nearby planets because they reflect the light of the Sun. The Earth is one of nine planets that revolve around the Sun. These planets, along with their satellites and other small bodie ...
Homework 2: Due 2/02/2010
... 4. Extra Credit (4pts). You want to detect the following objects, all of which emit (approximately) black body spectrum. At what wavelength should you look to maximize the flux you receive from the object? a. A star like the Sun with a temperature of 6000 K b. A planet like the Earth with a tempera ...
... 4. Extra Credit (4pts). You want to detect the following objects, all of which emit (approximately) black body spectrum. At what wavelength should you look to maximize the flux you receive from the object? a. A star like the Sun with a temperature of 6000 K b. A planet like the Earth with a tempera ...
Lecture Notes-PPT
... When stars are born they develop from large clouds of molecular gas. After the remnant gas is heated and blow away, the stars collect together by gravity. During the exchange of energy between the stars, some stars reach escape velocity from the protocluster and become runaway stars. The rest become ...
... When stars are born they develop from large clouds of molecular gas. After the remnant gas is heated and blow away, the stars collect together by gravity. During the exchange of energy between the stars, some stars reach escape velocity from the protocluster and become runaway stars. The rest become ...
Dark Matter: Inquiring Minds Want to Know ()
... • Einstein: Objects with “Energy” move according to the curve of space-time, regardless of whether they have mass or not ...
... • Einstein: Objects with “Energy” move according to the curve of space-time, regardless of whether they have mass or not ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.


![Dust [12.1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008843506_1-c0b3bc1292042697e2dbc020b2f06e1c-300x300.png)