I have heard people call Jupiter a "failed star" that just did not get big
... Stars form directly from the collapse of dense clouds of interstellar gas and dust. Because of rotation, these clouds form flattened disks that surround the central, growing stars. After the star has nearly reached its final mass, by accreting gas from the disk, the leftover matter in the disk is fr ...
... Stars form directly from the collapse of dense clouds of interstellar gas and dust. Because of rotation, these clouds form flattened disks that surround the central, growing stars. After the star has nearly reached its final mass, by accreting gas from the disk, the leftover matter in the disk is fr ...
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit-
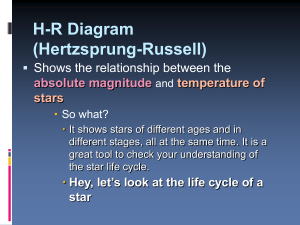
... The first stage is the Protostar. Once stable, it becomes a Main Sequence star. Upper left on the Sequence are the massive, hotter and more luminous Blue and White stars. The middle of the sequence has medium mass yellow (G) stars like our Sun. The lower section of the Main Sequence has smaller, coo ...
... The first stage is the Protostar. Once stable, it becomes a Main Sequence star. Upper left on the Sequence are the massive, hotter and more luminous Blue and White stars. The middle of the sequence has medium mass yellow (G) stars like our Sun. The lower section of the Main Sequence has smaller, coo ...
Content Clarification for Modeling the Universe: Earth and Space
... temperature, and age, but they appear to be made up of the same elements that are found on the earth and to behave according to the same physical principles. Unlike the sun, most stars are in systems of two or more stars orbiting around one another. • On the basis of scientific evidence, the univers ...
... temperature, and age, but they appear to be made up of the same elements that are found on the earth and to behave according to the same physical principles. Unlike the sun, most stars are in systems of two or more stars orbiting around one another. • On the basis of scientific evidence, the univers ...
The central star of the planetary nebula PB 8: a Wolf-Rayet
... Fig. 3. Contours of the ratio between the peak heights of N iv 7100 to N iii 4643. The thick contour represents the measured value. The open circles indicate the calculated models. Between these data points the contour lines are interpolated. The bestfitting model for PB 8 is indicated by the red sq ...
... Fig. 3. Contours of the ratio between the peak heights of N iv 7100 to N iii 4643. The thick contour represents the measured value. The open circles indicate the calculated models. Between these data points the contour lines are interpolated. The bestfitting model for PB 8 is indicated by the red sq ...
PPT
... This continues until Fe (iron created) Fusion stops (no more energy created) core collapses creating a supernova because of tremendous pressure, electrons join protons to become neutrons creates a neutron star no space between atoms; extremely dense ...
... This continues until Fe (iron created) Fusion stops (no more energy created) core collapses creating a supernova because of tremendous pressure, electrons join protons to become neutrons creates a neutron star no space between atoms; extremely dense ...
The Chemical Composition of the Local Interstellar Dust
... - metal column density via Wλ ~ N(X) fij σ(λ) - chemical homogeneity of gas-phase in solar neighbourhood from many sightlines: C, O, Mg, Si, S, Fe, Zr, Kr, ... ...
... - metal column density via Wλ ~ N(X) fij σ(λ) - chemical homogeneity of gas-phase in solar neighbourhood from many sightlines: C, O, Mg, Si, S, Fe, Zr, Kr, ... ...
Notes: 3.5 STAR EVOLUTION Name: ______ Star
... notes. Construct Ø All stars change into different STAGES or phases throughout their quiz questions life. using this Ø What a star ends as depends on its MASS. information. Write Ø A low mass star will evolve DIFFERENTLY than a high mass star. the questions next to the paragraph where the answers ...
... notes. Construct Ø All stars change into different STAGES or phases throughout their quiz questions life. using this Ø What a star ends as depends on its MASS. information. Write Ø A low mass star will evolve DIFFERENTLY than a high mass star. the questions next to the paragraph where the answers ...
sept2302
... orbital inclination not known, so we can only derive M sin(i) Are they really planetary-mass objects? HST can provide the precision astrometry required to determine i Positional residuals < 0.3 mas set upper limit of 30 MJ ...
... orbital inclination not known, so we can only derive M sin(i) Are they really planetary-mass objects? HST can provide the precision astrometry required to determine i Positional residuals < 0.3 mas set upper limit of 30 MJ ...
Chapter 7 - Colby College Wiki
... • Heinrich Hertz (1888) discovered that light striking the surface of certain metals causes ejection of electrons - the photoelectric effect. • Electrons were only ejected if the frequency of the light (v) was above a certain threshold frequency (vo) • The number of electrons ejected were proportion ...
... • Heinrich Hertz (1888) discovered that light striking the surface of certain metals causes ejection of electrons - the photoelectric effect. • Electrons were only ejected if the frequency of the light (v) was above a certain threshold frequency (vo) • The number of electrons ejected were proportion ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... image features roughly 65 meteors captured by the photographer between 12:30am and 4:30am. ...
... image features roughly 65 meteors captured by the photographer between 12:30am and 4:30am. ...
What Lies Beyond
... and Motions of the Stars Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light received from a celestial object This measure contrasts with luminosity – the rate at which electromagnetic energy is emitted from a celestial object Proper motion is the term for the angular velocity of a star as ...
... and Motions of the Stars Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light received from a celestial object This measure contrasts with luminosity – the rate at which electromagnetic energy is emitted from a celestial object Proper motion is the term for the angular velocity of a star as ...
5 Great Facts of Life - Westside Church of Christ
... Big Dipper, for example, are members of a nearby star cluster roughly 75 light-years away. Their light takes a human lifetime to reach Earth. Nestled between the constellations Perseus and Cassiopeia lies a twin cluster of stars-the Double Cluster. Their light travels for 7,000 years before it reach ...
... Big Dipper, for example, are members of a nearby star cluster roughly 75 light-years away. Their light takes a human lifetime to reach Earth. Nestled between the constellations Perseus and Cassiopeia lies a twin cluster of stars-the Double Cluster. Their light travels for 7,000 years before it reach ...
From galaxies to stars
... and the whole core compacts down to a ball of neutrons only 20 km across: a neutron star. Meanwhile, the outer layers of the star fall inwards until they hit the newborn neutron star. When they meet the core they “bounce” off it so hard that they are ejected outwards in blast wave which explodes the ...
... and the whole core compacts down to a ball of neutrons only 20 km across: a neutron star. Meanwhile, the outer layers of the star fall inwards until they hit the newborn neutron star. When they meet the core they “bounce” off it so hard that they are ejected outwards in blast wave which explodes the ...
CelestialSphere02
... Morning and Evening “Stars” We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
... Morning and Evening “Stars” We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
Lecture13 - University of Waterloo
... • 23 He is an intermediate species in the pp chain. It is most abundant at the top of the H-burning region, where the temperature is lower. • Abundances are homogeneous within the convective zone, since the plasma is effectively mixed ...
... • 23 He is an intermediate species in the pp chain. It is most abundant at the top of the H-burning region, where the temperature is lower. • Abundances are homogeneous within the convective zone, since the plasma is effectively mixed ...
Show Title Science Topic Science Topic Science Topic Grade Lower
... Show Title 0 PreK Sesame Street One World One Sky Amp’s Amazing Night Flight George & Oatmeal Save Santa 0.5 Kinder Wilbear’s Adventure Larry Cat in Space Solar System ...
... Show Title 0 PreK Sesame Street One World One Sky Amp’s Amazing Night Flight George & Oatmeal Save Santa 0.5 Kinder Wilbear’s Adventure Larry Cat in Space Solar System ...
Untitled
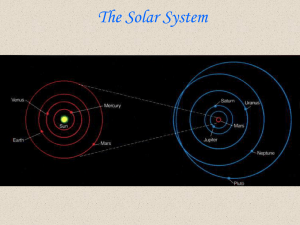
... constellation eastward each year. The Moon is left of Jupiter on the 10th. A small telescope shows Saturn as an oval, the rings and planet blended. Larger telescopes separate the planet and rings and may show Saturn's moons looking like faint stars close to the planet. Titan, one of the biggest moon ...
... constellation eastward each year. The Moon is left of Jupiter on the 10th. A small telescope shows Saturn as an oval, the rings and planet blended. Larger telescopes separate the planet and rings and may show Saturn's moons looking like faint stars close to the planet. Titan, one of the biggest moon ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 21. Galaxy Evolution
... • What are active galactic nuclei and quasars? • The nature of quasars was once hotly debated. What evidence supports the idea that they are the active galactic nuclei of ...
... • What are active galactic nuclei and quasars? • The nature of quasars was once hotly debated. What evidence supports the idea that they are the active galactic nuclei of ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.