AY2 - Overview of the Universe
... B) The composition of most stars (mostly hydrogen and helium) is about the same as the composition of our bodies. C) Nearly every atom from which we are made once (before the solar system formed) was inside of a star. D) Sagan thought that all of us have the potential to be movie (or TV) stars like ...
... B) The composition of most stars (mostly hydrogen and helium) is about the same as the composition of our bodies. C) Nearly every atom from which we are made once (before the solar system formed) was inside of a star. D) Sagan thought that all of us have the potential to be movie (or TV) stars like ...
EMS, HR, Star Lives classwork/homework
... 18. When a star begins to run out of fuel, what two types of stars can it become? 19. What happens to small and medium stars when they run out of fuel? ...
... 18. When a star begins to run out of fuel, what two types of stars can it become? 19. What happens to small and medium stars when they run out of fuel? ...
Cosmic Feedback from Supermassive Black Holes
... Every massive galaxy appears to have a massive black hole at its center whose mass is about 0.2% of the mass of the galaxy's bulge (Tremaine et al. 2002). It is now widely considered that the black hole may have brought about this correlation by regulating the amount of gas available for star format ...
... Every massive galaxy appears to have a massive black hole at its center whose mass is about 0.2% of the mass of the galaxy's bulge (Tremaine et al. 2002). It is now widely considered that the black hole may have brought about this correlation by regulating the amount of gas available for star format ...
here - York University
... Type of Stars • As discussed, stars like our Sun first targets. • In the Milky Way galaxy, stars with similar spectral types (F, G, K) constitutes 10% or more of all stars (30 billion or more). • Double, multiple, very luminous (and thus short lived) stars not suitable targets. • Specialization reg ...
... Type of Stars • As discussed, stars like our Sun first targets. • In the Milky Way galaxy, stars with similar spectral types (F, G, K) constitutes 10% or more of all stars (30 billion or more). • Double, multiple, very luminous (and thus short lived) stars not suitable targets. • Specialization reg ...
here
... it, we would expect large temperature fluctuations in the CMB, large density fluctuations all over the universe at early times, and for the universe to be much less smooth. 16: The luminosity changes by a factor of 100/0.0001 = 106 , but the temperature stays constant. Since the luminosity of a blac ...
... it, we would expect large temperature fluctuations in the CMB, large density fluctuations all over the universe at early times, and for the universe to be much less smooth. 16: The luminosity changes by a factor of 100/0.0001 = 106 , but the temperature stays constant. Since the luminosity of a blac ...
Study guide_2
... 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Trough c. Frequency d. Wavelength e. Amplitude 20. ...
... 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Trough c. Frequency d. Wavelength e. Amplitude 20. ...
Wednesday, April 23 - Otterbein University
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about 1.4 solar masses • Very predictable; used as a standard candle – Estimate distances to galaxies where they occur ...
... • Implosion of a white dwarf after it accretes a certain amount of matter, reaching about 1.4 solar masses • Very predictable; used as a standard candle – Estimate distances to galaxies where they occur ...
Geller Slides on Summary of Astrobiology
... A carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light and opaque to infrared radiation. B carbon dioxide is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to ultraviolet radiation. C ozone is transparent to ultraviolet radiation and opaque to infrared radiation. D methane is transparent to infrared radiati ...
... A carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light and opaque to infrared radiation. B carbon dioxide is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to ultraviolet radiation. C ozone is transparent to ultraviolet radiation and opaque to infrared radiation. D methane is transparent to infrared radiati ...
AST 1002
... Demonstrate the correct use of basic astronomical terms and their definitions. Describe the structure and orbital motion of the Earth, and explain why it leads to seasons and changes in the constellations of the night sky. Identify the fundamental types of astronomical telescopes. Describe how time ...
... Demonstrate the correct use of basic astronomical terms and their definitions. Describe the structure and orbital motion of the Earth, and explain why it leads to seasons and changes in the constellations of the night sky. Identify the fundamental types of astronomical telescopes. Describe how time ...
Astronomers Find The Most Distant Star Clusters Hidden Behind A
... discovered the most distant population of star clusters ever seen, hidden behind one of the nearest such clusters to Earth. At a distance of more than a billion lightyears, the newly discovered star clusters provide a unique probe of what similar systems in our own galaxy once looked like. See also: ...
... discovered the most distant population of star clusters ever seen, hidden behind one of the nearest such clusters to Earth. At a distance of more than a billion lightyears, the newly discovered star clusters provide a unique probe of what similar systems in our own galaxy once looked like. See also: ...
Test 1 Earth Science 1) According to the big bang timeline , as the
... small increase in the total numbers. Cellphones give off a form of radiation known as nonionizing radiation. The frequencies associated with this form of electromagnetic radiation are too low and the signal is too weak to be able to break biochemical bonds within body tissues and to be able to dama ...
... small increase in the total numbers. Cellphones give off a form of radiation known as nonionizing radiation. The frequencies associated with this form of electromagnetic radiation are too low and the signal is too weak to be able to break biochemical bonds within body tissues and to be able to dama ...
Black Holes - Troy University
... – 1 Big BH per galaxy (~ million-billion solar masses) – millions of little BHs per galaxy ( ~ solar mass) BHs are responsible for the most dramatic and energetic phenomena in the universe – BHs are “seen” via the light produced by infalling gas & the gravitational pull that they exert on nearby obj ...
... – 1 Big BH per galaxy (~ million-billion solar masses) – millions of little BHs per galaxy ( ~ solar mass) BHs are responsible for the most dramatic and energetic phenomena in the universe – BHs are “seen” via the light produced by infalling gas & the gravitational pull that they exert on nearby obj ...
Study Guide for Astronomy
... Corona – forms the sun’s outermost atmosphere Our sun is very average in size, temperature and color. It has been burning for approximately 4.6 billion years and scientists believe it will last about 10 million years total. Nuclear Fusion – developed by Einstein is signified by the equation E = mc2. ...
... Corona – forms the sun’s outermost atmosphere Our sun is very average in size, temperature and color. It has been burning for approximately 4.6 billion years and scientists believe it will last about 10 million years total. Nuclear Fusion – developed by Einstein is signified by the equation E = mc2. ...
chapter 17 measuring the stars
... Luminosity is an intrinsic property of a star – it does not depend in any way on the location or motion of the observer – it is sometimes referred to as the star’s absolute brightness. Absolute Brightness: How bright a star would appear if it were placed at a standard distance of 10 parsecs from E ...
... Luminosity is an intrinsic property of a star – it does not depend in any way on the location or motion of the observer – it is sometimes referred to as the star’s absolute brightness. Absolute Brightness: How bright a star would appear if it were placed at a standard distance of 10 parsecs from E ...
star
... temperature, color, and absolute brightness of a sample of stars. They are used to estimate the sizes of stars and their distances, and infer how stars change over time. If two stars a ...
... temperature, color, and absolute brightness of a sample of stars. They are used to estimate the sizes of stars and their distances, and infer how stars change over time. If two stars a ...
U7-Astronomy Note Packet
... -Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer during the late 1500’s to early 1600’s, developed three laws of motion of objects in the sky to help better explain and predict their motions. Before Kepler, most astronomers agreed that planetary orbits were circular. 1. Elliptical Orbits: _____________________ ...
... -Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer during the late 1500’s to early 1600’s, developed three laws of motion of objects in the sky to help better explain and predict their motions. Before Kepler, most astronomers agreed that planetary orbits were circular. 1. Elliptical Orbits: _____________________ ...
Comparing Earth, Sun and Jupiter
... Mostly Hydrogen and Helium High luminosity due to central fusion reactions Sunspots: cooler regions where magnetic field is strongest More features visible at other wavelengths Types of Stars Characterised mainly by their luminosity and colour Most stars lie on a tight correlation between L and colo ...
... Mostly Hydrogen and Helium High luminosity due to central fusion reactions Sunspots: cooler regions where magnetic field is strongest More features visible at other wavelengths Types of Stars Characterised mainly by their luminosity and colour Most stars lie on a tight correlation between L and colo ...
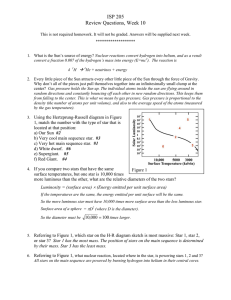
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
... Why don’t all of the pieces just pull themselves together into an infinitesimally small clump at the center? Gas pressure holds the Sun up. The individual atoms inside the sun are flying around in random directions and constantly bouncing off each other in new random directions. This keeps them from ...
... Why don’t all of the pieces just pull themselves together into an infinitesimally small clump at the center? Gas pressure holds the Sun up. The individual atoms inside the sun are flying around in random directions and constantly bouncing off each other in new random directions. This keeps them from ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... number of the current members of the committee have stated that they will not be standing for re-election this year. At the AGM all of the committee stand down and every position is up for grabs. Any fully paid up member of the society who is over the age of 18 can stand for election to the committe ...
... number of the current members of the committee have stated that they will not be standing for re-election this year. At the AGM all of the committee stand down and every position is up for grabs. Any fully paid up member of the society who is over the age of 18 can stand for election to the committe ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.