Nearly All the Clues Come From Light
... but most of the information we get at present come from LIGHT ...
... but most of the information we get at present come from LIGHT ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... 5) Suppose you measure the parallax angle for a particular star to be 0.01 arcsecond. The distance to this star is A) 100 light-years. B) 0.01 light-year. C) 0.01 parsec. D) 100 parsecs. E) impossible to determine. ...
... 5) Suppose you measure the parallax angle for a particular star to be 0.01 arcsecond. The distance to this star is A) 100 light-years. B) 0.01 light-year. C) 0.01 parsec. D) 100 parsecs. E) impossible to determine. ...
ppt document
... luminosity, but hotter tends to increase luminosity. The position of the newly forming star on the H-R diagram will move to the left as it heats up but wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time ...
... luminosity, but hotter tends to increase luminosity. The position of the newly forming star on the H-R diagram will move to the left as it heats up but wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time ...
Sky Science Review for Test Part A
... S.O. 4 – Understand that the Sun should never be viewed directly, nor by the use of simple telescopes or filters, and that safe viewing requires appropriate methods and safety precautions. Looking directly at the Sun causes damage to our eyes that cannot be repaired. It is also dangerous to look ...
... S.O. 4 – Understand that the Sun should never be viewed directly, nor by the use of simple telescopes or filters, and that safe viewing requires appropriate methods and safety precautions. Looking directly at the Sun causes damage to our eyes that cannot be repaired. It is also dangerous to look ...
No Slide Title
... Supernovae as Standard Candles • The brightest supernovae reach M = -19 at the peak of their output. In theory they can be seen up to 8000 Mly from Earth. This makes them potentially very interesting as Standard Candles. • Supernovae are divided into various types. Type 1 are thought to be formed b ...
... Supernovae as Standard Candles • The brightest supernovae reach M = -19 at the peak of their output. In theory they can be seen up to 8000 Mly from Earth. This makes them potentially very interesting as Standard Candles. • Supernovae are divided into various types. Type 1 are thought to be formed b ...
The Life of Stars
... blood, and the carbon in our apple pies were all made in the interior of collapsing stars. We are made of ...
... blood, and the carbon in our apple pies were all made in the interior of collapsing stars. We are made of ...
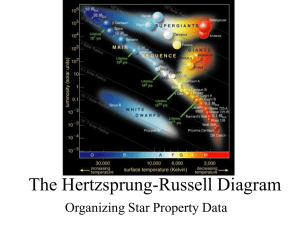
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Test#1
... c) equal areas in equal times, d) Fg=GMM/d2 A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion Newton invented this to help him solve Kepler's equations a) algebra, b) calculus, c) t ...
... c) equal areas in equal times, d) Fg=GMM/d2 A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion Newton invented this to help him solve Kepler's equations a) algebra, b) calculus, c) t ...
1 - Università degli Studi dell`Insubria
... > we sampled 80 values of v in the range 3x10- 3(M2/M)1/2 < v/Vc < 3x102(M2/M)1/2 > we sampled b and the four angles in order to reproduce a spherical distribution of incoming stars ...
... > we sampled 80 values of v in the range 3x10- 3(M2/M)1/2 < v/Vc < 3x102(M2/M)1/2 > we sampled b and the four angles in order to reproduce a spherical distribution of incoming stars ...
No Slide Title
... cluster because the galaxies are rather faint and small objects scattered across 15 degrees of the sky. Below is photograph of the centre of the cluster showing the inner 4°x4° region. Most of the brightest objects in this picture are galaxies. The elliptical galaxy in the centre is M87. On the righ ...
... cluster because the galaxies are rather faint and small objects scattered across 15 degrees of the sky. Below is photograph of the centre of the cluster showing the inner 4°x4° region. Most of the brightest objects in this picture are galaxies. The elliptical galaxy in the centre is M87. On the righ ...
In Pictures: Journey to the Stars
... hydrogen atoms smash together, forming helium and releasing huge amounts of energy that heats the gas. This is called nuclear fusion, and it’s why a star shines. As the hot gas pushed outward, it opposes the inward pull of gravity. This balance of forces is what makes a star, a star. It holds the st ...
... hydrogen atoms smash together, forming helium and releasing huge amounts of energy that heats the gas. This is called nuclear fusion, and it’s why a star shines. As the hot gas pushed outward, it opposes the inward pull of gravity. This balance of forces is what makes a star, a star. It holds the st ...
History of the Universe (in 10 minutes)
... § So the star we are seeing is really how the star looked a million years ago, not how it looks today. In the same way, our sun is 8 or so light minutes away. If the sun were to suddenly explode right now, we wouldn't know about it for eight minutes because that is how long it would take for the l ...
... § So the star we are seeing is really how the star looked a million years ago, not how it looks today. In the same way, our sun is 8 or so light minutes away. If the sun were to suddenly explode right now, we wouldn't know about it for eight minutes because that is how long it would take for the l ...
Study Questions and Problems
... The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can have integer values from –l through 0 to +l. The number of different values ...
... The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can have integer values from –l through 0 to +l. The number of different values ...
ES High mass star life cycle plus black holes
... What is the life cycle of a low mass star (5 stages)? What is the life cycle of a high mass star? What is the heaviest element forms in the center of a high mass star? Why is supernova crucial to our existence? Where is calcium formed in the life a high mass star? What is a supernova? What are the 2 ...
... What is the life cycle of a low mass star (5 stages)? What is the life cycle of a high mass star? What is the heaviest element forms in the center of a high mass star? Why is supernova crucial to our existence? Where is calcium formed in the life a high mass star? What is a supernova? What are the 2 ...
Study Guide: Solar System
... b. Copernicus: Proposed that the Sun was the center (heliocentric model) of the solar systems orbiting in perfect circles c. Kepler: Supported the heliocentric model but discovered that the orbits of the planets were not circular but elliptical. d. Galileo: Worked with the refracting telescopes ...
... b. Copernicus: Proposed that the Sun was the center (heliocentric model) of the solar systems orbiting in perfect circles c. Kepler: Supported the heliocentric model but discovered that the orbits of the planets were not circular but elliptical. d. Galileo: Worked with the refracting telescopes ...
Galaxies and Their Structure
... The Hubble Law In 1914 Vesto Slipher (lived 1870--1963) announced his results from the spectra of over 40 spiral galaxies (at his time people thought the ``spiral nebulae'' were inside the Milky Way). He found that over 90% of the spectra showed redshifts which meant that they were moving away from ...
... The Hubble Law In 1914 Vesto Slipher (lived 1870--1963) announced his results from the spectra of over 40 spiral galaxies (at his time people thought the ``spiral nebulae'' were inside the Milky Way). He found that over 90% of the spectra showed redshifts which meant that they were moving away from ...
TCE Syllabus Summary Blank
... – expansion and cooling of the Universe – subsequent loss of particle kinetic energy – gravitational attraction between particles lumpiness of the gas cloud that then allows gravitational collapse ...
... – expansion and cooling of the Universe – subsequent loss of particle kinetic energy – gravitational attraction between particles lumpiness of the gas cloud that then allows gravitational collapse ...
01-Introduction
... as a great spiral swarm of discrete particles. Each particle was in elliptic motion about the central nucleus. James Jeans (1916) and Harold Jeffreys proposed a new Tidal Hypothesis in 1917 while World War I was in progress. A passing or grazing star is supposed to have pulled out a long cigar-shape ...
... as a great spiral swarm of discrete particles. Each particle was in elliptic motion about the central nucleus. James Jeans (1916) and Harold Jeffreys proposed a new Tidal Hypothesis in 1917 while World War I was in progress. A passing or grazing star is supposed to have pulled out a long cigar-shape ...
A Modern Search for Wolf-Rayet Stars in the Magellanic Clouds. III
... For many years, our knowledge of the Wolf-Rayet (WR) population of the Magellanic Clouds (MCs) was considered essentially complete: twelve WRs were known in the SMC (Massey et al. 2003) and 134 were known in the LMC (Breysacher et al. 1999). These stars had been found by a combination of general obj ...
... For many years, our knowledge of the Wolf-Rayet (WR) population of the Magellanic Clouds (MCs) was considered essentially complete: twelve WRs were known in the SMC (Massey et al. 2003) and 134 were known in the LMC (Breysacher et al. 1999). These stars had been found by a combination of general obj ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... C. eight planets. D. eleven planets. 7. The Sun is part of a group of stars that are relatively close together, this group is called a A. galaxy. B. solar system. C. local cluster. D. universe. 8. Which statement about the Milky Way Galaxy is true? A. The Earth orbits the solar system approximately ...
... C. eight planets. D. eleven planets. 7. The Sun is part of a group of stars that are relatively close together, this group is called a A. galaxy. B. solar system. C. local cluster. D. universe. 8. Which statement about the Milky Way Galaxy is true? A. The Earth orbits the solar system approximately ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... This is very small, hot star, the last stage in the life cycle of a star like the Sun. White dwarfs have a mass similar to that of the Sun, but only 1% of the Sun's diameter; approximately the diameter of the Earth. The surface temperature of a white dwarf is 8000C or more, but being smaller than th ...
... This is very small, hot star, the last stage in the life cycle of a star like the Sun. White dwarfs have a mass similar to that of the Sun, but only 1% of the Sun's diameter; approximately the diameter of the Earth. The surface temperature of a white dwarf is 8000C or more, but being smaller than th ...
Spiral arms in the milky way galaxy and cosmic rays
... The disk is characterized with stars that move in nearly circular orbits around the galactic center. The Central Bulge is characterized with stars with large random motions. Therefore its distribution is ellipsoidal. The star in the disk has a differential velocity, meaning the star nearer to the ce ...
... The disk is characterized with stars that move in nearly circular orbits around the galactic center. The Central Bulge is characterized with stars with large random motions. Therefore its distribution is ellipsoidal. The star in the disk has a differential velocity, meaning the star nearer to the ce ...
Lecture 15 - Deaths of Stars, Supernovae
... up the main sequence to become an O star. toward the lower left in the H-R diagram. ...
... up the main sequence to become an O star. toward the lower left in the H-R diagram. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.