The Milky Way
... probably related to the deaths of very massive (> 25 Msun) stars. In a supernova-like explosion of stars this massive, the core might collapse not to a neutron star, but directly to a black hole. Such stellar explosions are ...
... probably related to the deaths of very massive (> 25 Msun) stars. In a supernova-like explosion of stars this massive, the core might collapse not to a neutron star, but directly to a black hole. Such stellar explosions are ...
ChESS: ChaMP Extended Stellar Survey
... as dM stars based on opti al spe tros opy are shown as the blue histogram. ...
... as dM stars based on opti al spe tros opy are shown as the blue histogram. ...
Stars: Part 2
... • In the same way there was a nebula of gas and dust before the star was born, a new nebula is created from the explosion. • Astronomers call the nebula after the explosion a planetary nebula. ...
... • In the same way there was a nebula of gas and dust before the star was born, a new nebula is created from the explosion. • Astronomers call the nebula after the explosion a planetary nebula. ...
Modified Newtonian Mechanics
... This hidden mass hypothesis has been widely accepted even though it raises a really tough question for which there is not yet an answer. Where did all that hidden mass come from? Cosmology suggests that hydrogen was first developed and then came together and formed stars. In the stars, nuclear react ...
... This hidden mass hypothesis has been widely accepted even though it raises a really tough question for which there is not yet an answer. Where did all that hidden mass come from? Cosmology suggests that hydrogen was first developed and then came together and formed stars. In the stars, nuclear react ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 8 Spiral Galaxies II 1 The Tully
... The classic spiral galaxy is called a grand design spiral, with two symmetric and well-defined arms. Others have more than two arms, or arms that appear fragmented. Galaxies without well-defined arms that can be traced over a large angular distance are called flocculent spirals. Grand design: ∼ 10% ...
... The classic spiral galaxy is called a grand design spiral, with two symmetric and well-defined arms. Others have more than two arms, or arms that appear fragmented. Galaxies without well-defined arms that can be traced over a large angular distance are called flocculent spirals. Grand design: ∼ 10% ...
Chapter 22 Instruments for Measuring Apsorption: Is It a Photometer
... Generally, these lamps are operated at a temperature of around 2900 K, which produces useful radiation from about 350 to 2200 nm. Tungsten/halogen lamps, also called quartz/halogen lamps, contain a small amount of iodine within the quartz envelope that houses the filament. Quartz allows the filament ...
... Generally, these lamps are operated at a temperature of around 2900 K, which produces useful radiation from about 350 to 2200 nm. Tungsten/halogen lamps, also called quartz/halogen lamps, contain a small amount of iodine within the quartz envelope that houses the filament. Quartz allows the filament ...
The coherence length of black
... coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interference patterns consist only of a central maximum (m = 0) flanked by two weak minima (m = ± 21 , s ...
... coherence length is slightly less than the mean or effective wavelength. That is why no fringes (modulation of intensity) of order |m| � 1 occur. So, in the case of unfiltered black-body radiation, interference patterns consist only of a central maximum (m = 0) flanked by two weak minima (m = ± 21 , s ...
Ontario Grade One Describe, using models or simulations, how the
... apparatus safely, accurately, and effectively (e.g., graph sunrise and sunset data and relate them to the motions of the Earth). Gather, organize, and record data through regular observations of the night sky and/or use of appropriate software programs, and use these data to identify and study the m ...
... apparatus safely, accurately, and effectively (e.g., graph sunrise and sunset data and relate them to the motions of the Earth). Gather, organize, and record data through regular observations of the night sky and/or use of appropriate software programs, and use these data to identify and study the m ...
solutions - Las Cumbres Observatory
... 2. How are the compositions of the two stars changing over their life times? T he larger star uses more of its fuel and its mass goes down visibly on the graph. The 1 solar mass star appears to lose very little ...
... 2. How are the compositions of the two stars changing over their life times? T he larger star uses more of its fuel and its mass goes down visibly on the graph. The 1 solar mass star appears to lose very little ...
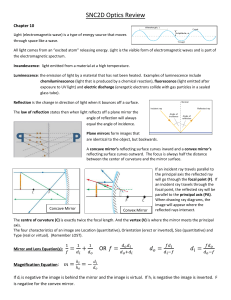
SNC2D Optics Review
... All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a high temperature. Luminescence: the emission of light by a material that has not been heated. Exa ...
... All light comes from an “excited atom” releasing energy. Light is the visible form of electromagnetic waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Incandescence: light emitted from a material at a high temperature. Luminescence: the emission of light by a material that has not been heated. Exa ...
13 Galaxies - Journigan-wiki
... number of faint, diffuse patches of light. To avoid confusing them with comets in the future he began to assign them numbers. Galaxies are still referred to by their “M” or Messier number. ...
... number of faint, diffuse patches of light. To avoid confusing them with comets in the future he began to assign them numbers. Galaxies are still referred to by their “M” or Messier number. ...
The Birth of Stars and Planets
... 2. How do large-scale (molecular) outflows and jets form? How do they get collimated? Where is exactly their origin? 3. Which role do magnetic fields play? Are they coupled to the disk? Are they important for the accretion process onto the star, e.g. by accretion through magnetospheric funnel flows? ...
... 2. How do large-scale (molecular) outflows and jets form? How do they get collimated? Where is exactly their origin? 3. Which role do magnetic fields play? Are they coupled to the disk? Are they important for the accretion process onto the star, e.g. by accretion through magnetospheric funnel flows? ...
Source: https://www
... the equilibrium temperature of the planet. However, modern models for the range of the habitable zone take into account more subtle effects, such as the effect of the carbonate-silicate cycle in regulating carbon dioxide in a planet's atmosphere. Work on this particular process by Penn State scienti ...
... the equilibrium temperature of the planet. However, modern models for the range of the habitable zone take into account more subtle effects, such as the effect of the carbonate-silicate cycle in regulating carbon dioxide in a planet's atmosphere. Work on this particular process by Penn State scienti ...
protostars and pre-main
... • Gas falling onto the protostar heats the surface and radiates directly. This additional luminosity is called ...
... • Gas falling onto the protostar heats the surface and radiates directly. This additional luminosity is called ...
Starending jeopardy
... Once hydrogen is depleted it can no longer fuse hydrogen into helium. With no energy source to cause outware pressure the gravity is able to collapse the core and change the star’s structure. ...
... Once hydrogen is depleted it can no longer fuse hydrogen into helium. With no energy source to cause outware pressure the gravity is able to collapse the core and change the star’s structure. ...
2. Velocity dispersions of galaxies
... launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 36A on March 3, 1972 at 01:49:00 UTC. Pioneer 10 is heading in the direction of Aldebaran, located in Taurus. By some definitions, Pioneer 10 has become the first artificial object to leave the solar system. It is the first human-built ...
... launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 36A on March 3, 1972 at 01:49:00 UTC. Pioneer 10 is heading in the direction of Aldebaran, located in Taurus. By some definitions, Pioneer 10 has become the first artificial object to leave the solar system. It is the first human-built ...
Waves – Light and Sound Quiz 4
... electromagnetic spectrum goes from __________wavelength -- radio, microwave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma rays – ___________________wavelength electromagnetic waves travel at the same ___________________in free space uses of electromagnetic radiations, • ___________________waves: ...
... electromagnetic spectrum goes from __________wavelength -- radio, microwave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma rays – ___________________wavelength electromagnetic waves travel at the same ___________________in free space uses of electromagnetic radiations, • ___________________waves: ...
The Warrumbungle Observer The Warrumbungle Observer
... Jupiter is the 5th planet from the Sun and the largest in the solar system. 11 earths can fit side by side across the equator. Jupiter is larger than all the other planets combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas Giant and is primarily composed of the same gas as the Sun, hydrogen. Though it is not ...
... Jupiter is the 5th planet from the Sun and the largest in the solar system. 11 earths can fit side by side across the equator. Jupiter is larger than all the other planets combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas Giant and is primarily composed of the same gas as the Sun, hydrogen. Though it is not ...
Practice Questions for Exam 3
... According to the inverse square law of light, how will the apparent brightness of an object change if its distance to us doubles? A. Its apparent brightness will increase by a factor of 4. B. Its apparent brightness will decrease by a factor of 4. C. Its apparent brightness will decrease by a factor ...
... According to the inverse square law of light, how will the apparent brightness of an object change if its distance to us doubles? A. Its apparent brightness will increase by a factor of 4. B. Its apparent brightness will decrease by a factor of 4. C. Its apparent brightness will decrease by a factor ...
www.aavso.org
... Even today, many amateur astronomers still measure magnitudes using their eyes and submit data to an organization such as the AAVSO (American Association of Variable Star Observers) which can be used by professional astronomers for research. ...
... Even today, many amateur astronomers still measure magnitudes using their eyes and submit data to an organization such as the AAVSO (American Association of Variable Star Observers) which can be used by professional astronomers for research. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.