Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45
... (easy if your data is already on a spreadsheet). You will have to rewrite the ...
... (easy if your data is already on a spreadsheet). You will have to rewrite the ...
DTU 8e Chap 5 Formation of the Solar System
... (a) A planet and its star both orbit around their common center of mass, always staying on opposite sides of that point. The star’s motion around the center of mass provides astronomers with the information that a planet is present. (b) As a planet moves toward or away from us, its star moves in the ...
... (a) A planet and its star both orbit around their common center of mass, always staying on opposite sides of that point. The star’s motion around the center of mass provides astronomers with the information that a planet is present. (b) As a planet moves toward or away from us, its star moves in the ...
Transcript of this week`s podcast
... From 10-35 of a second after its creation, the universe entered a phase that scientists since the early 1980s have called the inflationary epoch. During this inflationary epoch, the universe began expanding faster than the speed of light. What caused this expansion is unknown. Some scientists have s ...
... From 10-35 of a second after its creation, the universe entered a phase that scientists since the early 1980s have called the inflationary epoch. During this inflationary epoch, the universe began expanding faster than the speed of light. What caused this expansion is unknown. Some scientists have s ...
Life Cycle of stars
... can however be detected by x-rays due to the matter and energy being absorbed and consumed. Black holes are the end of massive stars. Black holes are very brutal and are not a pleasant way for a star to end its life cycle. Basically the life cycle of a star revolves around first having gravity pull ...
... can however be detected by x-rays due to the matter and energy being absorbed and consumed. Black holes are the end of massive stars. Black holes are very brutal and are not a pleasant way for a star to end its life cycle. Basically the life cycle of a star revolves around first having gravity pull ...
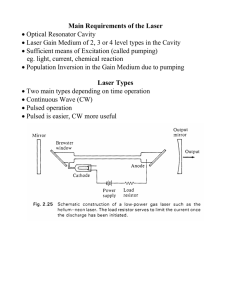
Main Requirements of the Laser • Optical Resonator Cavity • Laser
... • Results in frequency separation of peaks c 2L • Emission from the atomic transitions is a wider Gaussian • Result is axial modes imposed on Gaussian Transition spread ∆ν = ...
... • Results in frequency separation of peaks c 2L • Emission from the atomic transitions is a wider Gaussian • Result is axial modes imposed on Gaussian Transition spread ∆ν = ...
kd - The HST Treasury Program on Eta Carinae
... Detection of the secondary star is highly desirable because that would eliminate single-star models. Unfortunately, as we explained in sections 2—4 above, there is no proof that any emission seen with FUSE came from a second star. It’s not hard to imagine a single-star model. The equatorial photosph ...
... Detection of the secondary star is highly desirable because that would eliminate single-star models. Unfortunately, as we explained in sections 2—4 above, there is no proof that any emission seen with FUSE came from a second star. It’s not hard to imagine a single-star model. The equatorial photosph ...
Gökküre - itü | fizik mühendisliği
... stone falls down because it belongs to the Earth. Fire tends to rise up because it wants to reach the greatest fire (the Sun), the bubbles in water rise up because air is to be above water, etc. ...
... stone falls down because it belongs to the Earth. Fire tends to rise up because it wants to reach the greatest fire (the Sun), the bubbles in water rise up because air is to be above water, etc. ...
Spin-Orbit Angles as a Probe to Orbital Evolution
... Fig. 1a & b show that the fraction of aligned to misaligned objects is larger when planets orbit stars that have a massive outer convective layer (red triangles) corresponding to Teff <6150 K. Tides are dissipated more effectively when there is an outer convective layer (Zahn 1977). Winn et al. (2010) ...
... Fig. 1a & b show that the fraction of aligned to misaligned objects is larger when planets orbit stars that have a massive outer convective layer (red triangles) corresponding to Teff <6150 K. Tides are dissipated more effectively when there is an outer convective layer (Zahn 1977). Winn et al. (2010) ...
Chapter 13: Neutron Stars and Black Holes - Otto
... Millisecond pulsars • Spin hundreds of times per second • Period is several milliseconds • Mass of sun, several km in size, spinning almost 1000 times per second • Many are old (and should be slow) • Are spun-up by infalling matter from binary companion ...
... Millisecond pulsars • Spin hundreds of times per second • Period is several milliseconds • Mass of sun, several km in size, spinning almost 1000 times per second • Many are old (and should be slow) • Are spun-up by infalling matter from binary companion ...
t 0 (radioactive decay)
... unstable isotopes as a way to estimate the age of stars and the Milky Way Galaxy, and thus t0. Briefly, radioactive decay is the process by which “parent” isotopes spontaneously lose energy and turn into new “daughter” isotopes. The parent isotope’s half-life defines the rate at which this decay occ ...
... unstable isotopes as a way to estimate the age of stars and the Milky Way Galaxy, and thus t0. Briefly, radioactive decay is the process by which “parent” isotopes spontaneously lose energy and turn into new “daughter” isotopes. The parent isotope’s half-life defines the rate at which this decay occ ...
Chapter 22 - Bad Axe High School
... • Light colored objects reflect more light and heat and dark colored objects absorb more light and energy ...
... • Light colored objects reflect more light and heat and dark colored objects absorb more light and energy ...
ph507lecnote06
... sunspot cycle. At these times, the corona is much less regular and much more extended than at sunspot minimum. Astronomers believe that coronal heating is caused by surface activity on the Sun. The changing shape and size of the corona are the direct result of variations in prominence and flare acti ...
... sunspot cycle. At these times, the corona is much less regular and much more extended than at sunspot minimum. Astronomers believe that coronal heating is caused by surface activity on the Sun. The changing shape and size of the corona are the direct result of variations in prominence and flare acti ...
STAR UNIT FLASH BACKS
... 1. TRUE OR FALSE: If a star is colored red, that means that it is moving AWAY from us (due to Red Shift). 2. How long would it take for an F-22 Raptor jet flying at top speed (1,500 miles per hour) to fly from the earth to the sun? a.) 8 minutes ...
... 1. TRUE OR FALSE: If a star is colored red, that means that it is moving AWAY from us (due to Red Shift). 2. How long would it take for an F-22 Raptor jet flying at top speed (1,500 miles per hour) to fly from the earth to the sun? a.) 8 minutes ...
Handout 15: Virial Theorem E = P.E. + K.E = (1/2)P.E. = -K.E.
... drag causes r to decrease P.E. decreases |P.E.| increases K.E. increases Satellite speeds up! Gas drag causes speed to increase Half the decrease in P.E. goes into heating up the atmosphere ...
... drag causes r to decrease P.E. decreases |P.E.| increases K.E. increases Satellite speeds up! Gas drag causes speed to increase Half the decrease in P.E. goes into heating up the atmosphere ...
Essential Question
... 8.8(A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Hertsprung-Russell diagram for classification 8.8(B) recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times ...
... 8.8(A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Hertsprung-Russell diagram for classification 8.8(B) recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times ...
Clusters - El Camino College
... Forming Clusters When giant clouds of dust and gas form, the dust becomes thick enough to block visible and ultraviolet light (short wavelengths) from stars outside the cloud. Therefore, clouds cannot cool except by radiating away energy in other forms, such as infrared and radio radiation (long wav ...
... Forming Clusters When giant clouds of dust and gas form, the dust becomes thick enough to block visible and ultraviolet light (short wavelengths) from stars outside the cloud. Therefore, clouds cannot cool except by radiating away energy in other forms, such as infrared and radio radiation (long wav ...
R and FUV Observations of Star Formation in
... 4-6 Gyr since last major cluster merger, so there may not have been enough time for a steady state to be set up (cooling leads to cold gas leads to star formation). ...
... 4-6 Gyr since last major cluster merger, so there may not have been enough time for a steady state to be set up (cooling leads to cold gas leads to star formation). ...
Scientific Justification
... Scientific Justification As white dwarf stars cool over time, from hot planetary nebula nuclei down to the coolest temperatures possible given the finite age of the Galaxy, there are three narrow ranges of temperature where they can begin to pulsate. The interval where a given white dwarf will pulsa ...
... Scientific Justification As white dwarf stars cool over time, from hot planetary nebula nuclei down to the coolest temperatures possible given the finite age of the Galaxy, there are three narrow ranges of temperature where they can begin to pulsate. The interval where a given white dwarf will pulsa ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.