AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational
... The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers a gravitational collapse. Stars form with a range of different masses and begin their lives. ...
... The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers a gravitational collapse. Stars form with a range of different masses and begin their lives. ...
Properties of Supernovae
... Supernovae are rare events, occurring only once or twice per century in a typical galaxy. There have been just six supernovae seen in the Milky Way in recorded history, with the most recent occurring in 1604, just before the advent of telescopes. The perceptive reader will notice that this rate is m ...
... Supernovae are rare events, occurring only once or twice per century in a typical galaxy. There have been just six supernovae seen in the Milky Way in recorded history, with the most recent occurring in 1604, just before the advent of telescopes. The perceptive reader will notice that this rate is m ...
Lecture 6: Main Sequence Stars
... Opacity depends on composiCon, temperature, and density and will change with the wavelength of the light trying to pass through the material. It turns-‐out that opacity is a very strong funcCon of temp ...
... Opacity depends on composiCon, temperature, and density and will change with the wavelength of the light trying to pass through the material. It turns-‐out that opacity is a very strong funcCon of temp ...
Spectra
... Mass Spectra A typical molecule may fragment in several different places. The ion formed from the loss of the electron is called the parent ion. The parent ion may fragment into smaller pieces. Each fragment is deflected to a different extent . Hence each peak appears in the Mass Spectrum ...
... Mass Spectra A typical molecule may fragment in several different places. The ion formed from the loss of the electron is called the parent ion. The parent ion may fragment into smaller pieces. Each fragment is deflected to a different extent . Hence each peak appears in the Mass Spectrum ...
Lecture 18: Supernovae
... and carry off energy Makes the core collapse faster, as the insufficient pressure is decreased further ...
... and carry off energy Makes the core collapse faster, as the insufficient pressure is decreased further ...
Hypervelocity Globular: A beacon of merging clusters Oleg Gnedin with Alexey Vikhlinin
... While measuring radial velocities of globular clusters around M87 in Virgo Cluster, Caldwell et al. (2014) found an outlier… A triple interaction with a binary black hole (slingshot) can lead to a very high ejection velocity. ...
... While measuring radial velocities of globular clusters around M87 in Virgo Cluster, Caldwell et al. (2014) found an outlier… A triple interaction with a binary black hole (slingshot) can lead to a very high ejection velocity. ...
HP unit 12 - wave optics student handout
... If there are 37 dark and 37 bright lines starting from the end of the pair of glass plates that are touching to the other, how thick is the piece of plastic ...
... If there are 37 dark and 37 bright lines starting from the end of the pair of glass plates that are touching to the other, how thick is the piece of plastic ...
Assignment 8 - utoledo.edu
... b. because they just cannot get hot enough for the fusion of heavier nuclei c. because all such stars explode before they can make any other elements d. because all such elements become radioactive and their nuclei break apart rather quickly e. because the cores of such stars get too hot for further ...
... b. because they just cannot get hot enough for the fusion of heavier nuclei c. because all such stars explode before they can make any other elements d. because all such elements become radioactive and their nuclei break apart rather quickly e. because the cores of such stars get too hot for further ...
Wang_Project_Summery
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... components in CVn I from the LBC photometry and the much smaller extent of the young population surprisingly recalls their findings. A direct comparison of their spectroscopic sample with the LBC contour maps of the old and young populations is presented in Figure 3. Stars belonging to the kinematic ...
... components in CVn I from the LBC photometry and the much smaller extent of the young population surprisingly recalls their findings. A direct comparison of their spectroscopic sample with the LBC contour maps of the old and young populations is presented in Figure 3. Stars belonging to the kinematic ...
(r) and
... The most nearby large galaxy, M31, is 100 times farther away than the galactic center. proper motion timescales are a factor 100 longer; stellar mass density is a factor 1003 larger, therefore individual stars are not resolved. ...
... The most nearby large galaxy, M31, is 100 times farther away than the galactic center. proper motion timescales are a factor 100 longer; stellar mass density is a factor 1003 larger, therefore individual stars are not resolved. ...
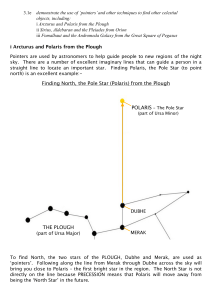
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
Global Doppler frequency shift detection with near-resonant interferometry A. Landolt
... issues. Because only the position of interference fringes needs to be determined in the post processing step, image intensity noise affects accuracy only in a minor way. The measurement range is much larger than for transmission based techniques, where it is limited to the shoulder of one absorption ...
... issues. Because only the position of interference fringes needs to be determined in the post processing step, image intensity noise affects accuracy only in a minor way. The measurement range is much larger than for transmission based techniques, where it is limited to the shoulder of one absorption ...
Incredible Shrinking Stars
... Eventually, the pulse becomes very weak. In addition, we don't even expect to see fresh, young pulsars because, in order for us to see the pulsed beams, they must be pointed at us! There's no reason why all pulsars in the universe should be oriented in such a way that their beams point toward Earth. ...
... Eventually, the pulse becomes very weak. In addition, we don't even expect to see fresh, young pulsars because, in order for us to see the pulsed beams, they must be pointed at us! There's no reason why all pulsars in the universe should be oriented in such a way that their beams point toward Earth. ...
l`Astrofilo - Astro Publishing
... The possibilities become more interesting for the wide binary M-G star scenarios. The primary star's radiation always has a greater magnitude than that of the distant secondary star; however, there are periods where a portion of the planet would be illuminated only by light from the less photosynthe ...
... The possibilities become more interesting for the wide binary M-G star scenarios. The primary star's radiation always has a greater magnitude than that of the distant secondary star; however, there are periods where a portion of the planet would be illuminated only by light from the less photosynthe ...
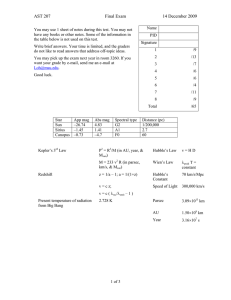
AST 207 Final Exam 14 December 2009
... a. (2 pts.) At the present time, how does the sun produce energy? What is used up and what is created? b. (1 pt.) What is the approximate age of the sun and earth? c. (1 pts.) What will the sun become when it completely exhausts its fuel? (1 pt.) How big will it be? (1 pt.) What will prevent gravity ...
... a. (2 pts.) At the present time, how does the sun produce energy? What is used up and what is created? b. (1 pt.) What is the approximate age of the sun and earth? c. (1 pts.) What will the sun become when it completely exhausts its fuel? (1 pt.) How big will it be? (1 pt.) What will prevent gravity ...
The Development of Constructed Response Astronomy Assessment
... the stars light is dispersed into a spectrum they are known as absorption lines. To an observer the color of a star is set by the wavelengths of light at which the star is most luminous. These dominant wavelengths are set by the stars thermal continuum emission. The absorption line processes are a ...
... the stars light is dispersed into a spectrum they are known as absorption lines. To an observer the color of a star is set by the wavelengths of light at which the star is most luminous. These dominant wavelengths are set by the stars thermal continuum emission. The absorption line processes are a ...
Galactic Center problem sheet
... Calculate the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole for the mass calculated in the previous problem. What is the distance of S2 star at the pericentre expressed in terms of Schwarzschild radii? • The emission from Sgr A* becomes optically thin (we can see through) for the wavelengths of about 1 mm. ...
... Calculate the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole for the mass calculated in the previous problem. What is the distance of S2 star at the pericentre expressed in terms of Schwarzschild radii? • The emission from Sgr A* becomes optically thin (we can see through) for the wavelengths of about 1 mm. ...
April Skies
... different constellations which form the asterism referred to as the winter hexagon and described by Carol Latta the January newsletter. Not only does the Milky Way pass through this asterism but so does the ecliptic – the plane of our solar system – the track in which you will find the planets, moon ...
... different constellations which form the asterism referred to as the winter hexagon and described by Carol Latta the January newsletter. Not only does the Milky Way pass through this asterism but so does the ecliptic – the plane of our solar system – the track in which you will find the planets, moon ...
Lecture 24: High Mass Star Formation Astro 6890/8980 Prof. Tom
... with a disk. Must overcome magnetic pressure, resulting in magnetospheric accretion for low mass stars. Must overcome photon pressure for high mass stars. ...
... with a disk. Must overcome magnetic pressure, resulting in magnetospheric accretion for low mass stars. Must overcome photon pressure for high mass stars. ...
closed-box model
... the Universe, while all metals (except for a very small fraction of Li) were produced through nucleosynthesis (nuclear burning) in stars. ...
... the Universe, while all metals (except for a very small fraction of Li) were produced through nucleosynthesis (nuclear burning) in stars. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.