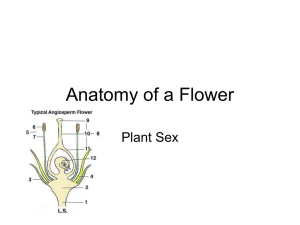
Seed Plants
... haploid stage in the life cycle of plants. Sporophyte: Sporophyte: The diploid form of a plant that produces , haploid, asexual spores through the process of meiosis – reduction division. ...
... haploid stage in the life cycle of plants. Sporophyte: Sporophyte: The diploid form of a plant that produces , haploid, asexual spores through the process of meiosis – reduction division. ...
Plant Diversity II
... Three disintegrate, one survives, divides by mitosis to produce 7 cells. One cell becomes the egg, one large central cell has two haploid nuclei These will fuse with sperm to form endosperm ...
... Three disintegrate, one survives, divides by mitosis to produce 7 cells. One cell becomes the egg, one large central cell has two haploid nuclei These will fuse with sperm to form endosperm ...
Plant Notes Fall2013
... a. Day-open (most of the time), release water & oxygen and take in carbon dioxide a. Night- close to prevent water loss ...
... a. Day-open (most of the time), release water & oxygen and take in carbon dioxide a. Night- close to prevent water loss ...
Unit 4 Notes #6 – ANGIOSPERMS – “The - Mr. Lesiuk
... 8) 1 sperm fertilizes the egg nucleus to form a diploid zygote; while the other sperm unites with the other 2 nuclei of the female endosperm. This triploid endosperm goes onto form the embryo’s food supply. The entire process is called double fertilization 9) Sepals, petals, and stamens then wither. ...
... 8) 1 sperm fertilizes the egg nucleus to form a diploid zygote; while the other sperm unites with the other 2 nuclei of the female endosperm. This triploid endosperm goes onto form the embryo’s food supply. The entire process is called double fertilization 9) Sepals, petals, and stamens then wither. ...
ANGIOSPERMS - E
... The other male gamete fuses with the two other female gametes inside the embryo sac and this forms the endosperm. The endosperm becomes the food that will keep the growing seed alive. This process is called double fertilisation because fertilisation happens twice in the plant. Once fertilisation ha ...
... The other male gamete fuses with the two other female gametes inside the embryo sac and this forms the endosperm. The endosperm becomes the food that will keep the growing seed alive. This process is called double fertilisation because fertilisation happens twice in the plant. Once fertilisation ha ...
Alteration of Generations, bryophyte, fern - MAH-SBHS
... Absorb moisture and minerals through above ground structures via diffusion and therefore grow in moist environments They do not have roots as such however they are anchored to the substrate they grow in by rhizoids They have small leaf like structures however they lack the specialised tissues of the ...
... Absorb moisture and minerals through above ground structures via diffusion and therefore grow in moist environments They do not have roots as such however they are anchored to the substrate they grow in by rhizoids They have small leaf like structures however they lack the specialised tissues of the ...
Document
... Angiosperms undergo a unique process called double fertilization -A pollen grain that lands on a stigma forms a pollen tube that pierces the style -While the pollen tube is growing, the generative cell divides to form 2 sperm cells -When pollen tube reaches the ovule, it enters one of the synergids ...
... Angiosperms undergo a unique process called double fertilization -A pollen grain that lands on a stigma forms a pollen tube that pierces the style -While the pollen tube is growing, the generative cell divides to form 2 sperm cells -When pollen tube reaches the ovule, it enters one of the synergids ...
Plant Reproduction 1 A plant that completes its life cycle in one
... Two nuclei found in pollen tube as it approaches the micropyle of the ovule. One will fertilise the egg and the other will join with the two polar nuclei to form the triploid (3n) endosperm nucleus. These are four haploid cells produced by meiosis in the ovule of a flower. Three of these cells will ...
... Two nuclei found in pollen tube as it approaches the micropyle of the ovule. One will fertilise the egg and the other will join with the two polar nuclei to form the triploid (3n) endosperm nucleus. These are four haploid cells produced by meiosis in the ovule of a flower. Three of these cells will ...
BIO120 LAB--PLANT DIVERSITY 1-
... – Genetically different/variable: offspring are different from parent and one another – Slower, riskier, more expensive, for parent – but creates potential for offspring to have new and different capabilities that could make them more successful or capable of dealing with a changing environment. ...
... – Genetically different/variable: offspring are different from parent and one another – Slower, riskier, more expensive, for parent – but creates potential for offspring to have new and different capabilities that could make them more successful or capable of dealing with a changing environment. ...
Plant Reproduction 2 Not involving gamete formation. No sex
... A period of rest, inactivity or non-vegetative state before growth, during which the rate of metabolism is reduced, e.g. in buds, seeds and spores. Seeds will not germinate during this time, even if given ideal conditions, because other requirements may be necessary before germination can occur. Thi ...
... A period of rest, inactivity or non-vegetative state before growth, during which the rate of metabolism is reduced, e.g. in buds, seeds and spores. Seeds will not germinate during this time, even if given ideal conditions, because other requirements may be necessary before germination can occur. Thi ...
Document
... stigma: receives the pollen during fertilization; it is sticky to grab and hold the pollen in place style: tube between the stigma and ovary through which the pollen tube must grow to deliver the sperm to the egg (ovule) ovary: organ where the ovules (eggs) are produced; will become the fruit ...
... stigma: receives the pollen during fertilization; it is sticky to grab and hold the pollen in place style: tube between the stigma and ovary through which the pollen tube must grow to deliver the sperm to the egg (ovule) ovary: organ where the ovules (eggs) are produced; will become the fruit ...
Examining Sexual Reproduction of Flowering Plants - PHS
... Sexual reproduction of flowering plants is the result of the male sperm in the pollen uniting with the female egg in a flower. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm with an egg. The ferti ...
... Sexual reproduction of flowering plants is the result of the male sperm in the pollen uniting with the female egg in a flower. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm with an egg. The ferti ...
Methods of Reproduction
... potatoes) or bulbs (e.g. tulips)… which are part of the parent plant ...
... potatoes) or bulbs (e.g. tulips)… which are part of the parent plant ...
Examining Sexual Reproduction of Flowering Plants
... Sexual reproduction of flowering plants is the result of the male sperm in the pollen uniting with the female egg in a flower. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm with an egg. The ferti ...
... Sexual reproduction of flowering plants is the result of the male sperm in the pollen uniting with the female egg in a flower. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm with an egg. The ferti ...
2 N - Malibu High School
... A form of duplication using only mitosis. Example, a new plant grows out of the root or a shoot from an existing plant. Produces only genetically identical offspring since all divisions are by mitosis. Offspring called clones meaning that each is an exact copy of the original organism This method ...
... A form of duplication using only mitosis. Example, a new plant grows out of the root or a shoot from an existing plant. Produces only genetically identical offspring since all divisions are by mitosis. Offspring called clones meaning that each is an exact copy of the original organism This method ...
Yr 9 Word Sheets – Genes and Inheritance
... A group of organisms that can reproduce with each other to produce offspring that will also be able to reproduce. ...
... A group of organisms that can reproduce with each other to produce offspring that will also be able to reproduce. ...
CHAPTER 4: REPRODUCTION SEXUAL AND ASEXUAL
... about 12 years old. The ovaries will stop producing ova when a woman is about 55 years old or when she reaches menopause. The ovum is the largest cell in the female body because it contains dense cytoplasm to provide food to the embryo at the early stage of its development. An ovum that is not ferti ...
... about 12 years old. The ovaries will stop producing ova when a woman is about 55 years old or when she reaches menopause. The ovum is the largest cell in the female body because it contains dense cytoplasm to provide food to the embryo at the early stage of its development. An ovum that is not ferti ...
Influence of Temperature on Pollen Germination
... Parthenocarpy Pollination Self-pollination Sexual reproduction Zygote ...
... Parthenocarpy Pollination Self-pollination Sexual reproduction Zygote ...
Document
... which undergo _____ to produce haploid microspores. a. Ovulate, diploid, meiosis b. Ovulate, haploid, mitosis c. Pollen, dipoid, meiosis d. Pollen, haploid, mitosis 42. Pollination and fertilization are different terms, in that a. Pollination occurs when the egg and sperm cells join b. Fertilization ...
... which undergo _____ to produce haploid microspores. a. Ovulate, diploid, meiosis b. Ovulate, haploid, mitosis c. Pollen, dipoid, meiosis d. Pollen, haploid, mitosis 42. Pollination and fertilization are different terms, in that a. Pollination occurs when the egg and sperm cells join b. Fertilization ...
Document
... which undergo _____ to produce haploid microspores. a. Ovulate, diploid, meiosis b. Ovulate, haploid, mitosis c. Pollen, dipoid, meiosis d. Pollen, haploid, mitosis 42. Pollination and fertilization are different terms, in that a. Pollination occurs when the egg and sperm cells join b. Fertilization ...
... which undergo _____ to produce haploid microspores. a. Ovulate, diploid, meiosis b. Ovulate, haploid, mitosis c. Pollen, dipoid, meiosis d. Pollen, haploid, mitosis 42. Pollination and fertilization are different terms, in that a. Pollination occurs when the egg and sperm cells join b. Fertilization ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.