* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 N - Malibu High School
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial insemination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Parthenogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
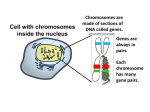
MEIOSIS by R.B. Perry The Marine Research Facility Malibu High School ASEXUAL vs SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Asexual (vegetative) reproduction A form of duplication using only mitosis. Example, a new plant grows out of the root or a shoot from an existing plant. Produces only genetically identical offspring since all divisions are by mitosis. Offspring called clones meaning that each is an exact copy of the original organism This method of reproduction is rapid and effective allowing the spread of an organism Since the offspring are identical, there is no mechanism for introducing diversity Sexual reproduction Formation of new individual by a combination of two haploid sex cells (gametes). Fertilization- combination of genetic information from two separate cells that have one half the original genetic information Gametes for fertilization usually come from separate parents Female- produces an egg Male - produces sperm Both gametes are haploid, with a single set of chromosomes The new individual is called a zygote, with two sets of chromosomes (diploid). WHAT IS MEIOSIS ?? MEIOSIS MEIOSIS IS THE PROCESS OF CUTTING BY HALF THE NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES TO FORM GAMETES and MEIOSIS MEIOSIS causes a change in the genetic information to increase diversity in the offspring. MEIOSIS Every normal body cell is DIPLOID …2 sets of chromosomes (except gametes). GAMETES: OVA ARE HAPLOID …one set of chromosomes SPERM ARE HAPLOID …one set of chromosomes OFFSPRING ARE DIPOLID …two sets of chromosomes One member of each pair comes from your mother. One member of each pair comes from your father. How does every cell end up with a pair of chromosomes, when one comes from each parent ? ovum sperm The answer is carried in the gametes. 1N ovum sperm The ovum carries one set of chromosomes. Symbol for 1 set of chromosomes = 1 N OVARIAN FOLLICLES MATURE THEN BURST, RELEASING AN OVUM. 1. This is a cross section through one ovarian follicle which are found in each ovary. 1. 2. 2. This is the young developing ovum inside the follicle. 1N ovum 1N sperm The sperm carry one set of chromosomes. Symbol for 1 set of chromosomes = 1 N 1. 2. This is a cross section through one seminferous tubule which makes up the testis. 1. These are the normal sperm producing cells (SPERMATOGONIA) in the wall of each tubule. 2. These are the young sperm just starting to swim. MEIOSIS IS THE PROCESS OF CUTTING BY HALF THE NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES FOUND IN GAMETES. This is the precursor cell found in the ovarian follicles or seminferous tubules. These are the steps and stages for cutting by half the chromosome number. The end product is gametes with only ONE set of chromosomes. OR CROSSING-OVER: (during the first meiotic division process) --Genetic material from the homologous chromosomes is randomly swapped. This creates four unique chromatids. --Since each chromatid is unique, the overall genetic diversity of the gametes is greatly increased ! 1N ovum 1N sperm MEIOSIS produces gametes that are HAPLOID. Symbol for 1 set of chromosomes = 1 N Sperm cell = 1N (one set of chromosomes) Egg cell = 1N (one set of chromosomes) 1N ovum 1N sperm fertilization 1n sperm ovum 1n Fertilization 1n + 1n = 2n haploid + haploid = diploid 1n + 1n = 2n Fertilization: restores the normal DIPLOID number for the offspring. 1N sperm 1N ovum 2N 4 week old human embryo 1N sperm 1N ovum 2N 6 week old human embryo 1N sperm 1N ovum 2N human fetus 1N ovum 1N sperm 2N ANIMATION LINK: http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/meiosis.html REVIEW CHECKPOINT: 1. What is meiosis ? 2. Explain why meiosis is necessary. 3. Name the only 2 kinds of human cells that do NOT have a full 2N set. 4. What is meiosis in females called ? males ? 5. Where does meiosis in females occur ? 6. Where does meiosis in males occur ? 7. Give the mathematical formula for fertilization using chromosome numbers. 8. What would happen to chromosome numbers after a few generations without meiosis ? 9. How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity? 10. How does sexual reproduction contribute to genetic diversity?