* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Notes Fall2013
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
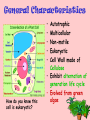
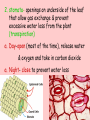
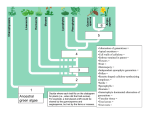
Intro to Plants and Non-vascular plants IN: 81a General Characteristics • • • • • How do you know this cell is eukaryotic? Autotrophic Multicellular Non-motile Eukaryotic Cell Wall made of Cellulose • Exhibit alternation of generation life cycle • Evolved from green algae What do Cladograms show us? Essentials for survival 1. Light 2.Water and minerals 3.Gas exchange ability 4.Ability to move water and nutrients Plant Adaptations to Life on Land Place the leaf crosssection on IN: 80a 1. Cuticle- waxy protective outer covering helps to prevent water loss & injury 2. stomata- openings on underside of the leaf that allow gas exchange & prevent excessive water loss from the plant (transpiration) a. Day-open (most of the time), release water & oxygen and take in carbon dioxide a. Night- close to prevent water loss 3. Cellulose-carbohydrate that strengthens the stems; found in plant cell walls In which group of organic compounds would you place cellulose? 4. Spores, seeds, fruits- reproductive structures 5. Leaves- photosynthetic organs 6. Roots- organs to help anchor and absorb water Vascular & Nonvascular Plants 1. Nonvascular Plants without vessels for water & mineral transport No true roots,stems or leaves Example-mosses 2. Vascular Plants which contain vessels for transport A. xylem- vessels transporting water & minerals up to leaves B. Phloem- vessel transporting sugar down to roots C. Cambium- found btw xylem & phloem: makes new xylem & phloem Example-flowers, trees Nonvascular Plants moss 1. “AKA” Bryophytes –Division name 2. Ex. Mosses, liverworts,hornworts 3. Small, soft plants which grow in clumps 4. Absorbs water like a sponge 5. Live in moist, shaded areas 6. Small in size (1-2 cm) 7. Pioneer plants: break down rock 8. Grow close to the ground liverwort 9. Depend on water for reproduction. 10. No true roots, stems or leaves hornwort Reproduction in Mosses a. alternation of generations: alternation between haploid & diploid stages b. Gametophyte- body form which produces gametes c. Sporophyte- form which produces spores, grows from a gametophyte & relies on it for water & minerals Label the moss diagram on your left page IN: 80b capsule sporophyte stalk Stemlike structure Leaflike structure gametophyte Steps in reproductive cycle of a Moss IN:80b 1. Spore(n) germinate & form gametophyte (n) generation. 2. Antheridium- forms male gametes(sperm) ay tips of gametophyte 3. Archegonium- forms female gametes(egg) at tips of gametophyte. n n 2n n 4. Sperm fertilizes egg & zygote (2n) is formed 5. Zygote divides and forms sporophtye (2n) 2n n