The Byzantine Empire - A Journey Across Time 2
... clergy enjoyed swelled the ranks of the clergy in the Eastern Church. ...
... clergy enjoyed swelled the ranks of the clergy in the Eastern Church. ...
Slide 1
... prepared to flee, but Theodora spoke up and gave a moving speech about the greater significance of the life of someone who died as a ruler, over that of someone who lived but was nothing. Her determined speech convinced Justinian and his officials and they attacked the Hippodrome, killing over 30,00 ...
... prepared to flee, but Theodora spoke up and gave a moving speech about the greater significance of the life of someone who died as a ruler, over that of someone who lived but was nothing. Her determined speech convinced Justinian and his officials and they attacked the Hippodrome, killing over 30,00 ...
Byzantine Empire and Early Middle Ages Part 1 Terms and People
... 17-Explain why the Byzantine Empire collapsed, and examine the empire’s lasting heritage. The Byzantine Empire In 1453 The Ottoman Turks (Muslims) attacked Constantinople after two month and the use of a new invention the cannon the Turks breached the walls that have never been breached before. The ...
... 17-Explain why the Byzantine Empire collapsed, and examine the empire’s lasting heritage. The Byzantine Empire In 1453 The Ottoman Turks (Muslims) attacked Constantinople after two month and the use of a new invention the cannon the Turks breached the walls that have never been breached before. The ...
Fusion Review Byzantine Russia
... The Byzantines at first followed Roman ways. Constantinople was known as the ‘New Rome.’ Its public buildings and palaces were built in the Roman style. The city even had an oval arena called the Hippodrome, where chariot races and other events were held. Byzantine political and social life also wer ...
... The Byzantines at first followed Roman ways. Constantinople was known as the ‘New Rome.’ Its public buildings and palaces were built in the Roman style. The city even had an oval arena called the Hippodrome, where chariot races and other events were held. Byzantine political and social life also wer ...
Byzantine Empire Questions
... In early years, Christians were persecuted in the Roman Empire until Constantine permitted the religion and then Theodosius made it the official religion of the Empire. The Byzantine Empire was Christian from the start, and this time it was the other regions that were persecuted. The Empire was base ...
... In early years, Christians were persecuted in the Roman Empire until Constantine permitted the religion and then Theodosius made it the official religion of the Empire. The Byzantine Empire was Christian from the start, and this time it was the other regions that were persecuted. The Empire was base ...
The Byzantine Empire - White Plains Public Schools
... - The first crisis actually began before Justinian’s death – a plague - Historians estimate that in 542, approximately 10,000 people were dying every day ...
... - The first crisis actually began before Justinian’s death – a plague - Historians estimate that in 542, approximately 10,000 people were dying every day ...
Hagia Sophia - cloudfront.net
... build magnificent buildings like Hagia Sophia? Q.- What were some important features of life in Constantinople? Q.-Who invented the Cyrillic alphabet and what was its purpose? ...
... build magnificent buildings like Hagia Sophia? Q.- What were some important features of life in Constantinople? Q.-Who invented the Cyrillic alphabet and what was its purpose? ...
The Byzantine Empire: Introduction While the Western Roman
... on the city of Constantinople, survived and thrived. Over time, influenced by its Greek heritage, Orthodox Christianity, and its Middle Eastern and Eastern European neighbors, the culture of the Eastern Roman Empire transformed. Greek replaced Latin as the language of the empire, and as Christianity ...
... on the city of Constantinople, survived and thrived. Over time, influenced by its Greek heritage, Orthodox Christianity, and its Middle Eastern and Eastern European neighbors, the culture of the Eastern Roman Empire transformed. Greek replaced Latin as the language of the empire, and as Christianity ...
Byzantine Empire Vocabulary Dowry
... Roman Empire. Then subsequently the city was, for more than a thousand years, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, the Greek-speaking Roman Empire of late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Constantinople was captured by the Ottoman Turks, becoming the capital of their empire, in 1453. The name of the c ...
... Roman Empire. Then subsequently the city was, for more than a thousand years, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, the Greek-speaking Roman Empire of late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Constantinople was captured by the Ottoman Turks, becoming the capital of their empire, in 1453. The name of the c ...
Orthodox Christianity in the East
... Justinian allowing Theodora to share his throne and take active part in ...
... Justinian allowing Theodora to share his throne and take active part in ...
byzantine empire
... Africa had to pass through the Byzantine Empire. Due to this strategic location, the Byzantine became a very wealthy empire for a time. ...
... Africa had to pass through the Byzantine Empire. Due to this strategic location, the Byzantine became a very wealthy empire for a time. ...
Byzantium
... 2. Codification of Roman law (impact on European legal codes) Reconquest of former Roman territories Expansion of trade 3. Rectangular.-Accurately shows areas around the Equator.Heavily distorts the polar areas. 4. Doric, Ionic and Corinthian 5. The wealthiest citizens of Rome ...
... 2. Codification of Roman law (impact on European legal codes) Reconquest of former Roman territories Expansion of trade 3. Rectangular.-Accurately shows areas around the Equator.Heavily distorts the polar areas. 4. Doric, Ionic and Corinthian 5. The wealthiest citizens of Rome ...
Bellwork - Moore Public Schools
... • Today we will explain why the Roman Empire split and eventually fell. We will discuss the rise of the Byzantine Empire and the effect that Emperor Justinian and his code had on the empire. We will also compare the Justinian code to present day issues and examples. ...
... • Today we will explain why the Roman Empire split and eventually fell. We will discuss the rise of the Byzantine Empire and the effect that Emperor Justinian and his code had on the empire. We will also compare the Justinian code to present day issues and examples. ...
Byzantium - Ms. Byrne's Social Studies Class Website
... • This era continued until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. • From the 13th c. onward, the continual loss of territory and resources meant that Byzantium was never again able to fully quell internal disorders or to exercise independence from outside powers. The empire became ...
... • This era continued until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. • From the 13th c. onward, the continual loss of territory and resources meant that Byzantium was never again able to fully quell internal disorders or to exercise independence from outside powers. The empire became ...
Byzantine Empire
... most of the territory around the Mediterranean Sea. •Due to being strategically located on an Isthmus called the Bosporus Straits, Constantinople became very prosperous by controlling trade routes between Asia, Europe, Russia and the Middle East. •The Byzantine Empire, once part of the greater Roman ...
... most of the territory around the Mediterranean Sea. •Due to being strategically located on an Isthmus called the Bosporus Straits, Constantinople became very prosperous by controlling trade routes between Asia, Europe, Russia and the Middle East. •The Byzantine Empire, once part of the greater Roman ...
Byzantine Empire
... – Slavs and Bulgars from the East – Germanic tribes retook Italy – Muslim tribes took Africa ...
... – Slavs and Bulgars from the East – Germanic tribes retook Italy – Muslim tribes took Africa ...
The Byzantine Empire
... By the early 1400s, the Byzantine Empire had been destroyed and consisted of only Constantinople and two small territories in Greece In 1453 the city of Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks, marking the end of the Byzantine Empire ...
... By the early 1400s, the Byzantine Empire had been destroyed and consisted of only Constantinople and two small territories in Greece In 1453 the city of Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks, marking the end of the Byzantine Empire ...
The Byzantine Empire
... excellent army protected Constantinople. The Byzantine Empire had also many excellent rulers who were wise as popular, who encouraged education and made reforms to laws and government contributing to the strength of their empire. ...
... excellent army protected Constantinople. The Byzantine Empire had also many excellent rulers who were wise as popular, who encouraged education and made reforms to laws and government contributing to the strength of their empire. ...
- Sweet Home Central School District
... and the movement of the capital from Rome to Constantinople in the East. When the capital moved, power shifted eastward. The eastern capital of Constantinople was closer to Silk Road trade and was, therefore, extremely wealthy. It was a crossroads between Europe and Asia. Emperor Constantine moved t ...
... and the movement of the capital from Rome to Constantinople in the East. When the capital moved, power shifted eastward. The eastern capital of Constantinople was closer to Silk Road trade and was, therefore, extremely wealthy. It was a crossroads between Europe and Asia. Emperor Constantine moved t ...
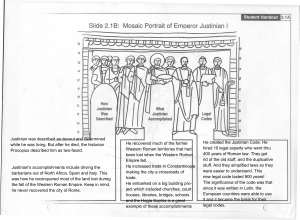
He created the Justinian Code. He hired 10 legal experts who went
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
Byzantine Empire Notesheet
... The Roman Empire had been divided since the reign of Diocletian in the late A.D. 200s. As the Roman empire fell, Diocletian controlled the Western half of the Roman empire and Constantine controlled the Eastern half. By 330, Constantine had built a splendid new capital in Constantinople, on the site ...
... The Roman Empire had been divided since the reign of Diocletian in the late A.D. 200s. As the Roman empire fell, Diocletian controlled the Western half of the Roman empire and Constantine controlled the Eastern half. By 330, Constantine had built a splendid new capital in Constantinople, on the site ...
The Byzantine Empire
... Emperor, if you wish to flee, well and good, you have the money, the ships are ready, the sea is clear. ...
... Emperor, if you wish to flee, well and good, you have the money, the ships are ready, the sea is clear. ...
Byzantine dress

Byzantine dress changed considerably over the thousand years of the Empire, but was essentially conservative. The Byzantines liked color and pattern, and made and exported very richly patterned cloth, especially Byzantine silk, woven and embroidered for the upper classes, and resist-dyed and printed for the lower. A different border or trimming round the edges was very common, and many single stripes down the body or around the upper arm are seen, often denoting class or rank. Taste for the middle and upper classes followed the latest fashions at the Imperial Court. As in the West during the Middle Ages, clothing was very expensive for the poor, who probably wore the same well-worn clothes nearly all the time; this meant in particular that any costume owned by most women needed to fit throughout the full term of a pregnancy.