Frequency domain optical parametric amplification - few
... Historically, the breakthrough in ultrafast high-power laser science came with chirped pulse amplification (CPA) in 1985.It enabled lowering the peak power during amplification by temporally stretching the pulses6. CPA systems, however, lack the capability of few-cycle operation as the gain of the amp ...
... Historically, the breakthrough in ultrafast high-power laser science came with chirped pulse amplification (CPA) in 1985.It enabled lowering the peak power during amplification by temporally stretching the pulses6. CPA systems, however, lack the capability of few-cycle operation as the gain of the amp ...
Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence
... interface, with a space constant that depends on the refractive index of the glass and the sample and the angle of incidence of the excitation light. The fluorophores at the glasssample interface that are within the evanescent field are excited by this excitation light. Excitation light for TIRF mic ...
... interface, with a space constant that depends on the refractive index of the glass and the sample and the angle of incidence of the excitation light. The fluorophores at the glasssample interface that are within the evanescent field are excited by this excitation light. Excitation light for TIRF mic ...
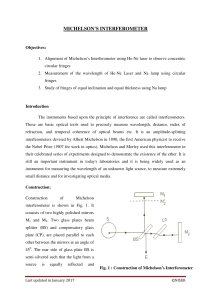
Experiment 24 - School of Physics
... Figure 24-1 shows the layout of the Michelson interferometer used in this experiment. The mirrors, beamsplitter and compensator plate are mounted on a marble slab for stability. The apparatus is housed in a clear plastic box to exclude drafts and to keep the optics clean. Light from the source is sp ...
... Figure 24-1 shows the layout of the Michelson interferometer used in this experiment. The mirrors, beamsplitter and compensator plate are mounted on a marble slab for stability. The apparatus is housed in a clear plastic box to exclude drafts and to keep the optics clean. Light from the source is sp ...
Observation of Localized States in Lieb Photonic
... modulation, as well as the intensity of the profile and the respective input polarization [28]). After this stage, we obtain an amplitude- and phase-modulated light pattern, with a given polarization. In our experiment, light is polarized in the horizontal direction x̂, in order to observe a larger ...
... modulation, as well as the intensity of the profile and the respective input polarization [28]). After this stage, we obtain an amplitude- and phase-modulated light pattern, with a given polarization. In our experiment, light is polarized in the horizontal direction x̂, in order to observe a larger ...
OFC - GEOCITIES.ws
... Single Mode Step Index Fibre: Refractive index changes abruptly at the core-cladding boundary. Light travels along a single path i.e. along the axis. This fibre has low value of NA and Intermodal dispersion does not exist (only one mode exist). With careful choice of material, dimension and wavel ...
... Single Mode Step Index Fibre: Refractive index changes abruptly at the core-cladding boundary. Light travels along a single path i.e. along the axis. This fibre has low value of NA and Intermodal dispersion does not exist (only one mode exist). With careful choice of material, dimension and wavel ...
Topic 8: Holography
... 1. Positive Bleach Replace silver with a transparent salt, phase different encoded in thickness of gelatin plus salts. 2. Reversal Bleach Remove silver and let gelatin fall to encode negative of phase distribution. Process works, but again chemistry difficult, Problems are ...
... 1. Positive Bleach Replace silver with a transparent salt, phase different encoded in thickness of gelatin plus salts. 2. Reversal Bleach Remove silver and let gelatin fall to encode negative of phase distribution. Process works, but again chemistry difficult, Problems are ...
Collective effects in the radiation pressure force
... of view, and as far as diffraction effects are concerned, the atomic cloud can be described as a dielectric medium with an effective complex refractive index, even when the atoms are separated by more than a wavelength. The real part of the index corresponds to the coherent scattering of the inciden ...
... of view, and as far as diffraction effects are concerned, the atomic cloud can be described as a dielectric medium with an effective complex refractive index, even when the atoms are separated by more than a wavelength. The real part of the index corresponds to the coherent scattering of the inciden ...
A few words about possible applications
... Photonic Crystal (TPC) suitable for applications in optical communication networks. To achieve this goal we investigate several aspects related to new material engineering, involving composite liquid crystal media. Photonic crystals – periodical structures with a period close to the wavelength of li ...
... Photonic Crystal (TPC) suitable for applications in optical communication networks. To achieve this goal we investigate several aspects related to new material engineering, involving composite liquid crystal media. Photonic crystals – periodical structures with a period close to the wavelength of li ...
Practical Aspects of Mirror Usage in Optical Systems for
... purchase a mirror, and is confronted by a large number of offerings. Each part description indicates it is to be used for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use fo ...
... purchase a mirror, and is confronted by a large number of offerings. Each part description indicates it is to be used for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use fo ...
Practical Aspects of Mirror Usage in Optical Systems for
... purchase a mirror, and is confronted by a large number of offerings. Each part description indicates it is to be used for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use fo ...
... purchase a mirror, and is confronted by a large number of offerings. Each part description indicates it is to be used for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use fo ...
Holographic 3-D Displays - Electro-holography within
... to reconstruct the wave field of a 3-D scene in space with coherent light. Such displays must operate at or near video rate to merit the name of video holography. Furthermore, real-time holography must not only display the hologram at video rate but also compute the hologram frames in real time to e ...
... to reconstruct the wave field of a 3-D scene in space with coherent light. Such displays must operate at or near video rate to merit the name of video holography. Furthermore, real-time holography must not only display the hologram at video rate but also compute the hologram frames in real time to e ...
here
... the results. We believe a better model of the Fresnel effects near the edge of the bubbles would improve some of the reflections. Compare the edges of the real bubble with the rendered bubble in figure 7. Also the bubble environment map is from the same location but a different angle. There is a not ...
... the results. We believe a better model of the Fresnel effects near the edge of the bubbles would improve some of the reflections. Compare the edges of the real bubble with the rendered bubble in figure 7. Also the bubble environment map is from the same location but a different angle. There is a not ...
Part 3 - MZA Associates Corporation
... might reach the given receiver. To do this, we basically need to determine what the image of the receiver would look like as seen from the source, taking into account any intervening optics, and also any physical effects entering in along the path. If the optical path is in vacuum or still air, the ...
... might reach the given receiver. To do this, we basically need to determine what the image of the receiver would look like as seen from the source, taking into account any intervening optics, and also any physical effects entering in along the path. If the optical path is in vacuum or still air, the ...
High resolution time-resolved imaging system in the
... 100 keV (0.01 nm). The X-rays with photon energies below and higher than 10 keV (0.12 nm) are called soft and hard X-rays respectively [15]. Soft X-rays are highly absorbed in conventional visible optics while hard X-rays are penetrable in materials. The characteristics of X-rays having short wavele ...
... 100 keV (0.01 nm). The X-rays with photon energies below and higher than 10 keV (0.12 nm) are called soft and hard X-rays respectively [15]. Soft X-rays are highly absorbed in conventional visible optics while hard X-rays are penetrable in materials. The characteristics of X-rays having short wavele ...
Light Propagation with Phase Discontinuities
... scattered light from a straight rod antenna made of a perfect electric conductor (20). The vertical dashed line indicates the first-order dipolar resonance of the antenna. (B) A V-antenna supports symmetric and antisymmetric modes, which are excited, respectively, by components of the incident field ...
... scattered light from a straight rod antenna made of a perfect electric conductor (20). The vertical dashed line indicates the first-order dipolar resonance of the antenna. (B) A V-antenna supports symmetric and antisymmetric modes, which are excited, respectively, by components of the incident field ...
aa f - Freie Universität Berlin
... Experiments and reports done in team work consisting of a group of 6 (3 pairs) under the assistance of a tutor. Completion of introductory reports on the subject matter and physical background, presentation of the experimental findings with a summary and critical discussion of the results as an exer ...
... Experiments and reports done in team work consisting of a group of 6 (3 pairs) under the assistance of a tutor. Completion of introductory reports on the subject matter and physical background, presentation of the experimental findings with a summary and critical discussion of the results as an exer ...
Quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry
... around the interferogram fringe frequency. However, at this point, it lacks some gradient information to recover a full two dimensional phase-field. Multiwave interferometry [18] extends this principle to more than one gradient direction. In the case of QWLSI, four replicas are created by a specific ...
... around the interferogram fringe frequency. However, at this point, it lacks some gradient information to recover a full two dimensional phase-field. Multiwave interferometry [18] extends this principle to more than one gradient direction. In the case of QWLSI, four replicas are created by a specific ...
Chapter 25: Interference and Diffraction
... Example (text problem 25.12): A Michelson interferometer is adjusted so that a bright fringe appears on the screen. As one of the mirrors is moved 25.8 m, 92 bright fringes are counted on the screen. What is the wavelength of the light used in the interferometer? Moving the mirror a distance d intr ...
... Example (text problem 25.12): A Michelson interferometer is adjusted so that a bright fringe appears on the screen. As one of the mirrors is moved 25.8 m, 92 bright fringes are counted on the screen. What is the wavelength of the light used in the interferometer? Moving the mirror a distance d intr ...
Nonlinear Raman-Nath second harmonic generation with structured
... 16] have been intensively studied in NPCs. And various patterns of 2D nonlinear photonic structures have also been demonstrated, including square, hexagonal lattices, annular periodical, or even random structures [17–21]. Especially, with holography concept introduced to nonlinear optics, arbitrary ...
... 16] have been intensively studied in NPCs. And various patterns of 2D nonlinear photonic structures have also been demonstrated, including square, hexagonal lattices, annular periodical, or even random structures [17–21]. Especially, with holography concept introduced to nonlinear optics, arbitrary ...
Michelson Interferometer
... difference along the line of intersection is zero and therefore, is same for all the wavelengths. When a source of white light is used we get central achromatic bright fringe. On either side of central fringe, few coloured straight fringes are observed. ...
... difference along the line of intersection is zero and therefore, is same for all the wavelengths. When a source of white light is used we get central achromatic bright fringe. On either side of central fringe, few coloured straight fringes are observed. ...
Design and use of guided mode resonance filters for
... Even though the principles of diffraction had been known since the time of Newton, it was Rittenhouse who in 1786, produced the first man-made diffraction grating from hairs spaced by the threads of two fine screws [1]. Years later, in 1902, Wood noticed unexpected rapid intensity variations in ligh ...
... Even though the principles of diffraction had been known since the time of Newton, it was Rittenhouse who in 1786, produced the first man-made diffraction grating from hairs spaced by the threads of two fine screws [1]. Years later, in 1902, Wood noticed unexpected rapid intensity variations in ligh ...
The generation of nondiffracting beams using
... wavefields associated with laser beams are of special interest in the undergraduate physics curricula. One problem arises when a laser beam is to be shaped to a particular profile. For most applications, it is desirable that most of the laser energy be confined to a small spot. Many laser resonators ...
... wavefields associated with laser beams are of special interest in the undergraduate physics curricula. One problem arises when a laser beam is to be shaped to a particular profile. For most applications, it is desirable that most of the laser energy be confined to a small spot. Many laser resonators ...
Light Measurement Handbook
... segment of the UV spectrum. The harmful effect at 270 nm is two times greater than at the 254 and 297 nm mercury lines, and 9000 times greater than at the 365 nm mercury line. The outlying extremes of the bandwidth are important to consider as well. If, for example, you are trying to assess the effe ...
... segment of the UV spectrum. The harmful effect at 270 nm is two times greater than at the 254 and 297 nm mercury lines, and 9000 times greater than at the 365 nm mercury line. The outlying extremes of the bandwidth are important to consider as well. If, for example, you are trying to assess the effe ...
Optical phase measurement emphasized
... change upon total internal reflection, which is revealed by modification of the polarization state. One can send a laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we ...
... change upon total internal reflection, which is revealed by modification of the polarization state. One can send a laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we ...
Optical Behavior of Pellicles
... less than 1.3). Thus, single layer pellicles are the most common at these wavelengths. A typical ArF pellicle will have a complex refractive index of n+i = 1.40 + i0.0001 and a thickness of 828 nm. While designed to protect the mask from particles, pellicles are in fact optical elements within the i ...
... less than 1.3). Thus, single layer pellicles are the most common at these wavelengths. A typical ArF pellicle will have a complex refractive index of n+i = 1.40 + i0.0001 and a thickness of 828 nm. While designed to protect the mask from particles, pellicles are in fact optical elements within the i ...
Diffraction grating

In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as the dispersive element. Because of this, gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers.For practical applications, gratings generally have ridges or rulings on their surface rather than dark lines. Such gratings can be either transmissive or reflective. Gratings which modulate the phase rather than the amplitude of the incident light are also produced, frequently using holography.The principles of diffraction gratings were discovered by James Gregory, about a year after Newton's prism experiments, initially with items such as bird feathers. The first man-made diffraction grating was made around 1785 by Philadelphia inventor David Rittenhouse, who strung hairs between two finely threaded screws. This was similar to notable German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer's wire diffraction grating in 1821.Diffraction can create ""rainbow"" colors when illuminated by a wide spectrum (e.g., continuous) light source. The sparkling effects from the closely spaced narrow tracks on optical storage disks such as CD's or DVDs are an example, while the similar rainbow effects caused by thin layers of oil (or gasoline, etc.) on water are not caused by a grating, but rather by interference effects in reflections from the closely spaced transmissive layers (see Examples, below). A grating has parallel lines, while a CD has a spiral of finely-spaced data tracks. Diffraction colors also appear when one looks at a bright point source through a translucent fine-pitch umbrella-fabric covering. Decorative patterned plastic films based on reflective grating patches are very inexpensive, and are commonplace.