Unit 1, Chapter 1 Test Review Key Issue 1: How Do Geographers
... primarily to ease the husband’s daily commute to work. Movem across space varies by ethnicity because in many neighborhoods the residents are virtually all white or virtually all persons of color. Cultural Identity in Contemporary Geography Thought The experiences of women differ from those of men, ...
... primarily to ease the husband’s daily commute to work. Movem across space varies by ethnicity because in many neighborhoods the residents are virtually all white or virtually all persons of color. Cultural Identity in Contemporary Geography Thought The experiences of women differ from those of men, ...
Eratosthenes
... struck the bottom of the well on the summer solstice, Eratosthenes determined that he could discover the circumference of the earth. •Eratosthenes measured the altitude of the noontime sun at Alexandria at its maximum on Jun 21st. • Erastosthenes also calculated the tilt of earths axis ...
... struck the bottom of the well on the summer solstice, Eratosthenes determined that he could discover the circumference of the earth. •Eratosthenes measured the altitude of the noontime sun at Alexandria at its maximum on Jun 21st. • Erastosthenes also calculated the tilt of earths axis ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... on the ground. The line represented the coastline where they stood. The local chief drew additional lines. A young man added piles of rocks to represent the village and nearby settlements. When they were done, they had an informal map of the ...
... on the ground. The line represented the coastline where they stood. The local chief drew additional lines. A young man added piles of rocks to represent the village and nearby settlements. When they were done, they had an informal map of the ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... Region: • Regions are fundamental organizing units of geography. • Geographers use regions to give order to the earth’s surface. • We organize space into regions every day. Every time we refer to an area by saying: – “I’m going downtown” or “down South,” or “I’d like to live in that neighborhood,” ...
... Region: • Regions are fundamental organizing units of geography. • Geographers use regions to give order to the earth’s surface. • We organize space into regions every day. Every time we refer to an area by saying: – “I’m going downtown” or “down South,” or “I’d like to live in that neighborhood,” ...
Map Skills
... charts, other sources and representations such as aerial and shuttle photographs, satellite-produced images, geographic information system (GIS), encyclopedias, almanacs, dictionaries, atlases, and computer-based technologies. Construct and use maps of locales, regions, continents, and the world tha ...
... charts, other sources and representations such as aerial and shuttle photographs, satellite-produced images, geographic information system (GIS), encyclopedias, almanacs, dictionaries, atlases, and computer-based technologies. Construct and use maps of locales, regions, continents, and the world tha ...
5 Themes of Geography
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE MEGA PACKET
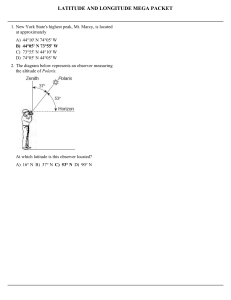
... the time-exposure photograph shown below. The photograph was taken by aiming a camera at a portion of the night sky above a New York State location and leaving the camera's shutter open for a period of time to record star trails. ...
... the time-exposure photograph shown below. The photograph was taken by aiming a camera at a portion of the night sky above a New York State location and leaving the camera's shutter open for a period of time to record star trails. ...
Capitolo 1
... This location is called the geomagnetic South Pole, and its antipodal point at (80.24°N,72.54W) is known as the geomagnetic North Pole. The axis passing through these two points defines the zaxis of the geomagnetic reference frame. The xaxis of this coordinate system is chosen in such a way that t ...
... This location is called the geomagnetic South Pole, and its antipodal point at (80.24°N,72.54W) is known as the geomagnetic North Pole. The axis passing through these two points defines the zaxis of the geomagnetic reference frame. The xaxis of this coordinate system is chosen in such a way that t ...
what is geography - Renton School District
... Geographers sift through “clues” to discover the reasons that places are the way they are and the reasons that people interact with the land the way they do. To organize their detective work, many geographers use the Five Fundamentals Themes of Geography. These fundamental themes, or basic ideas, ar ...
... Geographers sift through “clues” to discover the reasons that places are the way they are and the reasons that people interact with the land the way they do. To organize their detective work, many geographers use the Five Fundamentals Themes of Geography. These fundamental themes, or basic ideas, ar ...
SS Weekly Calendar for 8 8 16
... north and south poles; "the equator is the boundary between the northern and southern hemispheres" fertile - Soil that supports and maintains healthy and abundant plant growth Fertile Crescent - a geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to ...
... north and south poles; "the equator is the boundary between the northern and southern hemispheres" fertile - Soil that supports and maintains healthy and abundant plant growth Fertile Crescent - a geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to ...
5 Themes of Geography
... – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
Introduction to Geography
... Reveals how humans modify local environment. E.g.? What about Central Park? Pg 20 ...
... Reveals how humans modify local environment. E.g.? What about Central Park? Pg 20 ...
Five Themes of Geography
... Set your new “fly to” location to “Pará, Brazil.” Take a look around, then use the timeline feature. The timeline goes back to 1975. Compare the geography of Pará between then and now. Why do you think these changes have happened? Etc. _____________________________________________________ __________ ...
... Set your new “fly to” location to “Pará, Brazil.” Take a look around, then use the timeline feature. The timeline goes back to 1975. Compare the geography of Pará between then and now. Why do you think these changes have happened? Etc. _____________________________________________________ __________ ...
EUROPEAN GEOGRAPHY - Glassboro Public Schools
... The environment means different things to different people, depending on their cultural backgrounds and technological resources. In studying human/environment interaction, geographers look at all the effects—positive and negative—that occur when people interact with their surroundings. Sometimes a h ...
... The environment means different things to different people, depending on their cultural backgrounds and technological resources. In studying human/environment interaction, geographers look at all the effects—positive and negative—that occur when people interact with their surroundings. Sometimes a h ...
Chapter03b
... The Earth orbits the Sun on an almost circular orbit. The Earth axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the ecliptic at 23.5 degrees. The inclination of the of the Earth axis is the reason for the presence of seasons. ♦ The angle at which the sun rays hit the surface of the Earth at a given latit ...
... The Earth orbits the Sun on an almost circular orbit. The Earth axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the ecliptic at 23.5 degrees. The inclination of the of the Earth axis is the reason for the presence of seasons. ♦ The angle at which the sun rays hit the surface of the Earth at a given latit ...
Satellite communication 10EC662
... Ascending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from south to north. Descending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from north to south. Line of nodes:The line joining the ascending and descending nodes through the center of the earth. Incl ...
... Ascending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from south to north. Descending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane going from north to south. Line of nodes:The line joining the ascending and descending nodes through the center of the earth. Incl ...
1.1 The Geographer`s Tools
... • Absolute location– describes a place’s exact position on the Earth or geographic address • Relative location —the location of a place as described by places near it. ...
... • Absolute location– describes a place’s exact position on the Earth or geographic address • Relative location —the location of a place as described by places near it. ...
5 Themes of Geography
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
Geography Glossary - Arizona Geographic Alliance
... Place: Location having distinctive characteristics that give it meaning and character and distinguish it from other locations. Political boundaries: The limit or extent within which a system exists or functions (such as governments of cities, counties, states, countries). Population density: The nu ...
... Place: Location having distinctive characteristics that give it meaning and character and distinguish it from other locations. Political boundaries: The limit or extent within which a system exists or functions (such as governments of cities, counties, states, countries). Population density: The nu ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.