Five Themes of Geography
... the world into many types of regions. For example, countries, states, and cities are political regions. The people in any one of these places live under the same government. Other features, such as climate and culture, can be used to define regions. Therefore the same place can be found in more than ...
... the world into many types of regions. For example, countries, states, and cities are political regions. The people in any one of these places live under the same government. Other features, such as climate and culture, can be used to define regions. Therefore the same place can be found in more than ...
Chr_IRM_9e_Ch01-1
... 11. Define latitude and parallel and define longitude and meridian using a simple sketch with labels. On a map or globe, lines denoting angles of latitude run east and west, parallel to Earth’s equator. Latitude is an angular distance north or south of the equator measured from a point at the center ...
... 11. Define latitude and parallel and define longitude and meridian using a simple sketch with labels. On a map or globe, lines denoting angles of latitude run east and west, parallel to Earth’s equator. Latitude is an angular distance north or south of the equator measured from a point at the center ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... parts, or hemispheres. We divide our planet into North and South halves, OR into East and West halves. • Which 2 hemisphere’s do we live in? ...
... parts, or hemispheres. We divide our planet into North and South halves, OR into East and West halves. • Which 2 hemisphere’s do we live in? ...
Map Master Skills Handbook
... and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the study of Geography a little easier to understand, geographers have divided it up into 5 smaller topics, or themes. Let’s find out what they are! ...
... and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the study of Geography a little easier to understand, geographers have divided it up into 5 smaller topics, or themes. Let’s find out what they are! ...
St Ambrose RC Primary School GEOGRAPHY YEAR 6 CORE
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
Basics Review - Regional School District 17
... • Earth as a sphere is divided into 360º of longitude. – Divide 360º by 24 time zones (one for each hour of day) equals 15º. • Each 15º band of longitude is assigned to a standard time zone. • Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is… – Located at the prime meridian (0º longitude). • Passes through Royal Observ ...
... • Earth as a sphere is divided into 360º of longitude. – Divide 360º by 24 time zones (one for each hour of day) equals 15º. • Each 15º band of longitude is assigned to a standard time zone. • Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is… – Located at the prime meridian (0º longitude). • Passes through Royal Observ ...
Yr 5 Geography
... Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle. I can name the basic features of each planet in our solar system. I can use maps and aerial photographs and google earth to help me identify locations and specific features in Europe in relation to WW1. I can locate and name the features on the planet includin ...
... Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle. I can name the basic features of each planet in our solar system. I can use maps and aerial photographs and google earth to help me identify locations and specific features in Europe in relation to WW1. I can locate and name the features on the planet includin ...
St Ambrose RC Primary School GEOGRAPHY YEAR 4 CORE
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
Geography Powerpoint
... • Relative Location - The location of one place in relation to another • Absolute Location - the exact spot on the earth’s ...
... • Relative Location - The location of one place in relation to another • Absolute Location - the exact spot on the earth’s ...
St Ambrose RC Primary School GEOGRAPHY YEAR 5 CORE
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
... concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mo ...
Apparent Forces
... = 2Ωu cos φ + Dt a Where u = zonal wind, v = meridional wind, w = vertical wind, φ = latitude, and a = radius of earth. The second terms on the right side arise from curvature effects, and can be safely neglected through scale analysis since u << ΩR. Also, the quantity 2Ωsinφ is abbreviated with the ...
... = 2Ωu cos φ + Dt a Where u = zonal wind, v = meridional wind, w = vertical wind, φ = latitude, and a = radius of earth. The second terms on the right side arise from curvature effects, and can be safely neglected through scale analysis since u << ΩR. Also, the quantity 2Ωsinφ is abbreviated with the ...
Jeopardy Review
... Unlike a physical map, this kind of map tells only one kind of information such as elevation, rainfall, or population density. ...
... Unlike a physical map, this kind of map tells only one kind of information such as elevation, rainfall, or population density. ...
Mapping Earth`s Surface
... 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
... 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
Place & Regions
... north-south between the poles. --The equator is defined as 0 degrees --The North Pole is 90 degrees north --The South Pole is 90 degrees south --Lines of latitude are all parallel to each other, thus they are often referred to as parallels. They look like rungs on a ladder. Remember LA for ladder an ...
... north-south between the poles. --The equator is defined as 0 degrees --The North Pole is 90 degrees north --The South Pole is 90 degrees south --Lines of latitude are all parallel to each other, thus they are often referred to as parallels. They look like rungs on a ladder. Remember LA for ladder an ...
Ch.1 - Looking at the Earth
... seam very far away (are we there yet?). As you grew older, the distance to these locations probably seam to shrink ...
... seam very far away (are we there yet?). As you grew older, the distance to these locations probably seam to shrink ...
11NESRT Mapping Lab
... 3. Will the North Star be higher in the sky when viewed from Riverhead or Old Forge? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. In which city would Polaris appear at an altitude of 42 degrees? _________________________________ 5. At approximate ...
... 3. Will the North Star be higher in the sky when viewed from Riverhead or Old Forge? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. In which city would Polaris appear at an altitude of 42 degrees? _________________________________ 5. At approximate ...
FREE Sample Here
... The world’s time zones were established based on the relationship among: a. latitude, Earth’s rotation, and time b. longitude, Earth’s rotation, and time c. latitude, Earth’s revolution, and time d. longitude, Earth’s revolution, and time ...
... The world’s time zones were established based on the relationship among: a. latitude, Earth’s rotation, and time b. longitude, Earth’s rotation, and time c. latitude, Earth’s revolution, and time d. longitude, Earth’s revolution, and time ...
Location - SP Moodle
... distances east and west of the Prime Meridian. A place's absolute location is defined with latitude and longitude lines. This is its exact location. The geography theme of location can also deal with relative location. Relative location means how a place is related or connected to other places throu ...
... distances east and west of the Prime Meridian. A place's absolute location is defined with latitude and longitude lines. This is its exact location. The geography theme of location can also deal with relative location. Relative location means how a place is related or connected to other places throu ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... ♦ If you wanted to know about Australia and found out that they were dealing with a large amount of water pollution that was caused by factories dumping their sewage into the bodies of water, you would see one example of how people can shape their environment. In this case you would be dealing with ...
... ♦ If you wanted to know about Australia and found out that they were dealing with a large amount of water pollution that was caused by factories dumping their sewage into the bodies of water, you would see one example of how people can shape their environment. In this case you would be dealing with ...
Introduction to Geography
... -The central line of Longitude is called the Prime Meridian. It measures 0* Longitude. -This line runs directly through Greenwich, England. -Anything to the left of the Prime Meridian is West Longitude. -Anything to the right of the Prime Meridian is East Longitude. ...
... -The central line of Longitude is called the Prime Meridian. It measures 0* Longitude. -This line runs directly through Greenwich, England. -Anything to the left of the Prime Meridian is West Longitude. -Anything to the right of the Prime Meridian is East Longitude. ...
5themesofgeography
... • Describes where places are at on earth. • Types of Location: – ABSOLUTE: exact location on earth (fixed) • Doesn’t change – Latitude/Longitude – Hemispheres – Grid System – Address – RELATIVE: compared to other places (variable) • Changes dependent upon where you’re comparing it to. – Miles – Dist ...
... • Describes where places are at on earth. • Types of Location: – ABSOLUTE: exact location on earth (fixed) • Doesn’t change – Latitude/Longitude – Hemispheres – Grid System – Address – RELATIVE: compared to other places (variable) • Changes dependent upon where you’re comparing it to. – Miles – Dist ...
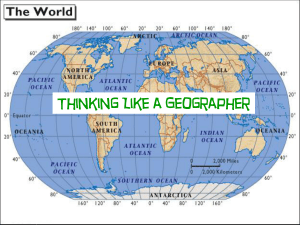
Thinking Like a Geographer
... Location is the position of a place on the Earth’s surface. Location explains: Where is it? Why is it there? ...
... Location is the position of a place on the Earth’s surface. Location explains: Where is it? Why is it there? ...
Termsand_Defs_AW1_2_
... The shape produced when mineral grains have freedom to form in any direction A solid substance whose atoms are locked together into fixed patterns; true of all minerals A substance that contains only one kind of atom A rough-estimate weight test for minerals Atoms of elements other than the key elem ...
... The shape produced when mineral grains have freedom to form in any direction A solid substance whose atoms are locked together into fixed patterns; true of all minerals A substance that contains only one kind of atom A rough-estimate weight test for minerals Atoms of elements other than the key elem ...
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts 1 Basic Concepts Chapter Outline
... because all latitude lines are parallel to the equator. The equator is the parallel with the greatest circumference and is the baseline for measuring latitude. Telling Time Longitude plays an important role in calculating time. If we let every fifteenth degree of longitude represent one time zone, a ...
... because all latitude lines are parallel to the equator. The equator is the parallel with the greatest circumference and is the baseline for measuring latitude. Telling Time Longitude plays an important role in calculating time. If we let every fifteenth degree of longitude represent one time zone, a ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.