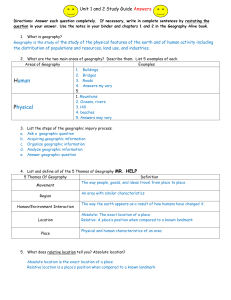
The Five Themes of Geography
... Movement looks at how and why things move. It looks at why people leave a country, how goods are moved, and how both affect the land or the people. ...
... Movement looks at how and why things move. It looks at why people leave a country, how goods are moved, and how both affect the land or the people. ...
Unit One Geography: It`s Nature and Perspectives
... means/resources to work around these limitations and adjust their environments. ...
... means/resources to work around these limitations and adjust their environments. ...
Relative Location
... takes to get there. • Psychological Distance refers to how people view distance. Studies show that the more familiar we become with a place, we think it is closer. ...
... takes to get there. • Psychological Distance refers to how people view distance. Studies show that the more familiar we become with a place, we think it is closer. ...
Why Is Each Point on Earth Unique?
... The contemporary cultural landscape approach in geography— sometimes called the regional studies approach—was initiated in France by Paul Vidal de la Blache (1845–1918) and Jean Brunhes (1869–1930). It was later adopted by several American geographers, including Carl Sauer (1889–1975) and Robert Pla ...
... The contemporary cultural landscape approach in geography— sometimes called the regional studies approach—was initiated in France by Paul Vidal de la Blache (1845–1918) and Jean Brunhes (1869–1930). It was later adopted by several American geographers, including Carl Sauer (1889–1975) and Robert Pla ...
The Five Themes of Geography student notes
... o 1. o 2. o 3. o 4 o 5. Location: Where is it? o Two types: _________________ location and ________________ location o ___________________ location: a specific place on the Earth’s surface, using a grid system (latitude and longitude); a global address Example: o ___________________location: whe ...
... o 1. o 2. o 3. o 4 o 5. Location: Where is it? o Two types: _________________ location and ________________ location o ___________________ location: a specific place on the Earth’s surface, using a grid system (latitude and longitude); a global address Example: o ___________________location: whe ...
1 - OnCourse
... Relief -- raised detail map which shows natural features like mountains and valleys Cardinal Directions—North, South, East, and West ...
... Relief -- raised detail map which shows natural features like mountains and valleys Cardinal Directions—North, South, East, and West ...
Unit-1-and-2-Study-Guide-Answers-
... Step 1: Find the compass rose and scale on the map. Use these tools to estimate the size of Europe from north to south and from east to west. Step 2: Look at the natural resource symbols on the map. On the map legend, circle the three or four most common resources you see on the map. Step 3: Study t ...
... Step 1: Find the compass rose and scale on the map. Use these tools to estimate the size of Europe from north to south and from east to west. Step 2: Look at the natural resource symbols on the map. On the map legend, circle the three or four most common resources you see on the map. Step 3: Study t ...
Chapter 1 Key Issue Essential Questions
... D. what is a "vernacular region"'? Give 3 examples. 14. What is "spatial association"? Why do we need this? 15. Regional Integration of Culture: what is "culture"? Different meanings? 16. What do geographers study within culture? List/discuss importance. 17. How do geographers divide up the world? W ...
... D. what is a "vernacular region"'? Give 3 examples. 14. What is "spatial association"? Why do we need this? 15. Regional Integration of Culture: what is "culture"? Different meanings? 16. What do geographers study within culture? List/discuss importance. 17. How do geographers divide up the world? W ...
OceaniaLearningTargetsTeacher 2016
... ● Climate, population, precipitation, physical features, political features, economics ...
... ● Climate, population, precipitation, physical features, political features, economics ...
The American Journey
... • The _________________________ and ___________________ rivers make up the longest and most important river system in the ...
... • The _________________________ and ___________________ rivers make up the longest and most important river system in the ...
Transverse Mercator Projection
... the globe. Scale changes are slight in the mid latitudes, amounting to only about 3 percent at 30 north or south from the equator. However, since the meridians do not converge, areas in the higher latitudes are greatly enlarged when the equator is used as the standard parallel. An outstanding featur ...
... the globe. Scale changes are slight in the mid latitudes, amounting to only about 3 percent at 30 north or south from the equator. However, since the meridians do not converge, areas in the higher latitudes are greatly enlarged when the equator is used as the standard parallel. An outstanding featur ...
Five Frequently Encountered Map Projections
... the globe. Scale changes are slight in the mid latitudes, amounting to only about 3 percent at 30 north or south from the equator. However, since the meridians do not converge, areas in the higher latitudes are greatly enlarged when the equator is used as the standard parallel. An outstanding featur ...
... the globe. Scale changes are slight in the mid latitudes, amounting to only about 3 percent at 30 north or south from the equator. However, since the meridians do not converge, areas in the higher latitudes are greatly enlarged when the equator is used as the standard parallel. An outstanding featur ...
Ch 13 Sec 1 Climate and Climate Change NoteTaking
... • ____________ is the distance north or south from the equator and is expressed in ____________ . • The equator is located at ______ latitude. The most northerly latitude is the North Pole, at ______ north, whereas the most southerly latitude is the South Pole, at ______ south. • Latitude strongly a ...
... • ____________ is the distance north or south from the equator and is expressed in ____________ . • The equator is located at ______ latitude. The most northerly latitude is the North Pole, at ______ north, whereas the most southerly latitude is the South Pole, at ______ south. • Latitude strongly a ...
5 Themes of Geography
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
100 points
... The 00 meridian is the same thing as the __________________ meridian. a. International date line b. Equator c. Prime d. Geographic grid ...
... The 00 meridian is the same thing as the __________________ meridian. a. International date line b. Equator c. Prime d. Geographic grid ...
BCS311 Module 1A
... scales, above, on, and beneath the Earth’s surface. In order to describe these phenomena, it is important to know where they occur in relation to the Earth’s surface: a coordinate grid system is needed. Earth scientists use a coordinate grid system consisting of parallels of latitude and meridians o ...
... scales, above, on, and beneath the Earth’s surface. In order to describe these phenomena, it is important to know where they occur in relation to the Earth’s surface: a coordinate grid system is needed. Earth scientists use a coordinate grid system consisting of parallels of latitude and meridians o ...
File - Team Impact
... • Uses latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... • Uses latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
What kind of place is it?
... East longitude Marshall Islands are 10o00' North latitude and 165o00' East longitude ...
... East longitude Marshall Islands are 10o00' North latitude and 165o00' East longitude ...
Mr. Johnson`s Geography
... To find a place you need to know it’s location. Location can be absolute or relative. • Absolute location provides a definite reference to locate a place. The reference can be latitude and longitude or a street address. For example, the absolute location of OCMS is 1404 South Main Street, Hartford, ...
... To find a place you need to know it’s location. Location can be absolute or relative. • Absolute location provides a definite reference to locate a place. The reference can be latitude and longitude or a street address. For example, the absolute location of OCMS is 1404 South Main Street, Hartford, ...
The ABC of Geography
... on the map. Exemple: 1:100,000 - one centimeter on the map equals 100,000 centimeters (1 kilometer) ...
... on the map. Exemple: 1:100,000 - one centimeter on the map equals 100,000 centimeters (1 kilometer) ...
Geographic coordinate systems
... datum would allow for a single datum to cover consistently North America and surrounding areas. The North American Datum of 1983 is based upon both earth and satellite observations, using the GRS80 spheroid. The origin for this datum is the earth’s center of mass. This affects the surface location o ...
... datum would allow for a single datum to cover consistently North America and surrounding areas. The North American Datum of 1983 is based upon both earth and satellite observations, using the GRS80 spheroid. The origin for this datum is the earth’s center of mass. This affects the surface location o ...
GY305 Lecture3 Geomagnetics
... • Paleo‐Polar Wandering over wide geographic areas is only apparent‐ the true pole position never strays far from the geographic pole • The actual reason for Paleo‐Polar Wandering is plate tectonic motions • Latitude migration changes the apparent latitude of the paleo‐pole • Longitude migratio ...
... • Paleo‐Polar Wandering over wide geographic areas is only apparent‐ the true pole position never strays far from the geographic pole • The actual reason for Paleo‐Polar Wandering is plate tectonic motions • Latitude migration changes the apparent latitude of the paleo‐pole • Longitude migratio ...
5 Themes of Geography Class Notes - Hewlett
... A region is a "world within a world" - an area with certain characteristics that make it distinct from surrounding areas. There are two kinds of regions: Physical regions: a land area with common features such as landscape or climate. Cultural regions: an area defined by its human traits such as ...
... A region is a "world within a world" - an area with certain characteristics that make it distinct from surrounding areas. There are two kinds of regions: Physical regions: a land area with common features such as landscape or climate. Cultural regions: an area defined by its human traits such as ...
2 - Earth Sun Climate Regions.pptx
... Indirect rays: When a hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, the direct rays of the sun or angle of incidence is lower and it is winter in that hemisphere. ...
... Indirect rays: When a hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, the direct rays of the sun or angle of incidence is lower and it is winter in that hemisphere. ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.