The Geographer`s Tools
... Location Absolute Location is the exact place on the earth where a geographic feature is found. (for example, Houston is located at 29°N , 95°W) 29°45′46″N 95°22′59″W Relative Location describes a place in comparison to other places around it. (for example: Galveston, TX is southeast of Houston, TX) ...
... Location Absolute Location is the exact place on the earth where a geographic feature is found. (for example, Houston is located at 29°N , 95°W) 29°45′46″N 95°22′59″W Relative Location describes a place in comparison to other places around it. (for example: Galveston, TX is southeast of Houston, TX) ...
Earth`s Rotation
... Changing Seasons If we are closer in January than in July, why is it that we have are coldest days of the year during this time? • Earth’s tilted axis combined with the revolution causes seasons to change ...
... Changing Seasons If we are closer in January than in July, why is it that we have are coldest days of the year during this time? • Earth’s tilted axis combined with the revolution causes seasons to change ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Where are we? • Absolute Location – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
... Where are we? • Absolute Location – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. ...
World Geography
... seam very far away (are we there yet?). As you grew older, the distance to these locations probably seam to shrink ...
... seam very far away (are we there yet?). As you grew older, the distance to these locations probably seam to shrink ...
Summary: What Is Geography?
... places. North Carolina's relative location is south of Virginia and north of South Carolina. Geographers also think about absolute location. They use lines of latitude and longitude to describe a place's absolute location. For example, Fayetteville, North Carolina, is located at 35 degrees north lat ...
... places. North Carolina's relative location is south of Virginia and north of South Carolina. Geographers also think about absolute location. They use lines of latitude and longitude to describe a place's absolute location. For example, Fayetteville, North Carolina, is located at 35 degrees north lat ...
File
... Conic Projection A conic projection comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Conic projections are best suited for showing limited east–west areas that are not too far from the Equator. For these uses, a conic projection can indicate distances and directions fairly accurately. ...
... Conic Projection A conic projection comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Conic projections are best suited for showing limited east–west areas that are not too far from the Equator. For these uses, a conic projection can indicate distances and directions fairly accurately. ...
THE PHILIPPINE ENVIRONMENT
... Where does water in your community come from? You collect them when the rain falls or get them from the river, deep well, or spring. But where does water from rivers, lakes, and springs originate? They come from a watershed – an area of land on a slope which drains its water into a stream and its t ...
... Where does water in your community come from? You collect them when the rain falls or get them from the river, deep well, or spring. But where does water from rivers, lakes, and springs originate? They come from a watershed – an area of land on a slope which drains its water into a stream and its t ...
5 Themes of Geography
... LOCATION Where are we? • Absolute Location • Exact Location • A latitude & longitude or a st. address • Paris France is o 48 North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. ...
... LOCATION Where are we? • Absolute Location • Exact Location • A latitude & longitude or a st. address • Paris France is o 48 North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Earth
... – angle north or south of the equator – 7 important latitudes: – Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn (23.5° N and S) – Equator (0°) – Poles (90° N and S) – Arctic and Antarctic Circles (66.5° N and S) ...
... – angle north or south of the equator – 7 important latitudes: – Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn (23.5° N and S) – Equator (0°) – Poles (90° N and S) – Arctic and Antarctic Circles (66.5° N and S) ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Where are we? • Absolute Location – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue. ...
... Where are we? • Absolute Location – A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). – Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. – The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue. ...
The Five Themes of Geography The Five Themes of Geography
... What language do people speak? Every place on Earth has a distinct group of physical features, such as its climate, landforms and bodies of water, and plant and animal life. Places can also have human characteristics, or features that human beings have created, such as cities and towns, governments, ...
... What language do people speak? Every place on Earth has a distinct group of physical features, such as its climate, landforms and bodies of water, and plant and animal life. Places can also have human characteristics, or features that human beings have created, such as cities and towns, governments, ...
File landforms&mapping
... Locations North of the equator are in north latitude and south of it are on south latitude ...
... Locations North of the equator are in north latitude and south of it are on south latitude ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... A Pre-Assessment Quiz 1. What is the difference between absolute and relative location? a. No difference. They are different terms, but they mean basically the same thing. b. Absolute location is an exact location determined by latitude and longitude. c. Absolute location describes how a place is re ...
... A Pre-Assessment Quiz 1. What is the difference between absolute and relative location? a. No difference. They are different terms, but they mean basically the same thing. b. Absolute location is an exact location determined by latitude and longitude. c. Absolute location describes how a place is re ...
Biomes
... • Warm air around the equator rises and flows north toward the pole • Earth’s rotation deflects air toward the right ...
... • Warm air around the equator rises and flows north toward the pole • Earth’s rotation deflects air toward the right ...
Focus: What are the physical geographical features that define the
... the Western Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere. Using this model, explain to students that the earth has been divided into imaginary lines. To describe the absolute location of a place, you can use lines of latitude and longitude. Lines of Longitude Maps and globes have a set of lines that run no ...
... the Western Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere. Using this model, explain to students that the earth has been divided into imaginary lines. To describe the absolute location of a place, you can use lines of latitude and longitude. Lines of Longitude Maps and globes have a set of lines that run no ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... The Great Lakes States The Soda-pop states The California state The New England states ...
... The Great Lakes States The Soda-pop states The California state The New England states ...
Earth`s Motion • Earth has two major types of motion • Earth`s
... questions as part of your study guide, in other words….DO NOT LOSE this ) 1. Which day has the MOST sunlight in the United States? ______________________________. What is this day called? ______________________. 2. How long would it take the Earth to complete 4 orbits around the Sun? ______________ ...
... questions as part of your study guide, in other words….DO NOT LOSE this ) 1. Which day has the MOST sunlight in the United States? ______________________________. What is this day called? ______________________. 2. How long would it take the Earth to complete 4 orbits around the Sun? ______________ ...
Why study geography?
... clock. As you move from time zone to time zone you increase or decrease you clock by 1 hour for each time zone you cross when traveling. If you head West, you lose an hour for each time zone you cross. If you head East, you add an hour for each time zone you cross. Each zone you cross is called a St ...
... clock. As you move from time zone to time zone you increase or decrease you clock by 1 hour for each time zone you cross when traveling. If you head West, you lose an hour for each time zone you cross. If you head East, you add an hour for each time zone you cross. Each zone you cross is called a St ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Is given in degrees of latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). o ...
... Is given in degrees of latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). o ...
File
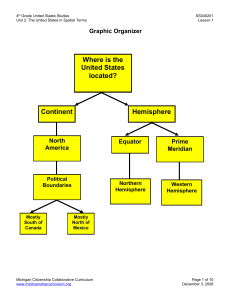
... Geographers investigate both the absolute and relative location of places. A variety of geographic representations including maps and globes can help answer the question: Where is the United States located? The United States is located on the continent of North America. The United States is ...
... Geographers investigate both the absolute and relative location of places. A variety of geographic representations including maps and globes can help answer the question: Where is the United States located? The United States is located on the continent of North America. The United States is ...
The Five Themes in Geography
... 1) Explain the difference between a physical and political map? 2) Give examples of special purpose maps and how they are used ...
... 1) Explain the difference between a physical and political map? 2) Give examples of special purpose maps and how they are used ...
Lesson 2-1 Guided Reading
... Geography are (1) location, (2) place, (3) humanenvironment interaction, (4) movement, and (5) regions. Geographers now divide their field into Six Essential Elements. Each element looks at a different set of facts about our world and the people in it. ...
... Geography are (1) location, (2) place, (3) humanenvironment interaction, (4) movement, and (5) regions. Geographers now divide their field into Six Essential Elements. Each element looks at a different set of facts about our world and the people in it. ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... Every place on Earth has a location. Location is defined in terms of absolute and relative location – Absolute location: the exact spot on Earth where something is found i.e. latitude & longitude – Relative location: the position of a place in relation to other places i.e. landmarks, etc. ...
... Every place on Earth has a location. Location is defined in terms of absolute and relative location – Absolute location: the exact spot on Earth where something is found i.e. latitude & longitude – Relative location: the position of a place in relation to other places i.e. landmarks, etc. ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.