Geography
... 1. Location – geographers begin to study a place by finding where it is, or its location. This is measured by the latitude and longitude coordinates on a map. 2. Place – geographers study the physical and human features of a location such as it’s weather, altitude, language, cultures, etc. 3. Human- ...
... 1. Location – geographers begin to study a place by finding where it is, or its location. This is measured by the latitude and longitude coordinates on a map. 2. Place – geographers study the physical and human features of a location such as it’s weather, altitude, language, cultures, etc. 3. Human- ...
EX - Greenwood School District 50
... --at International Dateline (180º long.) reverses: if go E (toward USA) turn back 24 hours; if go W (toward China) turn ahead 24 hours Kiribati (1997) changed its side of International Date Line...WHY? ...
... --at International Dateline (180º long.) reverses: if go E (toward USA) turn back 24 hours; if go W (toward China) turn ahead 24 hours Kiribati (1997) changed its side of International Date Line...WHY? ...
5 Themes of Geography ppt.
... Human-Environment Interaction • Decide whether the people in the pictures below are depending, adapting, or modifying the environment: ...
... Human-Environment Interaction • Decide whether the people in the pictures below are depending, adapting, or modifying the environment: ...
THE ROUND EARTH ON FLAT PAPER Geographers use a variety
... cross each other to form an imaginary grid over the earth. Because each degree can be broken into 60 minutes (') and each minute can be broken into 60 seconds (''), this grid can be used to fix the precise location of any point on the earth’s surface. The most important longitude is called the Green ...
... cross each other to form an imaginary grid over the earth. Because each degree can be broken into 60 minutes (') and each minute can be broken into 60 seconds (''), this grid can be used to fix the precise location of any point on the earth’s surface. The most important longitude is called the Green ...
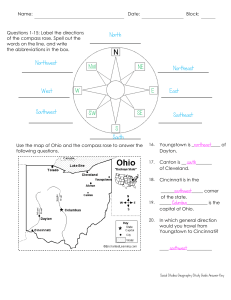
North Northeast East Southeast South Southwest
... Social Studies Geography Study Guide Answer Key ...
... Social Studies Geography Study Guide Answer Key ...
Pearson Social Studies
... believe is their territory on their traditional land. You use that to go out with a GPS unit and collect [data] points from each of the different spots. I actually took video interviews of them talking about the history of the spots that we went to.” Maijuna people took pictures of the spots, and Ja ...
... believe is their territory on their traditional land. You use that to go out with a GPS unit and collect [data] points from each of the different spots. I actually took video interviews of them talking about the history of the spots that we went to.” Maijuna people took pictures of the spots, and Ja ...
Unit I Questions
... ____ 10. Every map projection has some degree of distortion because: a. parallels and meridians never cross at right d. Earth is not a perfect sphere angles on a globe. b. a curved surface cannot be represented on e. latitude lines never intersect while a flat surface without distortion. meridians ...
... ____ 10. Every map projection has some degree of distortion because: a. parallels and meridians never cross at right d. Earth is not a perfect sphere angles on a globe. b. a curved surface cannot be represented on e. latitude lines never intersect while a flat surface without distortion. meridians ...
Lecture 5 - UCSB Geography
... • A coordinate system is a standardized method for assigning codes to locations so that locations can be found using the codes alone • Standardized coordinate systems use absolute locations • A map captured in the units of the paper sheet on which it is printed is based on relative locations or map ...
... • A coordinate system is a standardized method for assigning codes to locations so that locations can be found using the codes alone • Standardized coordinate systems use absolute locations • A map captured in the units of the paper sheet on which it is printed is based on relative locations or map ...
Glossary
... state of the environment Equator An invisible circle that divides the Earth into two hemispheres Equatorial Located at the equator or in the plane of the equator Equinox (equal night) when the sun crosses the equator, causing the length of day and night to be equal in both hemispheres Estuary Semi-i ...
... state of the environment Equator An invisible circle that divides the Earth into two hemispheres Equatorial Located at the equator or in the plane of the equator Equinox (equal night) when the sun crosses the equator, causing the length of day and night to be equal in both hemispheres Estuary Semi-i ...
AP Human Geography Notes
... Absolute Location • Absolute location describes a place using coordinates such as latitude and longitude • Notation – Latitude, Longitude – Degrees can be divided into minutes, and minutes can be divided into seconds • EX: Absolute Location of the United States Capitol Building – 38O 53 23 N, 77O 0 ...
... Absolute Location • Absolute location describes a place using coordinates such as latitude and longitude • Notation – Latitude, Longitude – Degrees can be divided into minutes, and minutes can be divided into seconds • EX: Absolute Location of the United States Capitol Building – 38O 53 23 N, 77O 0 ...
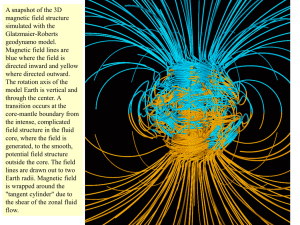
The geoid on a rotating earth 1 Potentials for Gravity and Magnetism
... amounts to a rather tiny correction to the first two terms (of the order of f2 compared to f). (4) The geoid is the actual equipotential surface that exists on the earth, with subtle undulations. This surface is approximated by the surface of the world's oceans after the effects of tides and ocean c ...
... amounts to a rather tiny correction to the first two terms (of the order of f2 compared to f). (4) The geoid is the actual equipotential surface that exists on the earth, with subtle undulations. This surface is approximated by the surface of the world's oceans after the effects of tides and ocean c ...
What is Geography?
... The environment is the surroundings in which people, plants, and animals live. People influence their environment, and are influenced by their environment. ...
... The environment is the surroundings in which people, plants, and animals live. People influence their environment, and are influenced by their environment. ...
lecture36
... outside the core. The field lines are drawn out to two Earth radii. Magnetic field is wrapped around the "tangent cylinder" due to the shear of the zonal fluid flow. ...
... outside the core. The field lines are drawn out to two Earth radii. Magnetic field is wrapped around the "tangent cylinder" due to the shear of the zonal fluid flow. ...
The Importance of Geography - White Plains Public Schools
... Under a Broken Sky (2003) “…For former herders like Bayarsakhan, the transition to city living has been wrenching. He grew up in Gobi-Altai province to the south, where his family had raised livestock for generations. Four summers ago, however, a severe drought was followed by an early frost, then a ...
... Under a Broken Sky (2003) “…For former herders like Bayarsakhan, the transition to city living has been wrenching. He grew up in Gobi-Altai province to the south, where his family had raised livestock for generations. Four summers ago, however, a severe drought was followed by an early frost, then a ...
Science of Location
... everyone and everything is located on Earth. However, they also want to know how we affect our environment. For this reason, geography includes five different themes. They are location, place, movement, human/environment interaction, and region. Location is the most well known part of geography. Exp ...
... everyone and everything is located on Earth. However, they also want to know how we affect our environment. For this reason, geography includes five different themes. They are location, place, movement, human/environment interaction, and region. Location is the most well known part of geography. Exp ...
Geography Common Assessment
... 79. Globalization and modern worldwide communication and transportation links have affected old world cultures by making them A. more different from each other B. more modern C. more isolated D. identical 80. Trade between nations and regions is necessary because A. it makes trading partners equal i ...
... 79. Globalization and modern worldwide communication and transportation links have affected old world cultures by making them A. more different from each other B. more modern C. more isolated D. identical 80. Trade between nations and regions is necessary because A. it makes trading partners equal i ...
Map Vocabulary Book - Sope Creek Elementary
... compass rose, scale, and a grid system to help easily describe a location through latitude and longitude lines. There are two special lines on a world globe that are important to remember, the Prime Meridian (longitude) and the Equator (latitude). ...
... compass rose, scale, and a grid system to help easily describe a location through latitude and longitude lines. There are two special lines on a world globe that are important to remember, the Prime Meridian (longitude) and the Equator (latitude). ...
Map Vocabulary Book - Sope Creek Elementary
... compass rose, scale, and a grid system to help easily describe a location through latitude and longitude lines. There are two special lines on a world globe that are important to remember, the Prime Meridian (longitude) and the Equator (latitude). ...
... compass rose, scale, and a grid system to help easily describe a location through latitude and longitude lines. There are two special lines on a world globe that are important to remember, the Prime Meridian (longitude) and the Equator (latitude). ...
World Geo Intro
... Examples: The United States is in the North American Region. However, the U.S. has several sub-regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, etc. ...
... Examples: The United States is in the North American Region. However, the U.S. has several sub-regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, etc. ...
Introduction to Regional Geography
... Examples: The United States is in the North American Region. However, the U.S. has several sub-regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, etc. ...
... Examples: The United States is in the North American Region. However, the U.S. has several sub-regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, etc. ...
Final Exam Study Guide KEY
... 1. What is geography? The study of the world, its people, and the landscapes they create 2. Name two reasons it is important to study geography. 1) Avoid mistakes Travel 2) Know where places are Knowledge 3. Fill out the following chart: What else are the lines called? ...
... 1. What is geography? The study of the world, its people, and the landscapes they create 2. Name two reasons it is important to study geography. 1) Avoid mistakes Travel 2) Know where places are Knowledge 3. Fill out the following chart: What else are the lines called? ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Grid System: Patterns formed as the lines of latitude (parallels) and longitude (meridians) cross each other. Hemispheres: The division of the earth into four equal quadrants utilizing the equator and the ...
... Grid System: Patterns formed as the lines of latitude (parallels) and longitude (meridians) cross each other. Hemispheres: The division of the earth into four equal quadrants utilizing the equator and the ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.