* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.1 The Geographer`s Tools
Enhanced 9-1-1 wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Geopolitics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
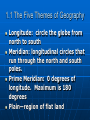
1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Geography 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Geography Latitude Parallel Degree Equator Longitude 7. Meridian 8. Prime Meridian 9. Plain 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Questions to Explore 1. What is geography? 2. How can the five themes of geography help you understand the world? 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Journal Entry What do you think the subject of geography covers? Create a definition in your own words, 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Geography is the study of the Earth Location • Absolute location– describes a place’s exact position on the Earth or geographic address • Relative location —the location of a place as described by places near it. Latitude—east-wet circles around the globe—also called parallels. Longitude—circle the globe from north to south—also called meridians. 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Location • Equator--An imaginary line that circles the globe at its widest point (halfway between the North and South poles), dividing Earth into two halves called hemispheres; used as a reference point from which north and south latitudes are measured. • Prime Meridian—runs through Greenwich, England, is 0 degrees longitude. 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Place—a location’s physical and human features. • Climate is hot or cold • The land is hilly • How many people live there? 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Human-Environment Interaction • Stresses how people affect their environment • The physical characteristics of their surroundings, and how their environment affects them • Used to discuss the consequences of people’s actions. 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Movement—helps geographers understand the relationship among places. helps explain how people, goods, and ideas get from one place to another. 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Regions help to make comparisons. A region has a unifying characteristic such as climate, land, population or history. 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography 1. 2. 3. 4. Make sure that you have completed the vocabulary. Make sure that you have completed the journal entry. Make sure that you have completed the questions to Explore. Complete 1.1 Review on p. 13 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Complete The Geographer’s Tools worksheet. Homework: 1. Draw a map of your neighborhood using absolute location. 2. Give directions to your house from school using relative location 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography Longitude: circle the globe from north to south Meridian: longitudinal circles that run through the north and south poles. Prime Meridian: 0 degrees of longitude. Maximum is 180 degrees Plain—region of flat land 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography absolute location—a place’s exact location on earth (longitude and latitude) Relative location—where a place is by describing places near it. Plain--a large area of flat or gently rolling land usually without many trees 1.1 The Five Themes of Geography United Streaming: • Exploring the World's Geography • Geography Basics: Globes, Maps, and Graphs