5.1 The Nature of Heat
... • Walls often have a cavity of air in between the layers • This air gap can be filled with insulation to eliminate convection currents within walls ...
... • Walls often have a cavity of air in between the layers • This air gap can be filled with insulation to eliminate convection currents within walls ...
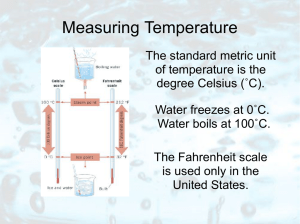
Measuring Temperature
... The 2nd Law of Thermodynamics stated as the Law of Entropy: The total entropy (or microscopic disorganization) of the participants in any physical process cannot decrease during that process, but it can increase. That's not to say that you can't create a little more order in some part of your world, ...
... The 2nd Law of Thermodynamics stated as the Law of Entropy: The total entropy (or microscopic disorganization) of the participants in any physical process cannot decrease during that process, but it can increase. That's not to say that you can't create a little more order in some part of your world, ...
ASLab_100Specific Heat Inquiry
... temperature? What if we mixed water with some other liquid? Would we get the same results? One characteristic or property of all solids and liquids is something called the Specific Heat, abbreviated as Cv. This quantity represents the amount of heat required to raise or lower a given quantity (a gra ...
... temperature? What if we mixed water with some other liquid? Would we get the same results? One characteristic or property of all solids and liquids is something called the Specific Heat, abbreviated as Cv. This quantity represents the amount of heat required to raise or lower a given quantity (a gra ...
More Carnot Cycle March 4, 2010 Efficiency = W/Qin = Qin
... Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules that make up the system There are different temperature scales: Kelvin (Absolute), Celsius, and Fahrenheit scales. Absolute Zero - it is the coolest temperature possible that cannot be reached (it is a limit). 0 K. K = ...
... Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules that make up the system There are different temperature scales: Kelvin (Absolute), Celsius, and Fahrenheit scales. Absolute Zero - it is the coolest temperature possible that cannot be reached (it is a limit). 0 K. K = ...
Optimal heating and cooling strategies for heat exchanger design
... In heat exchanger design the heat transfer is usually tied, whereas the amount of entropy produced depends on the way in which the process is carried out (primarily the temperature gradient). Since the entropy produced is equivalent to availability lost, this means that an improved heat exchanger de ...
... In heat exchanger design the heat transfer is usually tied, whereas the amount of entropy produced depends on the way in which the process is carried out (primarily the temperature gradient). Since the entropy produced is equivalent to availability lost, this means that an improved heat exchanger de ...
TW Series Key Features
... refrigerant. R-410A is a non-ozone depleting refrigerant since it does not contain any chlorine. R-410A is classified as an HFC (Hydrofluorocarbon) refrigerant as it only contains Hydrogen, Fluorine and Carbon. This refrigerant is the industry’s replacement for refrigerant R-22. Coaxial Heat Exchang ...
... refrigerant. R-410A is a non-ozone depleting refrigerant since it does not contain any chlorine. R-410A is classified as an HFC (Hydrofluorocarbon) refrigerant as it only contains Hydrogen, Fluorine and Carbon. This refrigerant is the industry’s replacement for refrigerant R-22. Coaxial Heat Exchang ...
Table S1: Properties of Antigorite as a Model
... conductivities are assumed to be 2.5 and 2.0 W m-1K-1 for the upper and lower continental crusts (both 15 km thick), respectively, 3.1 W m-1 K-1 for the continental mantle, and 2.9 W m-1K-1 for the subducting slab. Radiogenic heat production is assumed to be 1.2 and 0.6 W m-3 for the upper and lower ...
... conductivities are assumed to be 2.5 and 2.0 W m-1K-1 for the upper and lower continental crusts (both 15 km thick), respectively, 3.1 W m-1 K-1 for the continental mantle, and 2.9 W m-1K-1 for the subducting slab. Radiogenic heat production is assumed to be 1.2 and 0.6 W m-3 for the upper and lower ...
Ch. 5: Thermochemistry
... (P ΔV is the amount of work done by expanding gases, but in most reactions, there is a very small volume change, so ΔE ~ ΔH in many cases.) ...
... (P ΔV is the amount of work done by expanding gases, but in most reactions, there is a very small volume change, so ΔE ~ ΔH in many cases.) ...
Heat Recovery for Commercial Buildings
... One of the simplest forms of equipment used for heat recovery. Efficiencies range between 50 & 70%. Conduction, which is a mode of energy transfer between two ...
... One of the simplest forms of equipment used for heat recovery. Efficiencies range between 50 & 70%. Conduction, which is a mode of energy transfer between two ...
ABE 484
... methods. Learn how to interpret the data for the specific need of each problem. Promote critical thinking through problem solving processes. 4. Learn how to set up governing equations, boundary conditions, and initial conditions under various circumstances with different geometries. 5. Use requisite ...
... methods. Learn how to interpret the data for the specific need of each problem. Promote critical thinking through problem solving processes. 4. Learn how to set up governing equations, boundary conditions, and initial conditions under various circumstances with different geometries. 5. Use requisite ...
basic cooking principles 1
... 1.Fats are present in small quantities in most foods, they are present in larger quantities in: meats, poultry, fish eggs, and milk products. 2.Fats are important in cooking methods such as; frying. 3.Can be either solid or liquid at room temperature. Liquid fats are oils. Solid fats melt to become ...
... 1.Fats are present in small quantities in most foods, they are present in larger quantities in: meats, poultry, fish eggs, and milk products. 2.Fats are important in cooking methods such as; frying. 3.Can be either solid or liquid at room temperature. Liquid fats are oils. Solid fats melt to become ...
ch5 notesheet naked outline0015
... Practice: When 50.0 mL of 0.100 M AgNO3 and 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl are mixed in a constant pressure calorimeter, the temperature of the mixture increases from 22.30 oC to 23.11 oC. The temperature increase is caused by the following ...
... Practice: When 50.0 mL of 0.100 M AgNO3 and 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl are mixed in a constant pressure calorimeter, the temperature of the mixture increases from 22.30 oC to 23.11 oC. The temperature increase is caused by the following ...
Heat Work
... A P-V diagram for a reversible heat engine in which 1.00 mole of argon, a nearly ideal monatomic gas, is initially at STP (point a). Points b and c are on an isothermal. If the engine produces positive work, a) is the cycle clockwise or counter clockwise, b) what is the efficiency of the cycle? ...
... A P-V diagram for a reversible heat engine in which 1.00 mole of argon, a nearly ideal monatomic gas, is initially at STP (point a). Points b and c are on an isothermal. If the engine produces positive work, a) is the cycle clockwise or counter clockwise, b) what is the efficiency of the cycle? ...
Heat exchanger

A heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between one or more fluids. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air.