34.1 Flow of Charge
... • Voltage provides electric pressure to move electrons between terminals in a circuit (emf) • *Voltage causes current • *Charges/current flows through a circuit because of applied voltage across a ciruit. ...
... • Voltage provides electric pressure to move electrons between terminals in a circuit (emf) • *Voltage causes current • *Charges/current flows through a circuit because of applied voltage across a ciruit. ...
Split-phase electric power - University of Utah Physics
... Pole-mounted single-phase transformer with 3-wire center-tapped "split-phase" secondary. Note use of ground conductor as one leg of primary feeder. In Australia and New Zealand, remote loads are connected to the grid using SWER (Single Wire Earth Return) transmission lines (it is cheaper to run one ...
... Pole-mounted single-phase transformer with 3-wire center-tapped "split-phase" secondary. Note use of ground conductor as one leg of primary feeder. In Australia and New Zealand, remote loads are connected to the grid using SWER (Single Wire Earth Return) transmission lines (it is cheaper to run one ...
POWER QUALITY -- An Indian Perspective
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
Topic 12.3 Transmission of Electrical Power
... • The resistance in a wire due to the flow of electrons over long distances also has a heating effect. If the thickness of the copper wire used in the core of the transmission line is increased, then the resistance can be decreased. However, there are practical considerations such as weight and the ...
... • The resistance in a wire due to the flow of electrons over long distances also has a heating effect. If the thickness of the copper wire used in the core of the transmission line is increased, then the resistance can be decreased. However, there are practical considerations such as weight and the ...
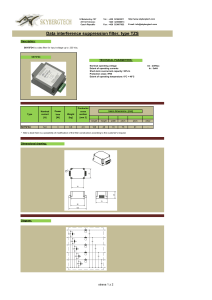
TZS - Skybergtech
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
Section 13.3: Alternating Current
... 2. Yes, the voltage is proportional to the current. In alternating current electricity, as the voltage increases, the conventional current in the wire increases in the positive direction and as the voltage decreases, the conventional current in the wire decreases. This shows that the voltage is prop ...
... 2. Yes, the voltage is proportional to the current. In alternating current electricity, as the voltage increases, the conventional current in the wire increases in the positive direction and as the voltage decreases, the conventional current in the wire decreases. This shows that the voltage is prop ...
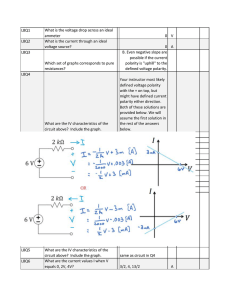
L8Q1 What is the voltage drop across an ideal ammeter 0 V L8Q2
... What are the IV characteristics of a 3 mA current source? Use polarities defined in sub-circuit 2. What are the IV characteristics of a 3kΩ resistor? Use polarities defined in subcircuit 2. ...
... What are the IV characteristics of a 3 mA current source? Use polarities defined in sub-circuit 2. What are the IV characteristics of a 3kΩ resistor? Use polarities defined in subcircuit 2. ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... voltage must be reduced once more. These transformers are much smaller in size and can be located on power line poles or on the ground, as large boxed objects. ...
... voltage must be reduced once more. These transformers are much smaller in size and can be located on power line poles or on the ground, as large boxed objects. ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... Why do we need transformers? Keeping the current low means electricity can be transported long distances without losing too much energy. ...
... Why do we need transformers? Keeping the current low means electricity can be transported long distances without losing too much energy. ...
Magnetism 4 Electromagnets
... Galvanometer Moving coil electric current detector. The amount of deflection of a needle attached to the coil is proportional to the current passing through the coil. ...
... Galvanometer Moving coil electric current detector. The amount of deflection of a needle attached to the coil is proportional to the current passing through the coil. ...
TDC-UC-330-DX - T-Opto
... Thank you for your interest in T-OptoTM! We have the largest selection of new-style LEDs and power supplies for the general illumination market. Our products add a whole new dimension to your lighting design toolbox and are applicable to all types of high-reliability, high-efficiency, high-brightnes ...
... Thank you for your interest in T-OptoTM! We have the largest selection of new-style LEDs and power supplies for the general illumination market. Our products add a whole new dimension to your lighting design toolbox and are applicable to all types of high-reliability, high-efficiency, high-brightnes ...
Electric Circuits
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).