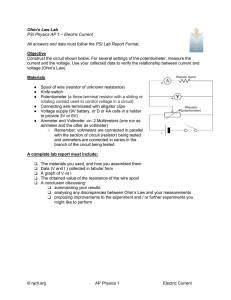
17.16 Using and measuring electrical power
... The power (P) of any electrical device can also be obtained, from the voltage (V) it uses and the current (I) it carries, by using the formula: Power (watts) = Voltage (volts) × Current (amps). This formula is often written as P = VI and can transpose to I = P/V. Look again at the label from the Sun ...
... The power (P) of any electrical device can also be obtained, from the voltage (V) it uses and the current (I) it carries, by using the formula: Power (watts) = Voltage (volts) × Current (amps). This formula is often written as P = VI and can transpose to I = P/V. Look again at the label from the Sun ...
Voltage/DC current
... Does anyone remember the purpose of a battery? Voltage Definition: The measurement of electrical energy. - It is usually measured as a difference of electrical energy between two points. - Voltage is the energy that causes the electrons to want to go to from one place to another. - It is measured in ...
... Does anyone remember the purpose of a battery? Voltage Definition: The measurement of electrical energy. - It is usually measured as a difference of electrical energy between two points. - Voltage is the energy that causes the electrons to want to go to from one place to another. - It is measured in ...
Homework 5
... is proportional to VDD/(VDD – Vt), where threshold voltage Vt = 0.5V. A low energy mode uses a lower supply voltage and a reduced frequency clock. Determine the voltage and clock frequency that will minimize the average energy consumption per cycle. Compare the power consumption and energy per cycle ...
... is proportional to VDD/(VDD – Vt), where threshold voltage Vt = 0.5V. A low energy mode uses a lower supply voltage and a reduced frequency clock. Determine the voltage and clock frequency that will minimize the average energy consumption per cycle. Compare the power consumption and energy per cycle ...
EE 201 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
... (b) If R1 R2 R3 R4 2 , I 2 1 A , and Vs 2 V find the values of the currents. (c) If we want to replace the voltage source with a current source while still keeping the values of the currents in part (b), what should be the value of this current source? ...
... (b) If R1 R2 R3 R4 2 , I 2 1 A , and Vs 2 V find the values of the currents. (c) If we want to replace the voltage source with a current source while still keeping the values of the currents in part (b), what should be the value of this current source? ...
Using and making transformers - School
... VOLTAGE across it. ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 5. 5. The wires in each coil are insulated so that the current flows all around the cores and magnetises them. Uninsulated wire would allow the current to short circuit its route. 6. In the national grid, transmitting POWER over a long distance is made mo ...
... VOLTAGE across it. ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION 5. 5. The wires in each coil are insulated so that the current flows all around the cores and magnetises them. Uninsulated wire would allow the current to short circuit its route. 6. In the national grid, transmitting POWER over a long distance is made mo ...
R Ch 37 Electric Induction pg 1
... R Ch 37.8 Electromagnetic Waves pg 12 • Electromagnetic waves move at the speed of light 300,000 km/s or 186,000 miles/s • Because a changing electric field is creates a magnetic field & a changing magnetic field is creates a electric field the two fields ...
... R Ch 37.8 Electromagnetic Waves pg 12 • Electromagnetic waves move at the speed of light 300,000 km/s or 186,000 miles/s • Because a changing electric field is creates a magnetic field & a changing magnetic field is creates a electric field the two fields ...
The Design Process Abstraction & Synthesis
... • Voltage Range (Full Charge to Discharge) • Number of Cells Required • Battery Life (ie. mA Hr Capacity) ...
... • Voltage Range (Full Charge to Discharge) • Number of Cells Required • Battery Life (ie. mA Hr Capacity) ...
Physics Gang Signs Review
... Faraday’s Law says that you can create (induce) more voltage by 1) moving the B-field faster 2) moving it into and out of more coils of wire **the amount of current produced by electromagnetic induction depends not only on the induced voltage but the resistance of the coil and circuit to which it’s ...
... Faraday’s Law says that you can create (induce) more voltage by 1) moving the B-field faster 2) moving it into and out of more coils of wire **the amount of current produced by electromagnetic induction depends not only on the induced voltage but the resistance of the coil and circuit to which it’s ...
An Introduction to Electric Power Systems
... well separated from each other, to prevent arcing (sparks) and injury or people or animals. • Why use such high voltages? Using very high voltages on the transmission lines reduces the amount of energy wasted heating up the wires. ...
... well separated from each other, to prevent arcing (sparks) and injury or people or animals. • Why use such high voltages? Using very high voltages on the transmission lines reduces the amount of energy wasted heating up the wires. ...
Electricity notes - Lesmahagow High School
... 7. STAYING SAFE WITH ELECTRICITY Passing a current in a wire causes it to heat up. If the current in a wire gets too high, ...
... 7. STAYING SAFE WITH ELECTRICITY Passing a current in a wire causes it to heat up. If the current in a wire gets too high, ...
Rad T 110
... • Velocity = frequency x wavelength – Remember, photons all travel at the speed of light, 186,000 miles/second so velocity is in effect a constant ...
... • Velocity = frequency x wavelength – Remember, photons all travel at the speed of light, 186,000 miles/second so velocity is in effect a constant ...
24 V AC Power Supply (Rev0): FA24AC/50, FA24AC/60
... 100 - 240 V AC input 12 V DC output, 24 W High efficiency ...
... 100 - 240 V AC input 12 V DC output, 24 W High efficiency ...
Design and Analysis of DSTATCOM for Reactive Power
... voltage disturbances A DSTATCOM, connected at the point of common coupling (PCC), has been utilized to mitigate both types of PQ problems. When operating in current control mode (CCM), it injects reactive and harmonic components of load currents to make source currents balanced, sinusoidal, and in p ...
... voltage disturbances A DSTATCOM, connected at the point of common coupling (PCC), has been utilized to mitigate both types of PQ problems. When operating in current control mode (CCM), it injects reactive and harmonic components of load currents to make source currents balanced, sinusoidal, and in p ...
Analysis and Simulation of Bus Loading conditions on Voltage Sag
... Deals with the generation, transmission and distribution of electric power as well as the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. ...
... Deals with the generation, transmission and distribution of electric power as well as the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. ...
Electric Current and Electrical Energy
... Current As long as there is a voltage between two points on a wire, charge will flow in the wire. The amount of the current depends on the voltage. • Varying Nature of Voltage Different devices need different levels of ...
... Current As long as there is a voltage between two points on a wire, charge will flow in the wire. The amount of the current depends on the voltage. • Varying Nature of Voltage Different devices need different levels of ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).