What Is Direct Current (DC)? What Is Alternating Current (AC)?
... load (electrical devices and so on) connected to the distribution network. For example, when all the houses in a neighborhood are using the air conditioning during the afternoon in the middle of the summer, the voltage drops. There are also momentary stoppages in distribution and distortion to wave ...
... load (electrical devices and so on) connected to the distribution network. For example, when all the houses in a neighborhood are using the air conditioning during the afternoon in the middle of the summer, the voltage drops. There are also momentary stoppages in distribution and distortion to wave ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
Brad`s Lecture on Electricity and Power Supplies
... PARTS OF THE TRANSFORMER CONSIST OF ONLY ONE DEVICE! THE TRANSFORMER ITSELF! IT CONSIST OF 2 COILS WHICH “STEP DOWN” OR REDUCE THE VOLTAGE DOWN TO 5 AND 12 VOLTS ...
... PARTS OF THE TRANSFORMER CONSIST OF ONLY ONE DEVICE! THE TRANSFORMER ITSELF! IT CONSIST OF 2 COILS WHICH “STEP DOWN” OR REDUCE THE VOLTAGE DOWN TO 5 AND 12 VOLTS ...
“Switch-On” Electronics - Cleveland State University
... • One amp of current means a flow of one Coulomb (6.241 × 1018 electrons) per second Amps = Coulombs / second ...
... • One amp of current means a flow of one Coulomb (6.241 × 1018 electrons) per second Amps = Coulombs / second ...
Условие - Reshaem
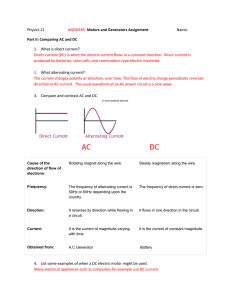
... current: direct and alternating. A direct current flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit. An alternating current is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating ...
... current: direct and alternating. A direct current flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit. An alternating current is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating ...
How Power Plants Work
... • Particles like protons and electrons have a certain charge associated with them • Whenever charge builds up in a particular location, there are associated fields and potentials that are created • Since protons are several orders of magnitude heavier than electrons, we are interested in the movemen ...
... • Particles like protons and electrons have a certain charge associated with them • Whenever charge builds up in a particular location, there are associated fields and potentials that are created • Since protons are several orders of magnitude heavier than electrons, we are interested in the movemen ...
Electricity and magnetism connection
... create and electric current This was discovered separately and simultaneously by Michael Faraday in Great Britain and Joseph Henry in America in 1831. Both moved a coil of wire over a magnet and saw a current was created, and the current created a ...
... create and electric current This was discovered separately and simultaneously by Michael Faraday in Great Britain and Joseph Henry in America in 1831. Both moved a coil of wire over a magnet and saw a current was created, and the current created a ...
Generator and Transformer
... How does electric energy transmit over large distances? How much power is wasted when 10000W of power is transmitted along a cable with a resistance of 1 at 200V? What would be lost if transmitted at 2000V instead? Much less lost when travels at a higher V and lower I ...
... How does electric energy transmit over large distances? How much power is wasted when 10000W of power is transmitted along a cable with a resistance of 1 at 200V? What would be lost if transmitted at 2000V instead? Much less lost when travels at a higher V and lower I ...
Name____________________________ Reading
... 2. If electricity is made of negative electrons, and if protons are locked in the nucleus and cannot flow, why is current defined as the flow of positive charge. ...
... 2. If electricity is made of negative electrons, and if protons are locked in the nucleus and cannot flow, why is current defined as the flow of positive charge. ...
GENERATORS AND TRANSFORMERS
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
generators and transformers
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
Self Study Unit 1.0 - Tri County Amateur Radio Club WX4TC
... (T5A09) Frequency is the term that describes the number of times per second that an alternating current reverses direction. (T5A12) Alternating current, or AC, is what is available from your home’s wall sockets. Power supplies convert the AC into DC, which is required for most modern amateur radio e ...
... (T5A09) Frequency is the term that describes the number of times per second that an alternating current reverses direction. (T5A12) Alternating current, or AC, is what is available from your home’s wall sockets. Power supplies convert the AC into DC, which is required for most modern amateur radio e ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).