Introduction to Photovoltaics Powerpoint
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... are the moving charges. When charges are not flowing, the net charge in the wire is zero. When charges are flowing the net charge in the wire is zero because for every one charge that enters one side, another charge leaves the other side and the total number of protons and neutrons doesn’t change. D ...
... are the moving charges. When charges are not flowing, the net charge in the wire is zero. When charges are flowing the net charge in the wire is zero because for every one charge that enters one side, another charge leaves the other side and the total number of protons and neutrons doesn’t change. D ...
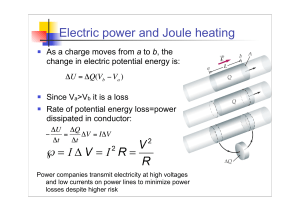
Electric power and Joule heating
... and supply a whole neighborhood. This is because the higher voltage used in Europe (380 V vs 230 V) may be carried over a greater distance with acceptable power loss. An advantage of the North American setup is that failure or maintenance on a single transformer will only affect a few customers. Adv ...
... and supply a whole neighborhood. This is because the higher voltage used in Europe (380 V vs 230 V) may be carried over a greater distance with acceptable power loss. An advantage of the North American setup is that failure or maintenance on a single transformer will only affect a few customers. Adv ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... To understand how electricity is distributed in the UK via the National Grid ...
... To understand how electricity is distributed in the UK via the National Grid ...
Electricity & Magnetism
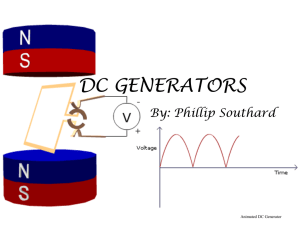
... 5. A.C. – Alternating Current: A current consisting of Charges that move back and forth in a circuit. (home) 6. Electric Generator: A device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy – Opposite of an electric motor. *A generator uses motion in a magnetic field to produce an electrica ...
... 5. A.C. – Alternating Current: A current consisting of Charges that move back and forth in a circuit. (home) 6. Electric Generator: A device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy – Opposite of an electric motor. *A generator uses motion in a magnetic field to produce an electrica ...
Functions of Electrical Transformer
... Functions of Electrical Transformer Electrical transformers are used to "transform" voltage from one level to another, usually from a higher voltage to a lower voltage. They do this by applying the principle of magnetic induction between coils to convert voltage and or current levels. In this way, e ...
... Functions of Electrical Transformer Electrical transformers are used to "transform" voltage from one level to another, usually from a higher voltage to a lower voltage. They do this by applying the principle of magnetic induction between coils to convert voltage and or current levels. In this way, e ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name - Science 9 Portfolio
... 2. What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? A fuse can only be used once where as a curciuit breaker can be reset and used again 3. Describe three ways in which electric energy could be conserved with respect to home lighting. Turn off lights when you leave Use lower voltage Fluo ...
... 2. What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? A fuse can only be used once where as a curciuit breaker can be reset and used again 3. Describe three ways in which electric energy could be conserved with respect to home lighting. Turn off lights when you leave Use lower voltage Fluo ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
Microelectronics… - Oakland University
... Design and develop an energy harvesting and electrical energy storage system. • Utilizes vertical and horizontal water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
... Design and develop an energy harvesting and electrical energy storage system. • Utilizes vertical and horizontal water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
Current, Voltage and Resistance
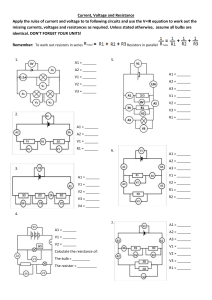
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
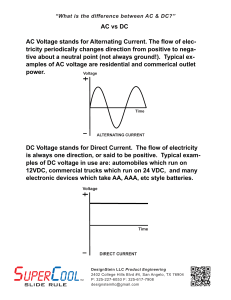
AC vs DC AC Voltage stands for Alternating Current. The flow of elec
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
Alternating current
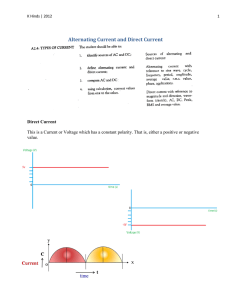
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).