Chapter 3 - Ancient Egypt and Nubia MP
... “Hymn to the Nile” Lord of the fish, during the inundation, no bird alights on the crops. You create the grain, you bring forth the barley, assuring perpetuity to the temples. If you cease your toil and your work, then all that exists is in anguish. If the gods suffer in heaven, then the faces of m ...
... “Hymn to the Nile” Lord of the fish, during the inundation, no bird alights on the crops. You create the grain, you bring forth the barley, assuring perpetuity to the temples. If you cease your toil and your work, then all that exists is in anguish. If the gods suffer in heaven, then the faces of m ...
Four Surveyors of the Gods: In the XVIII Dynasty of Egypt – New
... This could not be more distant from the facts ! In reality, even though the harpedonaptae (“rope stretchers”) who were the surveyor’s assistants were not individually known, the master surveyors were not only well known but each even had his own tomb adorned with wall paintings and hieroglyphics of ...
... This could not be more distant from the facts ! In reality, even though the harpedonaptae (“rope stretchers”) who were the surveyor’s assistants were not individually known, the master surveyors were not only well known but each even had his own tomb adorned with wall paintings and hieroglyphics of ...
“10 Arguments That Prove Ancient Egyptians Were Black,” by A
... general agreement that the Ethiopians, Egyptians, Colchians, and people of the Southern Levant were among the only people on earth practicing circumcision, which confirms their cultural affiliations, if not their ethnic affiliation.” He added: “The Egyptian style of (adolescent) circumcision was dif ...
... general agreement that the Ethiopians, Egyptians, Colchians, and people of the Southern Levant were among the only people on earth practicing circumcision, which confirms their cultural affiliations, if not their ethnic affiliation.” He added: “The Egyptian style of (adolescent) circumcision was dif ...
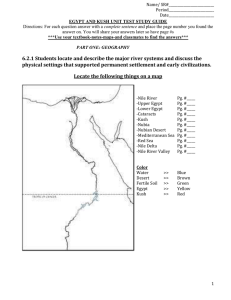
egypt and kush unit test study guide
... Kush: The kingdom to the south of Egypt, which shared a very complex relationship. They shared many cultural similarities and often were at peace and war. Pharaoh: the ruler of the Egyptian people, also thought to be a god. The pharaoh was in charge of keeping the Egyptians happy and safe. If things ...
... Kush: The kingdom to the south of Egypt, which shared a very complex relationship. They shared many cultural similarities and often were at peace and war. Pharaoh: the ruler of the Egyptian people, also thought to be a god. The pharaoh was in charge of keeping the Egyptians happy and safe. If things ...
Unit 3 Digging Deeper
... - In early Egyptian society, pharaohs ruled as gods and were at the top of the social structure - Religion shaped Egyptian life. - The pyramids of Egypt were built as tombs for the pharaohs. 1. Recall – To what does the term Old Kingdom refer? 2. Analyze – Why was the pharaoh’s authority never quest ...
... - In early Egyptian society, pharaohs ruled as gods and were at the top of the social structure - Religion shaped Egyptian life. - The pyramids of Egypt were built as tombs for the pharaohs. 1. Recall – To what does the term Old Kingdom refer? 2. Analyze – Why was the pharaoh’s authority never quest ...
Chapter 4: Egypt, 3100 B.C.
... Nile reaches the sea, it branches to form a fan-shaped area of fertile land called a delta. Most ancient Egyptians lived in this area. For a long time, they were protected from foreign invasions by the desert, the sea, and waterfalls called cataracts (kat’ uh rakts). ...
... Nile reaches the sea, it branches to form a fan-shaped area of fertile land called a delta. Most ancient Egyptians lived in this area. For a long time, they were protected from foreign invasions by the desert, the sea, and waterfalls called cataracts (kat’ uh rakts). ...
Chapter 3
... 1. What made the Egyptian economy more prosperous? 2. How did the growth of trade in the Middle Kingdom affect Egypt’s economy? New Kingdom Pharaohs: 1. Why did Akhenaten’s advisors take control? 2. What was different about how some pharaohs ruled during the new Kingdom? Nubia and Egypt Lands South ...
... 1. What made the Egyptian economy more prosperous? 2. How did the growth of trade in the Middle Kingdom affect Egypt’s economy? New Kingdom Pharaohs: 1. Why did Akhenaten’s advisors take control? 2. What was different about how some pharaohs ruled during the new Kingdom? Nubia and Egypt Lands South ...
Sample of Egyptian Mummy Portraits
... humanity and its art represent the pinnacle of divine creation.”7 Egyptian art before the Greeks was inspired by the portrayal of ideal divinity. Egyptian life revolved around religion and religion revolved around life; the Egyptian every day was consumed with the idea of the sun and its conquest ov ...
... humanity and its art represent the pinnacle of divine creation.”7 Egyptian art before the Greeks was inspired by the portrayal of ideal divinity. Egyptian life revolved around religion and religion revolved around life; the Egyptian every day was consumed with the idea of the sun and its conquest ov ...
The New Kingdome, as archaeologists call it, was from
... happened (though much of it was exaggerated a little by those scribes who wanted to gain favor from their ruler). Many of Egypt’s most interesting Pharaohs ruled at this time. One extraordinary individual was Pharaoh Hatshepsut (1473-1458), who was really a woman. She was the wife of Thutmosis II, w ...
... happened (though much of it was exaggerated a little by those scribes who wanted to gain favor from their ruler). Many of Egypt’s most interesting Pharaohs ruled at this time. One extraordinary individual was Pharaoh Hatshepsut (1473-1458), who was really a woman. She was the wife of Thutmosis II, w ...
File
... In respect of eating and drinking, the Persians were in the earlier times noted for their temperance and sobriety. Their ordinary food was wheaten bread, barley-cakes, and meat simply roasted or boiled, which they seasoned with salt and with bruised cress-seed, a substitute for mustard. The sole dri ...
... In respect of eating and drinking, the Persians were in the earlier times noted for their temperance and sobriety. Their ordinary food was wheaten bread, barley-cakes, and meat simply roasted or boiled, which they seasoned with salt and with bruised cress-seed, a substitute for mustard. The sole dri ...
INSTRUCTIONAL OVERVIEW Teacher: Ray White Class: 7th World
... Learning Target: Generalize the cultural accomplishments of Egyptian society. Teaching Strategy Used: Summary/Note Taking and Homework/Practice. Essential Questions of the Day: How were the pyramids built? Assessment: Egyptian Religion Questions/Pyramids Cornell Notes. ...
... Learning Target: Generalize the cultural accomplishments of Egyptian society. Teaching Strategy Used: Summary/Note Taking and Homework/Practice. Essential Questions of the Day: How were the pyramids built? Assessment: Egyptian Religion Questions/Pyramids Cornell Notes. ...
Chapter 1
... • During this period of time the pharaohs had a new concern for the people. • The pharaoh was now portrayed as a shepherd of the people. • He was expected to build public works and provide for the people’s welfare. • Swampland was drained and a new canal connected the Nile River and the Red Sea. ...
... • During this period of time the pharaohs had a new concern for the people. • The pharaoh was now portrayed as a shepherd of the people. • He was expected to build public works and provide for the people’s welfare. • Swampland was drained and a new canal connected the Nile River and the Red Sea. ...
Slide 1 - Crest Ridge R-VII
... He even had his name put on statues that were not statues of himself. He did this to bolster people’s confidence in ...
... He even had his name put on statues that were not statues of himself. He did this to bolster people’s confidence in ...
Egyptian Number System
... remembers them, is that they created a religious revolution in which they worshiped only one god; Aten, or The Sun. Can you show me which number card in front of you stands for the Egyptian number 1? Before this time, ancient Egyptians worshiped many gods. They worshiped gods such as Baast, Hathor, ...
... remembers them, is that they created a religious revolution in which they worshiped only one god; Aten, or The Sun. Can you show me which number card in front of you stands for the Egyptian number 1? Before this time, ancient Egyptians worshiped many gods. They worshiped gods such as Baast, Hathor, ...
Name: Date: ______ Class: ______ Famous Pyramids of Egypt
... The Step Pyramid was originally intended to be a large square mastaba built over an underground burial chamber but further extensions were added making a six-layered Step Pyramid 186 feet in height. A mastaba was the earliest form of tomb to be built in Egypt. They were square platforms that protect ...
... The Step Pyramid was originally intended to be a large square mastaba built over an underground burial chamber but further extensions were added making a six-layered Step Pyramid 186 feet in height. A mastaba was the earliest form of tomb to be built in Egypt. They were square platforms that protect ...
Egyptian myths
... Egyptians often buried their dead on the West bank of the Nile River due to their belief the underworld was located in the west where the sun died each day. Relatives of the dead often buried miniature boats in their tombs to transport the soul in the afterlife imitating the transport of the body ov ...
... Egyptians often buried their dead on the West bank of the Nile River due to their belief the underworld was located in the west where the sun died each day. Relatives of the dead often buried miniature boats in their tombs to transport the soul in the afterlife imitating the transport of the body ov ...
Mes-Egy-Overview
... The Israelites were monotheistic, believing in one true God. At the time, most other people worshiped many gods. The Israelites believed God to be all-knowing, all-powerful, and present everywhere. The Israelites believed that they were God’s “chosen people.” They believed that God would lead them t ...
... The Israelites were monotheistic, believing in one true God. At the time, most other people worshiped many gods. The Israelites believed God to be all-knowing, all-powerful, and present everywhere. The Israelites believed that they were God’s “chosen people.” They believed that God would lead them t ...
Ancient Egypt
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
Egypt
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
Egypt
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
... • The Egyptians viewed the heart as the seat of intellect and emotion. • Before entering the pleasures of eternity, the dead person had to pass a test in which Anubis, the god of the dead, weighed the person’s heart against Ma’at, the goddess of justice and truth, who was represented by a ...
Ancient Egypt Society Map—Semenza Galbo Government and Laws
... *Who was the first pharaoh and what was his great accomplishment (pg. 89)? The first Egyptian pharaoh was Menes. He was king of Upper Egypt. His armies swept north into the Nile Delta, in about 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new ...
... *Who was the first pharaoh and what was his great accomplishment (pg. 89)? The first Egyptian pharaoh was Menes. He was king of Upper Egypt. His armies swept north into the Nile Delta, in about 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new ...
SSWGEegy - Mr Boayue`s Social Studies site
... not know how to read them. • In 1799 a French soldier found the Rosetta Stone, a huge, stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, Greek, and a later form of Egyptian. • Because the message in all three languages was the same, scholars who knew Greek were able to translate the ...
... not know how to read them. • In 1799 a French soldier found the Rosetta Stone, a huge, stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, Greek, and a later form of Egyptian. • Because the message in all three languages was the same, scholars who knew Greek were able to translate the ...
Ancient Egypt Textbook Powerpoint presentation
... not know how to read them. • In 1799 a French soldier found the Rosetta Stone, a huge, stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, Greek, and a later form of Egyptian. • Because the message in all three languages was the same, scholars who knew Greek were able to translate the ...
... not know how to read them. • In 1799 a French soldier found the Rosetta Stone, a huge, stone slab inscribed with hieroglyphics, Greek, and a later form of Egyptian. • Because the message in all three languages was the same, scholars who knew Greek were able to translate the ...
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death (the after life). These rituals and protocols included mummifying the body, casting of magic spells, and burial with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the Egyptian afterlife.The burial process used by the ancient Egyptians evolved throughout time as old customs were discarded and new ones adopted, but several important elements of the process persisted. Although specific details changed over time, the preparation of the body, the magic rituals involved, and the grave goods provided were all essential parts of a proper Egyptian funeral.