Frequently Asked Temperature Questions
... accurate than RTD’s or thermocouples, but they have a much more limited temperature range. They are also subject to selfheating. INFRARED SENSORS can be used to measure temperatures higher than any of the other devices and do so without direct contact with the surfaces being measured. However, they ...
... accurate than RTD’s or thermocouples, but they have a much more limited temperature range. They are also subject to selfheating. INFRARED SENSORS can be used to measure temperatures higher than any of the other devices and do so without direct contact with the surfaces being measured. However, they ...
VCM TCM LCM Data Sheet/Manual PDF
... provides protection against oil, water, dirt, and mechanical damage. They can be quickly and easily mounted to most surfaces by using the self-stick adhesive pad. ...
... provides protection against oil, water, dirt, and mechanical damage. They can be quickly and easily mounted to most surfaces by using the self-stick adhesive pad. ...
1998 Strategic Communications Plan
... Modern ADCs have differential inputs, which should be routed tightly coupled and symmetrically routed. To minimize stray capacitance, analog anti-aliasing filter could have the ground plane below it notched out. Terminate analog inputs and clock inputs with terminations placed at the device input pi ...
... Modern ADCs have differential inputs, which should be routed tightly coupled and symmetrically routed. To minimize stray capacitance, analog anti-aliasing filter could have the ground plane below it notched out. Terminate analog inputs and clock inputs with terminations placed at the device input pi ...
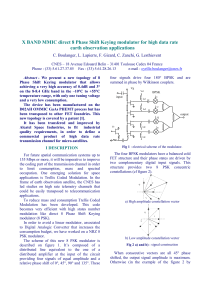
X BAND MMIC direct 8 Phase Shift Keying modulator for
... achieving a very high accuracy of 0.4dB and 3° on the 8-8.4 GHz band in the –10°C to +55°C temperature range, with only one tuning voltage and a very low consumption. The device has been manufactured on the D02AH OMMIC GaAs PHEMT process but has been transposed to other FET foundries. This new topol ...
... achieving a very high accuracy of 0.4dB and 3° on the 8-8.4 GHz band in the –10°C to +55°C temperature range, with only one tuning voltage and a very low consumption. The device has been manufactured on the D02AH OMMIC GaAs PHEMT process but has been transposed to other FET foundries. This new topol ...
AD7484 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The AD7484 provides excellent ac and dc performance specifications. Factory trimming ensures high dc accuracy, resulting in very low INL, offset, and gain errors. The part uses advanced design techniques to achieve very low power dissipation at high throughput rates. Power consumption in the normal ...
... The AD7484 provides excellent ac and dc performance specifications. Factory trimming ensures high dc accuracy, resulting in very low INL, offset, and gain errors. The part uses advanced design techniques to achieve very low power dissipation at high throughput rates. Power consumption in the normal ...
Chapter 4 - Digital Transmission file - Elearning-KL
... Note In NRZ-L the level of the voltage determines the value of the bit. In NRZ-I the inversion or the lack of inversion determines the value of the bit. ...
... Note In NRZ-L the level of the voltage determines the value of the bit. In NRZ-I the inversion or the lack of inversion determines the value of the bit. ...
First Year Lab Introductory Electronics
... – Ground – shorts scope input to ground – kills signal, allows you to find 0V and set using Vert Position – DC – the ‘normal’ mode, what you see is what you got – AC – removes any DC component of a signal, useful for seeing a small oscillating voltage on a big DC background ...
... – Ground – shorts scope input to ground – kills signal, allows you to find 0V and set using Vert Position – DC – the ‘normal’ mode, what you see is what you got – AC – removes any DC component of a signal, useful for seeing a small oscillating voltage on a big DC background ...
Hardware Conditioning of Sensor Signals
... The specific signal conditioning circuits that are needed in a sensor application depend on the type of sensor employed. For example, a sensor that generates output voltages according to the magnitude of the physical parameter being measured would require different signal conditioning from a sensor ...
... The specific signal conditioning circuits that are needed in a sensor application depend on the type of sensor employed. For example, a sensor that generates output voltages according to the magnitude of the physical parameter being measured would require different signal conditioning from a sensor ...
Example: The Input Offset Voltage
... Recall, however, that the input offset voltage is typically very small (i.e., Vos 5 mV ), so that v1 v2 . The current into each terminal of the op-amp is still zero, so that: i1 i2 ...
... Recall, however, that the input offset voltage is typically very small (i.e., Vos 5 mV ), so that v1 v2 . The current into each terminal of the op-amp is still zero, so that: i1 i2 ...
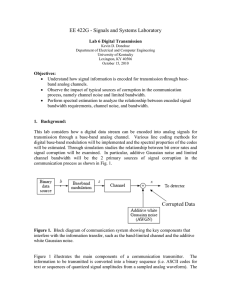
Lab6_EE422 - University of Kentucky College of Engineering
... binary data source emits a series of 1’s and 0’s (bits) and represents the communication system source. The baseband modulation operation codes each bit into a continuous waveform for sending the source sequence over a physical channel. A channel is medium through which changes in a measurable phen ...
... binary data source emits a series of 1’s and 0’s (bits) and represents the communication system source. The baseband modulation operation codes each bit into a continuous waveform for sending the source sequence over a physical channel. A channel is medium through which changes in a measurable phen ...
412 Laboratory #1: Input Resistance, Output Resistance, and
... Q4: Based on this measurement only, determine the apparent smallsignal voltage gain Av vo vi with this output load applied. Q5: Now use your equivalent amplifier circuit model (i.e., not the equivalent small-signal MOSFET model) to calculate the theoretic voltage gain. In other words, connect the ...
... Q4: Based on this measurement only, determine the apparent smallsignal voltage gain Av vo vi with this output load applied. Q5: Now use your equivalent amplifier circuit model (i.e., not the equivalent small-signal MOSFET model) to calculate the theoretic voltage gain. In other words, connect the ...
DM7442A BCD to Decimal Decoder
... body, or (b) support or sustain life, and (c) whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the user. www.fairchildsemi.com ...
... body, or (b) support or sustain life, and (c) whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the user. www.fairchildsemi.com ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).