P S C
... think it is working, challenge yourself to set a low-frequency AC signal for vvertical(t), and then change its magnitude and frequency. What is going on? Explain in few sentences what happens with the signal as you are changing R3 and vvertical(t) (you may write in the space provided below). Bouncin ...
... think it is working, challenge yourself to set a low-frequency AC signal for vvertical(t), and then change its magnitude and frequency. What is going on? Explain in few sentences what happens with the signal as you are changing R3 and vvertical(t) (you may write in the space provided below). Bouncin ...
Tiny Temperature Sensors for Remote Systems
... such as the ADCV0831 and those found on most CMOS ASICs, there is a requirement that the signal source provide a large peak current at the time of sampling. The LM20 output cannot provide this current and settle its output voltage in the time before the ADC acquisition window ends. The solution is t ...
... such as the ADCV0831 and those found on most CMOS ASICs, there is a requirement that the signal source provide a large peak current at the time of sampling. The LM20 output cannot provide this current and settle its output voltage in the time before the ADC acquisition window ends. The solution is t ...
AD7171 数据手册DataSheet下载
... access the data register of the ADC. Eight status bits accompany each data read. See Figure 13 for further details. The DOUT/RDY falling edge can be used as an interrupt to a processor, indicating that new data is available. If the data is not read after the conversion, the pin goes high before the ...
... access the data register of the ADC. Eight status bits accompany each data read. See Figure 13 for further details. The DOUT/RDY falling edge can be used as an interrupt to a processor, indicating that new data is available. If the data is not read after the conversion, the pin goes high before the ...
Determining Minimum Acquisition Times for
... As shown in Figure 5, k2(t) is going to decay faster than k1(t) when t2 << t1. In fact, Equation 6 and Equation 7 show that t1 will always be greater than t2 . Under these conditions, Equation 8 can be approximated as a function with only time constant t1, or: A(t) » 1 - ...
... As shown in Figure 5, k2(t) is going to decay faster than k1(t) when t2 << t1. In fact, Equation 6 and Equation 7 show that t1 will always be greater than t2 . Under these conditions, Equation 8 can be approximated as a function with only time constant t1, or: A(t) » 1 - ...
FUNCTION manual
... Apply Trigger or Gate to Trigger IN. Take output from End Of Rise. RISE parameter will set the delay and Fall parameter will adjust width of the resulting delayed pulse.Voltage Controlled Flam Apply Trigger, Clock or Gate to Trigger IN. Set Rise for Full CCW. Fall for at least 50%. Take output 1 fro ...
... Apply Trigger or Gate to Trigger IN. Take output from End Of Rise. RISE parameter will set the delay and Fall parameter will adjust width of the resulting delayed pulse.Voltage Controlled Flam Apply Trigger, Clock or Gate to Trigger IN. Set Rise for Full CCW. Fall for at least 50%. Take output 1 fro ...
abworks Inc. L - Labworks Inc.
... Vibration testing just got more economical. The SG-135 is a high quality sine signal source which provides simultaneous manual control of both frequency and amplitude. There are two digital readouts. One indicates the frequency of the output signal and the other displays acceleration in g's peak fro ...
... Vibration testing just got more economical. The SG-135 is a high quality sine signal source which provides simultaneous manual control of both frequency and amplitude. There are two digital readouts. One indicates the frequency of the output signal and the other displays acceleration in g's peak fro ...
Voltage-to-Frequency and Frequency-to
... output. A pull-up resistor is usually connected to a 5V logic supply to create standard logic-level pulses. It can, however, be connected to any power supply up to +VCC. Output pulses have a constant duration and positive-going during the oneshot period. Current flowing in the open-collector output ...
... output. A pull-up resistor is usually connected to a 5V logic supply to create standard logic-level pulses. It can, however, be connected to any power supply up to +VCC. Output pulses have a constant duration and positive-going during the oneshot period. Current flowing in the open-collector output ...
Digital Storage Oscilloscopes
... The software provides a seamless synchronization between the oscilloscope and PC, effortlessly allowing quick imports of captured waveform data and measurement results into Microsoft Excel for further analysis. ...
... The software provides a seamless synchronization between the oscilloscope and PC, effortlessly allowing quick imports of captured waveform data and measurement results into Microsoft Excel for further analysis. ...
Ch.6 Fixed-Point vs. Floating Point
... • In IIR filters, the fixed-point representation of the coefficients can cause the poles to shift in the z-plane. • The amount of shift due to the quantization of a single coefficient is influenced by the positions of all the other poles. • To reduce this effect, IIR filters are often implemented as ...
... • In IIR filters, the fixed-point representation of the coefficients can cause the poles to shift in the z-plane. • The amount of shift due to the quantization of a single coefficient is influenced by the positions of all the other poles. • To reduce this effect, IIR filters are often implemented as ...
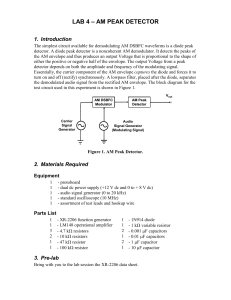
AM PEAK DETECTOR
... In this section, we examine the operation of an AM peak detector. The input waveform to an AM peak detector comprises a carrier frequency and its upper and lower side frequencies (i.e., an AM envelope). A diode is a nonlinear device. Therefore, nonlinear mixing (heterodyning) occurs between the carr ...
... In this section, we examine the operation of an AM peak detector. The input waveform to an AM peak detector comprises a carrier frequency and its upper and lower side frequencies (i.e., an AM envelope). A diode is a nonlinear device. Therefore, nonlinear mixing (heterodyning) occurs between the carr ...
Delta Modulation For Voice Transmission
... of digitizing voice for secure, reliable communications and for voice I/O in data processing. To illustrate basic principles, a very simple delta modulator and demodulator are illustrated in Figure 1. The modulator is a sampled data system employing a negative feedback loop. A comparator senses whet ...
... of digitizing voice for secure, reliable communications and for voice I/O in data processing. To illustrate basic principles, a very simple delta modulator and demodulator are illustrated in Figure 1. The modulator is a sampled data system employing a negative feedback loop. A comparator senses whet ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).